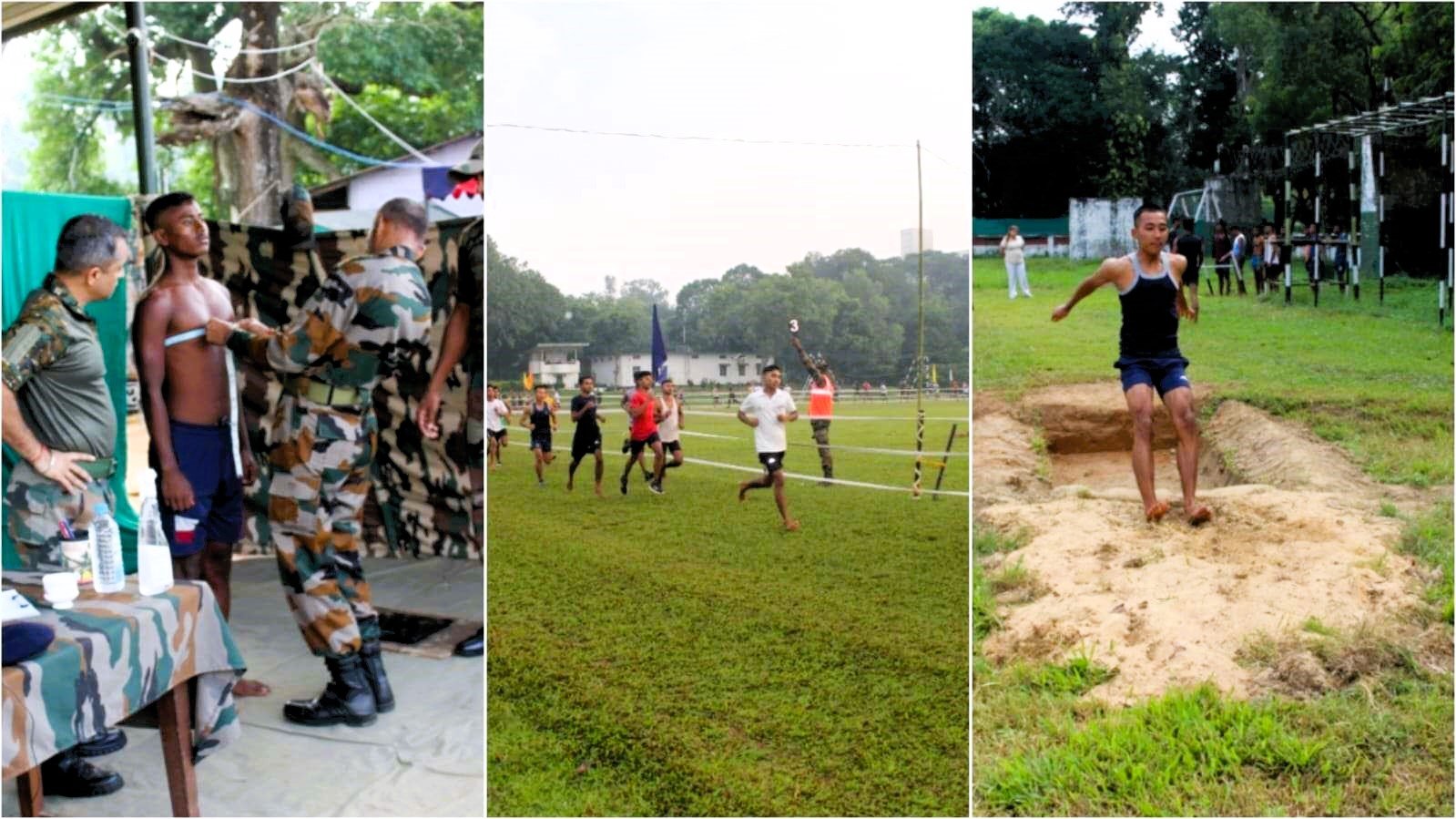
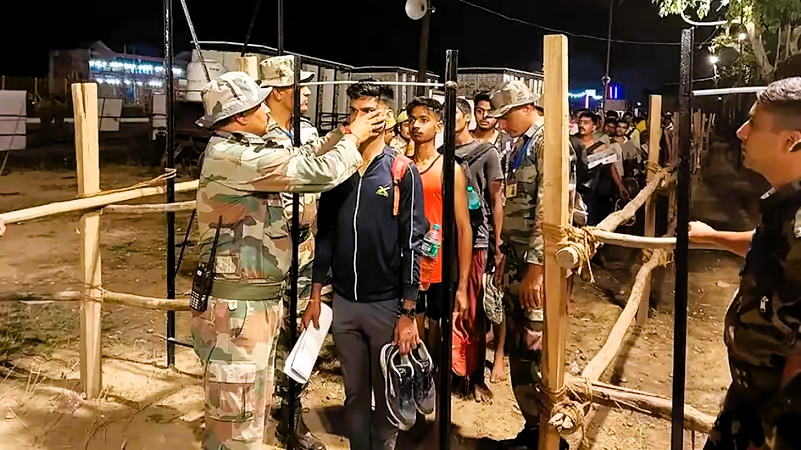
Physical fitness is a cornerstone of military service, integral to the effectiveness and resilience of soldiers. This importance cannot be overstated for anyone aspiring to join the military, particularly young individuals who dream of serving their country. For a 14-year-old with aspirations of a military career, understanding the significance of fitness is foundational. It shapes not just physical abilities, but also mental resilience and overall readiness for the myriad challenges faced in military service.
Introduction to Physical Fitness in the Military
Envision yourself as a soldier, prepared to defend national borders or engage in humanitarian missions. The tasks you will undertake include carrying heavy equipment, enduring prolonged marches, navigating tough terrains, and engaging in combat scenarios. These responsibilities require more than just physical strength; they demand agility, resilience, and robust physical conditioning. Physical fitness in the military context is about comprehensive preparedness—being strong, agile, and enduring under diverse and challenging conditions.
The Physical Demands of Military Service
General Demands Across Branches
Military life universally demands physical robustness, regardless of the specific branch—army, navy, air force, or marines. Common physical activities in the military include running, hiking with heavy gear, climbing obstacles, and performing rigorous physical drills. Such activities necessitate a high level of physical fitness to perform effectively and reduce the risk of injuries.
Specific Demands by Branch
| Branch | Specific Physical Demands |
|---|---|
| Army | Long marches, obstacle courses, carrying heavy gear, and engaging in infantry combat. |
| Navy | Swimming, shipboard operations, handling heavy equipment, and potentially long periods at sea requiring endurance and stability. |
