What are the key features of RTI Act?
- The Right to Information is a fundamental right under Article 19 (1) of the Indian Constitution.
- Government enacted the RTI act in 2005 which provides machinery for exercising this fundamental right.
- RTI 2005, came into force in order to encourage a corruption free, transparent, and accountable form of government in which the citizens feel a sense of power and safety.
- Under the Act, a citizen can demand from any public or government authority any information as long as it does not pertain to national security and defence or some personal information
- The authority is supposed to respond within a period of 30 days to the application.
- “Public authority” means any authority or body or institution of self-government established or constituted—
- Under the constitution
- Law made by parliament/state legislature.
- Notification issued or order made by the appropriate government
SC: No Audit of PM-CARES Funds by CAG
- SC said PMCARES is a Public Charitable Trust.
- Hence, there is no occasion for audit of Prime Minister’s Citizen Assistance and Relief in Emergency Situations Fund (PM-CARES Fund) by the CAG of India.
- It also refused to order transfer of funds from the PM CARES Fund to the National Disaster Response Fund (NDRF)
- The Court ruled that while NDRF is to be audited by the CAG of India according to the Disaster Management Act, 2005,
- A public charitable trust like PM-CARES Fund need not be.
- The PM CARES Fund is a charitable trust registered under the Registration Act, 1908.
- The trust does not receive any Budgetary support or any Government money.
- While NDRF, formed under Section 46 of the DM Act of 2005, were provided for by Central and State Budgets.
- PM-CARES Fund is not a Public Authority under the ambit of Section 2(h) of the RTI Act, 2005. However, relevant information in respect of PM-CARES Fund may be seen on its website.
National Recruitment Agency
- The Union Cabinet chaired by Prime Minister Narendra Modi has decided to set up a National Recruitment Agency (NRA).
- The proposed NRA will conduct a common preliminary examination for various recruitments in the central government.
- At present, candidates seeking government jobs must appear for separate examinations conducted by multiple recruiting agencies for various posts, for which similar eligibility conditions.
- On an average, 2.5 crore to 3 crore candidates appear in each of these examinations.
- National Recruitment Agency
- A multi-agency body will conduct a Common Eligibility Test (CET) to screen/shortlist candidates for the Group B and C (non-technical) posts.
- NRA will have representatives of Ministry of Railways, Ministry of Finance/Department of Financial Services, the SSC, RRB & IBPS.
- The test will be conducted for three levels: graduate, higher secondary (12th pass) and the matriculate (10th pass) candidates.
- CET Score to be valid for three years, no bar on attempts
- Major Relief to poor Candidates and Women candidates to benefit greatly.
Cabinet approves leasing out 3 airports through PPP
- To ensure quality services for air passengers, Cabinet approves leasing out 3 airports through Public-Private Partnership.
- The three airports are Jaipur, Guwahati, and Thiruvananthapuram airports.
- Government had leased out the Airports Authority of India’s airports at Delhi and Mumbai on Public Private Partnership for Operation, Management and Development about a decade ago.
- PPP helped AAI in enhancing its revenues and focusing on developing airports and Air Navigation infrastructure.
MP to provide reservation to locals
- The Chief Minister of Madhya Pradesh Shivraj Singh Chauhan has announced that the government jobs will be reserved for the “children” of the state and legal provisions will be made for the same.
- After this MP will become the first state of India to reserve seats for all state government jobs for the domicile population.
- Similar moves:
- The state of Jharkhand announced a reservation of 75% private-sector jobs for permanent residents.
- The state of Haryana cleared an ordinance with the same 75% reservation quota as Jharkhand.
- In Maharashtra, only those living in the state for over 15 years with fluency in Marathi are eligible.
- In Jammu and Kashmir, government jobs are reserved for “domiciles”
- Article 16(1) provides for equality of opportunity for all citizens in matters relating to ’employment or appointment’ to any office under the State.
- Article 16(2) provides that there cannot be any discrimination on grounds only of religion, race, caste, sex, descent, place of birth, residence or any of them.
- Article 16(3) allows for making provisions in government appointments with respect to residence (not place of birth).
- Such move encourages regionalism and threatens the unity of the nation but also it can help in rightful allocation of the resources of the state and would encourage people to work within the boundaries of their state.
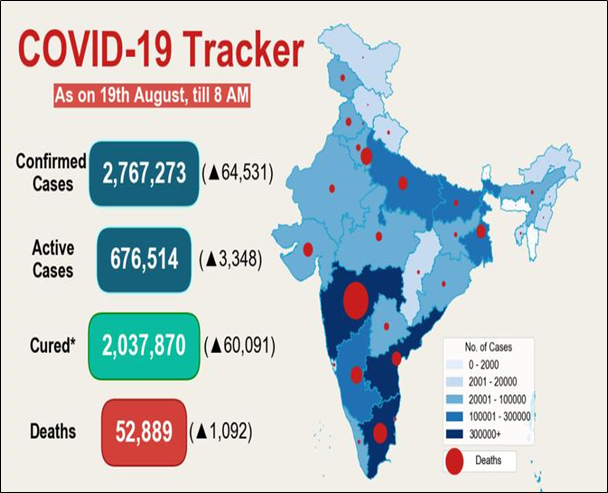
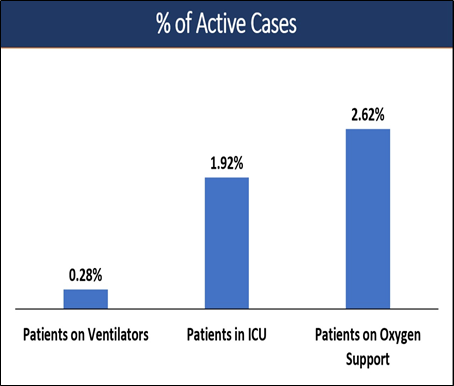
Current COVID19 Situation in India
QUIZ TIME
NDRF formed under Section 46 of the:
- Disaster Management Act, 2005
- Disaster Management Act, 2010
- Disaster Management Act, 2020
- Disaster Management Act, 2000
Answer – A
NRA will have representatives of:
- Ministry of Railways
- Ministry of Finance/Department of Financial Services
- IBPS
- All of the above
Answer – D
Which of the following article provides for equality of opportunity for all citizens in matters relating to ’employment or appointment’ ?
- Article 15(2)
- Article 16(1)
- Article 17(2)
- Article 18(2)
Answer – B
Question of the Day
What is National Disaster Management Plan (NDMP)?
Answer in next session…







