The Indian Armed Forces, comprising the Indian Army, Indian Air Force, and Indian Navy, play a pivotal role in safeguarding the nation’s security and sovereignty. These three branches work in close coordination, drawing upon their distinct roles and capabilities to protect the country’s interests. At the heart of this well-organized military structure lies a meticulously designed hierarchy of ranks, each representing the dedication, expertise, and authority of the personnel who serve in these esteemed institutions. This article delves into the Ranks in Indian Army, Airforce and Navy.
10 Powerful Countries In The World 2024
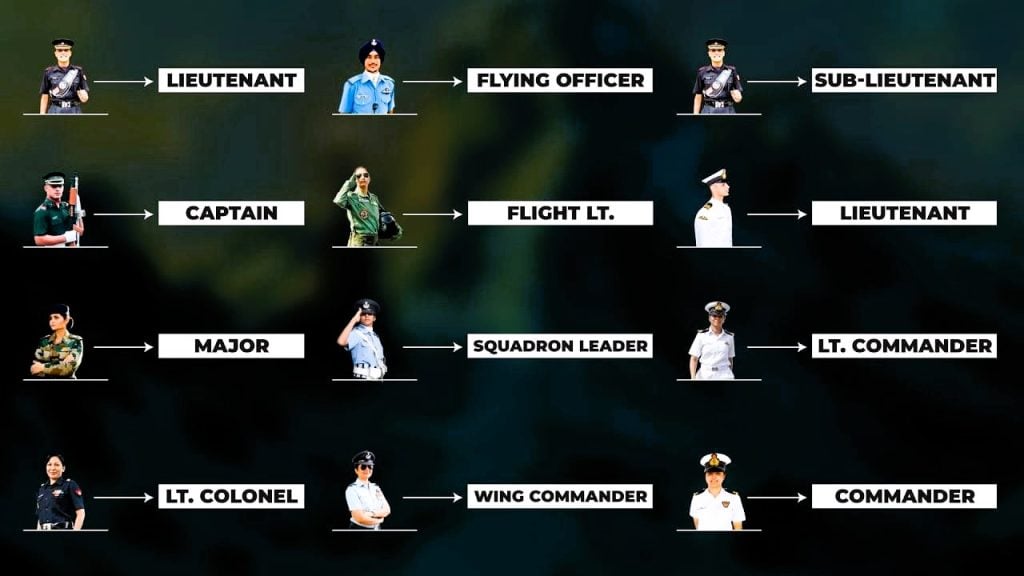
Understanding Commissioned Officer Ranks
The Indian Armed Forces are led by a cadre of Commissioned Officers, who are entrusted with the responsibility of commanding and managing the forces. These officers hold corresponding ranks across the three branches, ensuring seamless communication and effective collaboration.
Indian Army Ranks
The Indian Army’s commissioned officer ranks begin with the highest position of Field Marshal, followed by General, Lieutenant General, Major General, Brigadier, Colonel, Lieutenant Colonel, Major, and Captain. Each rank signifies the individual’s experience, decision-making authority, and the scope of their responsibilities.
Indian Navy Ranks
The Indian Navy‘s commissioned officer ranks include Admiral of the Fleet, Admiral, Vice Admiral, Rear Admiral, Commodore, Captain, Commander, and Lieutenant Commander. These ranks reflect the naval officers’ expertise in maritime operations and their ability to lead their respective units.
Indian Air Force Ranks
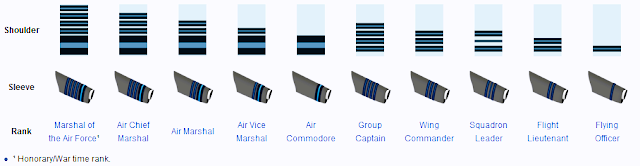
The Indian Air Force‘s commissioned officer ranks comprise Marshal of the Indian Air Force, Air Chief Marshal, Air Marshal, Air Vice Marshal, Air Commodore, Group Captain, Wing Commander, Squadron Leader, and Flight Lieutenant. These ranks are tailored to the unique demands of aerial warfare and the strategic oversight required in the air domain.