| Air Force | Aerobic conditioning, strength training for handling aircraft and equipment, and mental stamina for high-stress environments. |
| Marines | Intense physical training, amphibious assaults, hand-to-hand combat, and maintaining peak physical condition in varied and often extreme environments. |
Benefits of Being Fit in the Military
Performance Enhancement
Physical fitness directly correlates with enhanced performance. A fit soldier can move faster, react quicker, and sustain longer periods of physical exertion during both training exercises and real-world missions. This capability is crucial for operational success and personal safety.
Injury Prevention
Regular fitness training emphasizes proper body mechanics, significantly reducing the risk of injuries. Soldiers are trained in techniques for safely lifting heavy objects, moving with agility, and maintaining proper posture under stress. These skills are vital for preventing common injuries associated with military activities.
Mental Resilience
Physical fitness extends beyond muscular strength to encompass mental toughness. Regular exercise releases endorphins, improving mood and reducing stress—essential qualities for military personnel who frequently face high-pressure situations. This mental resilience is crucial for maintaining focus and composure in challenging circumstances.
The Role of Fitness in Combat Situations
Swift Movement and Effective Cover
In combat, physical fitness can be lifesaving. Fit soldiers can move swiftly, take cover effectively, and execute maneuvers with precision. These abilities are critical for survival and mission success in hostile environments.
Carrying Wounded Comrades
One of the most critical roles of a soldier in combat is the ability to assist wounded comrades. This often involves carrying or dragging injured personnel to safety, a task that requires significant strength and endurance.
