The Central Reserve Police Force (CRPF) stands as a premier central police force of the Union of India, entrusted with the critical task of maintaining internal security.
CRPF Foundation Day 2024
The Central Reserve Police Force (CRPF) stands as a premier central police force of the Union of India, entrusted with the critical task of maintaining internal security. Initially established as the Crown Representatives Police on July 27, 1939, in response to escalating political turmoil and unrest within the princely states, the CRPF has evolved into one of the oldest and most distinguished central paramilitary forces in the country.
The force’s creation was notably influenced by the Madras Resolution of the All-India Congress Committee in 1936, which underscored the need for a robust internal security apparatus. Post-independence, the CRPF underwent a significant transformation. On December 28, 1949, through an Act of Parliament, it was renamed as the Central Reserve Police Force.
Over time, the CRPF has evolved into a formidable organization, now comprising 246 battalions. The force is headed by a Director General and is further divided into four zones located in Jammu, Kolkata, Hyderabad, and Guwahati, each under the command of Special Directors General (DGs).
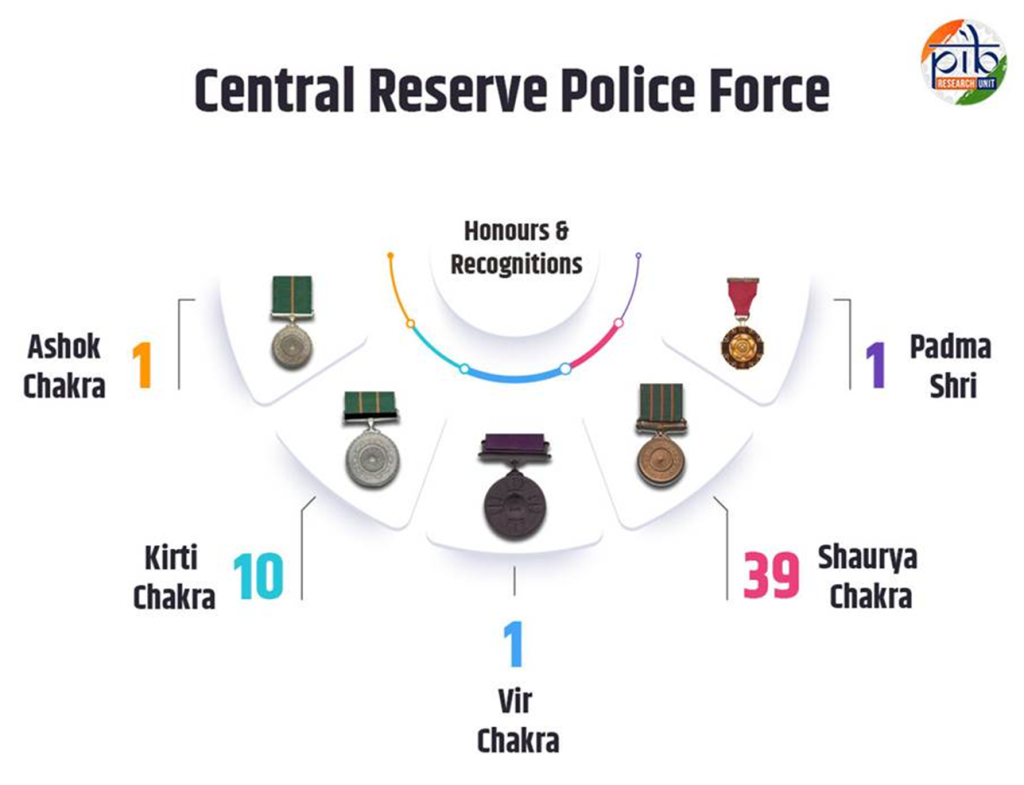
As we commemorate the 86th Foundation Day of the CRPF we reflect on the enduring legacy and invaluable contributions of this formidable force.
Achievements and Contributions
The CRPF’s dedication to national security extends beyond its daily duties. Throughout its history, the force has amassed a remarkable record of achievements and contributions.
Historical Significance
Played a crucial role in the integration of princely states and managing the Partition riots.
Bravely fought alongside the Indian Army during wars, including the battles at Hot Springs (1959) and Sardar Post (1965).
Safeguarding National Security
Thwarted attacks on the Indian Parliament (2001) and Ayodhya (2005).
Played a pivotal role in controlling militancy in Punjab (1980s) and insurgency in Tripura (1990s).
Designated as the primary internal security force in 2001.
Combatting Left-Wing Extremism
Over one-third of the force deployed in Naxal-affected areas.
Significant contributions to eradicating Naxalism in West Bengal, Bihar, and Jharkhand.
Neutralized top Maoist leader Kishanji (2011) and conducted major operations in liberated Naxal zones.
Disaster Relief
Actively participated in relief efforts during natural disasters like the Orissa Super Cyclone (1999), Gujarat Earthquake (2001), Tsunami (2004), and Jammu and Kashmir Earthquake (2005).
International Service
Demonstrated capabilities in UN peacekeeping missions in Sri Lanka, Haiti, Kosovo, and Liberia.