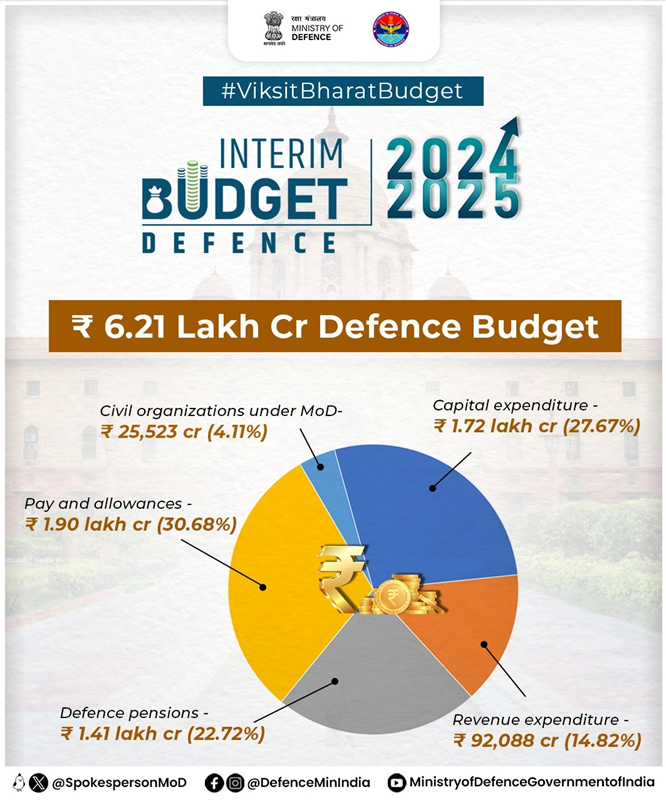
In the current geopolitical scenario and with the twin objective of promoting self reliance and exports, the Defence Budget has touched Rs 6,21,540.85 crore in the Financial Year 2024-25. This comes out to be 13.04% of total Union Budget, which was presented by Finance Minister Smt Nirmala Sitharaman in Parliament on February 01, 2024.
Ministry of Defence in Interim Union Budget 2024-25
Record Over Rs 6.21 Lakh Crore Allocation To MoD
- In the current geopolitical scenario and with the twin objective of promoting self reliance and exports, the Defence Budget has touched Rs 6,21,540.85 crore in the Financial Year 2024-25. This comes out to be 13.04% of total Union Budget, which was presented by Finance Minister Smt Nirmala Sitharaman.
- The MoD continues to receive the highest allocation among the Ministries. The budgetary allocation to Defence for FY 24-25 is higher by approx. one lakh crore (18.35%) over the allocation for the FY 2022-23 and 4.72% more than allocation of FY 23-24.
- Of this, a major share of 27.67% goes to capital, 14.82% for revenue expenditure on sustenance and operational preparedness, 30.68% for Pay and allowances, 22.72% for defence pensions and 4.11% for civil organisations under MoD.
Upward trend continues in Defence Capital Expenditure promoting ‘Aatmanirbharta’
- Budgetary allocation for capital expenditure in Defence for FY 24-25 is Rs 1.72 lakh crore which is 20.33% higher than the actual expenditure of FY 22-23 and 9.40 % more than the Revised Allocation of FY 23-24.
- As per the Economic Survey of India report 2023, in the ship-building sector, the investment multiplier is around 1.82, which means that an infusion of approx. Rs 1.5 lakh crore in naval ship-building projects would accrue a circulation of Rs 2.73 lakh crore in the ship building sector due to the multiplier effect.
Enhanced higher allocation sustained for operational readiness under Revenue Expenditure
- Allocation to the Armed Forces for revenue expenditure (Other than Salary) meant for sustenance and operational commitment for FY 24-25 continues to be high at Rs 92,088 crore, which is 48% higher than the budgetary allocation of FY 2022-23.
- During the mid-year review, the allocation on this head was increased by 82% over the budgetary allocation of FY 22-23 crossing the figure of Rs one lakh crore for the first time.
Defence Pension Budget increased to Rs 1.41 lakh crore
- Total Budgetary allocation on account of Defence pensions is Rs 1,41,205 crore which is 2.17% higher than the allocation made during 2023-24. It will be incurred on monthly pension to approx. 32 lakh pensioners through SPARSH and through other pension disbursing authorities.
Unprecedented Allocation to ECHS ensuring better healthcare facilities to Veterans
- The total allocation to Ex-Servicemen Welfare Scheme for FY 2024-25 is 28% higher than the allocation for FY 23-24 (From Rs 5,431.56 crore to Rs 6,968 crore).
- This is in addition to the unprecedented allocation at revised estimate stage during the current year where the budgetary allocation to ECHS was enhanced by 70% over BE of 2023-24 and was made to Rs 9,221.50 crore.
Strengthening the need of improving Border Infrastructure for strategic requirements
- In the light of the continued threat perception faced at the Indo-China border, there continues a jump in the Capital Budget allocation to the Border Roads Organisation. The allocation for BE 2024-25 is Rs 6,500 crore, which is 30% higher than the allocation for FY 23-24 and 160% higher over the allocation of FY 2021-22.
Strengthening the Multi Mission Service led by Indian Coast Guard
- Allocation to the ICG for this FY 2024-25 is Rs 7.651.80 crore which is 6.31% higher over the allocation of FY 2023-24. Of this, Rs 3,500 crore is to be incurred only on capital expenditure, adding teeth to the arsenal of the ICG to address the emerging challenges posed in water and provide humanitarian assistance to other nations.
DRDO
- The budgetary allocation to DRDO has been increased to Rs 23,855 crore in FY 2024-25 from Rs 23,263.89 crore in FY 2023-24. Of this allocation, a major share of Rs 13,208 crore is allocated for capital expenditure.
The Raksha Mantri added that there is big push for infrastructure, construction, manufacturing, housing and technology development in this Budget. “During the COVID-19 when the world was faltering India emerged as the beacon of hope. This Budget is perfectly aligned with PM’s ‘Panchamrit Goals’ and it also paves the way for the next five years of unprecedented growth,” he said.
On the increase of capital expenditure outlay, Shri Rajnath Singh described it as a massive push, which will provide a big boost to making India a five trillion dollar economy by 2027.
Central Forces, Border, Intel, Census Focus of MHA Budget
- A substantial amount has been allocated for improving infrastructure along the international border, women’s safety, police infrastructure and modernisation of police forces.
- For the vibrant village programme along the China border, ₹1,050 crore has been allocated as compared to ₹300 crore in 2023-24. For the modernisation of police forces, ₹3,720 crore has been allocated. The decadal exercise has been postponed for the past two years due to Covid-19. The newly created UTs of Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh have been allocated ₹43,235 crore.
- Central Reserve Police Force, which is mostly deployed during the general elections, internal security duties and fighting militancy in Jammu and Kashmir, has been allocated ₹32,809.65 crore in comparison to ₹31,772.23 crore in 2023-24.
- Border Security Force, which guards India’s border with Pakistan and Bangladesh, besides handling internal security assignments, has been given ₹25,027.52 crore as compared to ₹24,771.28 crore in the previous budget.
- CISF, which protects vital installations such as nuclear projects, airports and metro networks, has been given ₹13,655.53 crore as compared to ₹3,214.68 crore allocated earlier.