Sustained Focus and Durability
Combat situations demand prolonged periods of high alertness and physical exertion. Soldiers who are physically fit are better equipped to maintain their focus and durability throughout extended engagements.
Leadership and Fitness
Leading by Example
Military leaders are expected to lead by example, demonstrating the importance of physical fitness through their own physical readiness. This not only inspires confidence among their troops but also fosters a culture of fitness and discipline within the unit.
Building Team Cohesion
A fit leader contributes to team cohesion and morale. Soldiers are more likely to trust and follow a leader who exemplifies the standards they are expected to meet. This leadership by example is crucial for maintaining a motivated and cohesive unit.
Health and Well-being
Long-term Health Benefits
Physical fitness promotes overall health and well-being, reducing the risk of lifestyle-related diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and obesity. For military personnel, this translates to fewer medical issues and a longer, healthier career.
Enhanced Cognitive Function
Regular physical activity has been shown to enhance cognitive function, improving memory, attention, and decision-making skills. These cognitive benefits are invaluable for military personnel who need to make quick, accurate decisions in high-stress environments.
Improved Sleep and Energy Levels
Fitness routines improve sleep quality and boost energy levels, which are essential for maintaining high performance during training and missions. Better sleep and higher energy contribute to overall readiness and effectiveness.
Training and Fitness Programs in the Military
Basic Training and Fitness Assessments
All branches of the military include rigorous fitness programs as part of their basic training. These programs are designed to assess and enhance the physical capabilities of recruits, ensuring they meet the required standards.
Ongoing Fitness Requirements
Military personnel must maintain their fitness levels throughout their careers. Regular fitness assessments ensure soldiers remain in peak condition, capable of performing their duties effectively.
Specialized Training Programs
In addition to general fitness, specialized training programs are available for different roles within the military. These programs focus on the specific physical and mental demands of particular tasks, such as special operations or aviation.
| Fitness Assessment Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Cardiovascular Endurance | Tests like the 2-mile run or swimming assessments measure the cardiovascular fitness of soldiers. |
| Strength and Power | Exercises such as push-ups, pull-ups, and weightlifting assess muscular strength and power. |
| Agility and Flexibility | Obstacle courses and flexibility tests measure a soldier’s agility and flexibility. |
Conclusion
Physical fitness is a fundamental aspect of military service, influencing not only physical capabilities but also mental resilience and overall operational effectiveness. For young individuals aspiring to join the military, understanding and embracing the importance of fitness is crucial. It lays the foundation for a successful military career, ensuring readiness for the diverse and demanding challenges that lie ahead. Maintaining peak physical condition is not just a requirement; it is a commitment to excellence, health, and the mission of serving and protecting one’s country.
FAQs
1. Why is physical fitness crucial in the armed forces?
Physical fitness is crucial in the armed forces because it ensures that soldiers are capable of meeting the physical demands of their roles, which include carrying heavy equipment, enduring long marches, navigating challenging terrains, and engaging in combat. It also enhances overall performance, reduces injury risk, and builds mental resilience, all of which are essential for mission success and personal safety.
2. How does physical fitness enhance performance in the military?
Physical fitness enhances performance by enabling soldiers to move faster, react quicker, and sustain longer periods of physical activity. This improved capability is vital during both training exercises and real-world missions, where physical endurance and agility can significantly impact the outcome.
3. What types of physical activities are common in military training?
Common physical activities in military training include running, hiking with heavy gear, climbing obstacles, swimming, and performing strength and endurance drills. These activities are designed to build cardiovascular endurance, muscular strength, agility, and overall physical readiness.
4. How does physical fitness help in injury prevention?
Physical fitness helps in injury prevention by teaching soldiers proper body mechanics and movement techniques. Regular fitness training improves muscle strength and flexibility, which reduces the likelihood of strains, sprains, and other common injuries. Additionally, fit soldiers can better handle the physical stresses of military tasks, further reducing injury risk.
5. What role does mental resilience play in military fitness?
Mental resilience is a critical component of military fitness. Regular physical exercise releases endorphins, which improve mood and reduce stress. This mental toughness is essential for soldiers who face high-pressure situations, helping them maintain focus, make quick decisions, and stay composed under duress.