The head of the ISRO, S Somanath, announced plans to launch 50 satellites over the next five years for geo-intelligence gathering. This initiative involves deploying satellites in various orbits to monitor troop movements and capture images of extensive areas.
ISRO’s Military Satellites
Somanath explained that spacecraft can effectively observe national borders and neighboring regions, providing a comprehensive understanding of activities. The ISRO chief revealed that 50 satellites have already been configured for launch in the next five years to enhance India’s geo-intelligence capabilities.
The current size of India’s satellite fleet is not enough for realising India’s ambition to become a strong nation and it should be “ten times what we have today”, he said while speaking at ‘Techfest’, an annual science and technology event organised by the Indian Institute of Technology Bombay (IIT-B).
He further added that it is important to improve the ability of satellites to detect changes, to bring in more of AI-related and data-driven approach to analyse data, reduce data downloads and get only the necessary information.
- CDS 1 2024 Notification, Exam Date, Vacancies, Eligibility, Syllabus And Age Limits
- CDS Exam 2024 Age Limits – Who Can Apply For CDS 1 2024 And CDS 2 2024
- Join Indian Air Force Academy – CDS 1 2024
- Join Indian Military Academy – CDS 1 2024
- Join Officers Training Academy – CDS 1 2024 Notification
Spacecrafts are capable of observing a country’s borders and neighbouring regions, the ISRO chief noted.
“All of it can be seen from satellites. This capability gives us enormous potential. We have been launching satellites to handle this, but there is a different way of thinking now and we need to look at it in a much more critical manner because the power of (any) nation is the ability to understand what is happening around it,” PTI quoted Somanath as saying.
Objective
The goal is to mitigate threats to the country by deploying a diverse array of satellites, spanning from geostationary equatorial orbit (GEO) to lower earth orbit (LEO) and very low earth orbit. This multi-orbit approach allows for critical assessment of different situations, incorporating optical, synthetic aperture radar (SAR), thermal, and other technologies.
Aditya-L1 on schedule
Speaking at the annual science and technology festival at IIT Bombay, the ISRO chief also informed the audience that the Aditya L1 spacecraft is on schedule and will reach its designated cosmic location, Lagrange Point 1 (L1), on January 6, 2024, as planned.
India’s Military Satellites
• GSAT-7A
•RISAT Series
•EMISAT- Electromagnetic Intelligence Gathering Satellite
•Cartosat-2E
•Hyperspectral Imaging Satellite (HySIS)
•Microsat-R
Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO)
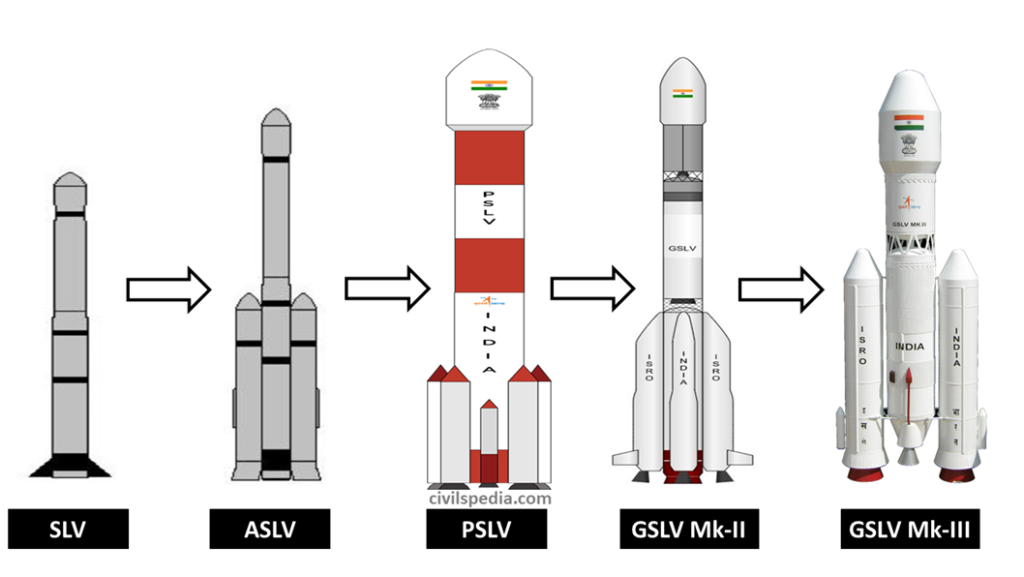
ISRO is the space agency under the Department of Space of Government of India, headquartered in the city of Bengaluru, Karnataka. Shri S. Somanath is the incumbent chairman of ISRO. ISRO’s Launch Vehicles
ISRO’s Launch Vehicles
PSLV (Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle) and GSLV (Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle) are the satellite-launch vehicles developed by ISRO.
ISRO’s Launch Vehicles
PSLV delivers the “earth-observation” or “remote-sensing” satellites in polar orbit.
ISRO’s Launch Vehicles
GSLV delivers the communication-satellites to the Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO) of about 36000 Km altitude.