Tabular view of ranks in the Indian Air Force, Army, and Navy:
| Air Force | Army | Navy |
|---|---|---|
| Marshal of the Indian Air Force | Field Marshal | Admiral of the Fleet |
| Air Chief Marshal | General | Admiral |
| Air Marshal | Lieutenant General (Army Commodore / VCOAS) | Vice Admiral / FOC-in-C / VCNS |
| Air Vice Marshal | Lieutenant General | Vice Admiral |
| Air Commodore | Brigadier | Captain |
| Group Captain | Colonel | Captain |
| Wing Commander | Lieutenant Colonel | Commander |
| Squadron Leader | Major | Lieutenant Commander |
| Flight Lieutenant | Captain | Lieutenant |
| Flying Officer | Lieutenant | Sub Lieutenant |
| Flight Cadet | – | – |
10 Brave Soldiers Of Indian Army
Non-Commissioned Officer Ranks
Alongside the Commissioned Officers, the Indian Armed Forces also rely on the expertise and dedication of Non-Commissioned Officers (NCOs) and Junior Commissioned Officers (JCOs). These individuals serve as a vital link between the officers and the soldiers, ensuring the smooth execution of orders and maintaining overall discipline.
Indian Army NCO and JCO Ranks
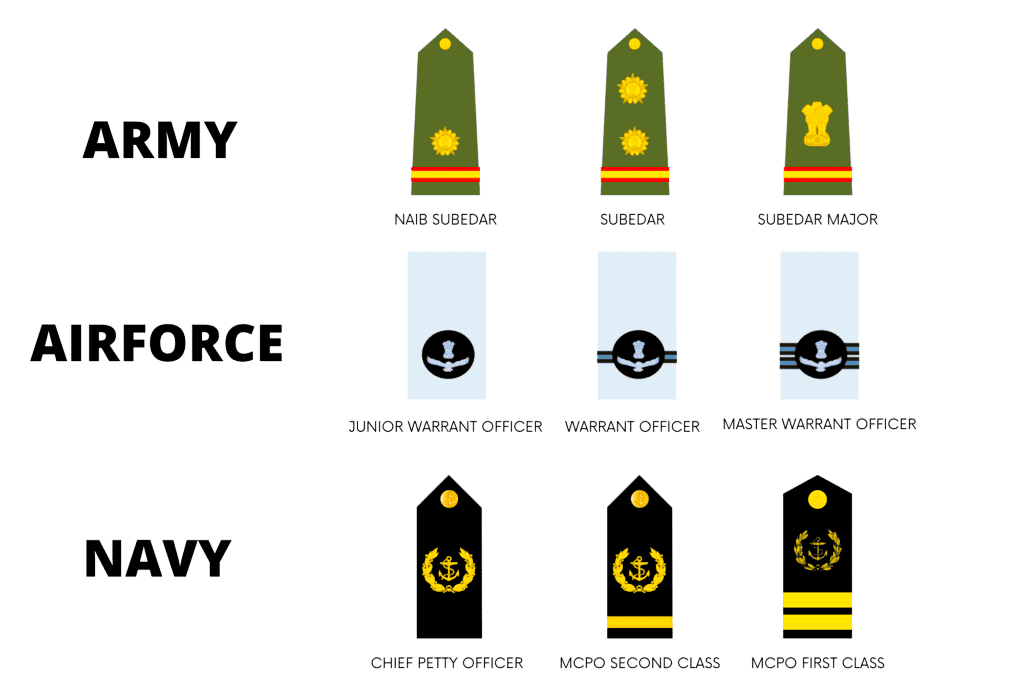
In the Indian Army, the NCO and JCO ranks include Subedar Major, Subedar, Naib Subedar, Havildar, Naik, Lance Naik, and Sepoy. These individuals play a crucial role in bridging the gap between the officers and the troops, facilitating effective communication and operational efficiency.
Tabular view for JCO ranks in the Indian Army, Navy, and Air Force:
| Indian Army Rank | Indian Navy Rank | Indian Air Force Rank |
|---|---|---|
| Subedar Major | Master Chief Petty Officer I | Warrant Officer |
| Subedar | Master Chief Petty Officer II | Warrant Officer |
| Naib Subedar | Chief Petty Officer | Junior Warrant Officer |
Indian Navy NCO and JCO Ranks
The Indian Navy’s NCO and JCO ranks consist of Master Chief Petty Officer I, Master Chief Petty Officer II, Chief Petty Officer, Petty Officer, Leading Seaman, Able Seaman, and Seaman. These personnel are responsible for maintaining the operational readiness of the naval fleet and ensuring the seamless execution of maritime operations.
Indian Air Force NCO and JCO Ranks
The Indian Air Force’s NCO and JCO ranks encompass Warrant Officers, Junior Warrant Officers, Sergeants, Corporals, Leading Aircraftsmen, and Aircraftsmen. These individuals play a crucial role in the maintenance and operation of the Air Force’s sophisticated aircraft and equipment, contributing to the overall combat readiness of the service.
Tabular view for NCO/Other ranks in the Indian Army, Navy, and Air Force:
| Indian Army Rank | Indian Navy Rank | Indian Air Force Rank |
|---|---|---|
| Havildar | Petty Officer | Sergeant |
| Naik | Able Seaman | Corporal |
| Lance Naik | Leading Seaman | Leading Aircraftsman |
| Sepoy | Seaman | Aircraftman |
The Significance of Ranks
The ranks within the Indian Armed Forces serve as more than just designations; they represent the dedication, expertise, and authority of the personnel who defend the nation’s interests. This hierarchical structure ensures the efficient execution of orders, the maintenance of discipline, and the overall operational effectiveness of the military.
Responsibilities and Authority
Each rank in the Indian Armed Forces carries with it a specific set of responsibilities and decision-making authority. The higher the rank, the greater the scope of an individual’s leadership, strategic planning, and operational oversight. This structured system enables the seamless coordination and collaboration among the various branches of the military.
Progression and Advancement
The ranks within the Indian Armed Forces also serve as a framework for professional advancement and career progression. Soldiers, sailors, and airmen can aspire to climb the ranks through a combination of training, experience, and exemplary performance, ultimately reaching the highest echelons of their respective services.
Interoperability and Cooperation
The equivalent ranks across the Indian Army, Air Force, and Navy facilitate effective communication and cooperation during joint operations and cross-service initiatives. This shared understanding of rank hierarchy ensures the smooth integration of personnel and resources, enabling the Armed Forces to respond to complex security challenges with a unified and coordinated approach.
The Evolving Landscape of Ranks
The ranks within the Indian Armed Forces have evolved over time, adapting to the changing demands of modern warfare and the evolving strategic landscape. Continuous improvements in training, technology, and operational doctrine have led to the refinement of the rank structure, ensuring its relevance and effectiveness in the 21st century.
Modernization and Adaptability
As the Indian Armed Forces modernize and adapt to new challenges, the rank structure has also undergone periodic updates to align with emerging requirements. This flexibility allows the military to maintain its competitive edge and ensure the optimal deployment of personnel and resources.
Specialized Roles and Designations
In addition to the traditional rank structure, the Indian Armed Forces have also introduced specialized roles and designations to cater to the increasingly complex nature of military operations. These specialized positions, such as technical experts, strategic planners, and joint task force commanders, further enhance the overall capabilities of the armed forces.
Future Trends and Considerations
As the global security landscape continues to evolve, the Indian Armed Forces must remain vigilant and adaptable. The rank structure will likely undergo further refinements to accommodate emerging technologies, new operational doctrines, and the changing nature of warfare. Maintaining a robust and responsive rank hierarchy will be crucial in ensuring the Indian military’s readiness to meet the challenges of the future.
10 Top Anti Tank Missiles in the World
Conclusion
The ranks within the Indian Armed Forces are the backbone of the nation’s military might, representing the dedication, expertise, and authority of the personnel who safeguard its security and sovereignty. From the Commissioned Officers to the Non-Commissioned Officers and Junior Commissioned Officers, each rank plays a vital role in the seamless execution of operations, the maintenance of discipline, and the overall operational effectiveness of the Indian military. As the armed forces continue to evolve and adapt to new challenges, the rank structure will remain a critical component in ensuring the nation’s defense and the protection of its citizens.
FAQs
Q1: What is the highest rank in the Indian Armed Forces?
The highest rank in the Indian Armed Forces is Field Marshal, which is the pinnacle of the commissioned officer ranks.
Q2: How do the ranks in the Indian Army, Navy, and Air Force correspond to each other?
The ranks in the Indian Army, Navy, and Air Force have corresponding equivalents to ensure effective communication and collaboration during joint operations. For example, the Indian Army’s General rank corresponds to the Indian Navy’s Admiral and the Indian Air Force’s Air Chief Marshal.
Q3: What is the role of Non-Commissioned Officers (NCOs) and Junior Commissioned Officers (JCOs) in the Indian Armed Forces?
NCOs and JCOs serve as a vital link between the officers and the soldiers, ensuring the smooth execution of orders and maintaining overall discipline. They play a crucial role in bridging the gap between the leadership and the troops, contributing to the operational efficiency of the armed forces.
Q4: How has the rank structure in the Indian Armed Forces evolved over time?
The rank structure within the Indian Armed Forces has evolved to adapt to the changing demands of modern warfare and the evolving strategic landscape. Continuous improvements in training, technology, and operational doctrine have led to the refinement of the rank structure, ensuring its relevance and effectiveness in the 21st century.