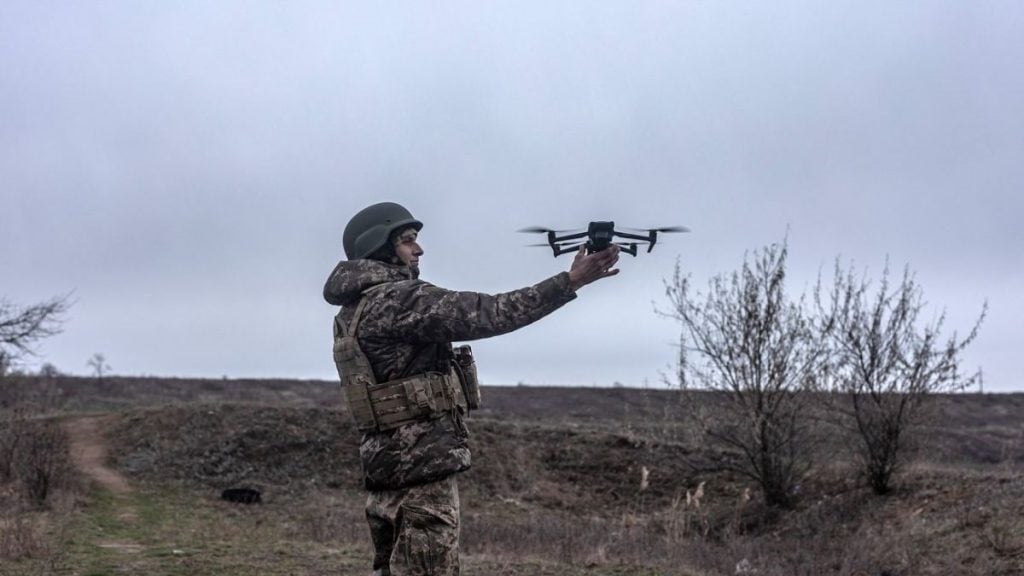
Modern warfare has witnessed a remarkable transformation, with the emergence of cutting-edge technologies that have redefined the battlefield landscape. Among the most captivating advancements are the first-person view (FPV) drones, which have become a game-changer in the realm of military operations. These agile, high-speed aerial platforms offer an unparalleled level of immersion, precision, and tactical advantage, making them a formidable asset for both state and non-state actors.
As the ongoing Russia-Ukraine conflict has strikingly demonstrated, FPV drones have become a crucial component of the military arsenal, blurring the lines between traditional and unconventional warfare. By seamlessly integrating advanced sensors, autonomous capabilities, and precision strike mechanisms, these drones have emerged as a cost-effective and scalable solution to address a wide range of operational challenges.
In this comprehensive article, we will delve into What Are FPV Drones?, exploring their unique features, operational capabilities, and the transformative impact they are having on modern warfare. From the cutting-edge innovations driving their development to the strategic implications of their widespread adoption, this exploration will provide a deep understanding of this transformative technology and its role in shaping the future of military operations.
Unveiling the FPV Drone Advantage
At the heart of the FPV drone revolution lies a fundamental shift in the way these aerial platforms are controlled and experienced. Unlike traditional drones, which are piloted from a ground-based perspective, FPV drones offer a truly immersive experience, where the operator sees the world through the drone’s onboard camera. This first-person view allows for a heightened sense of situational awareness, enhanced maneuverability, and precise target engagement, making FPV drones a formidable asset in a variety of military applications.
The Immersive Advantage
The FPV drone’s ability to provide a seamless first-person perspective is a game-changer, offering pilots an unparalleled level of immersion and control. By directly streaming the drone’s camera feed to the operator’s goggles or display, FPV drones create a virtual cockpit experience, allowing pilots to navigate and engage targets with unprecedented precision. This level of immersion not only enhances the operator’s situational awareness but also fosters a deeper sense of connection and responsiveness, enabling swift decision-making and lightning-fast reactions.
Enhanced Maneuverability and Precision
The FPV drone’s focus on speed, agility, and maneuverability sets it apart from its traditional counterparts. Designed to navigate complex, confined spaces and execute tight turns, these drones excel in close-quarter battle (CQB) scenarios, where precision and responsiveness are critical. The low-latency video transmission and direct control interface allow FPV pilots to make split-second decisions, guiding the drone with pinpoint accuracy to engage targets or navigate through intricate environments.
Versatile and Cost-Effective
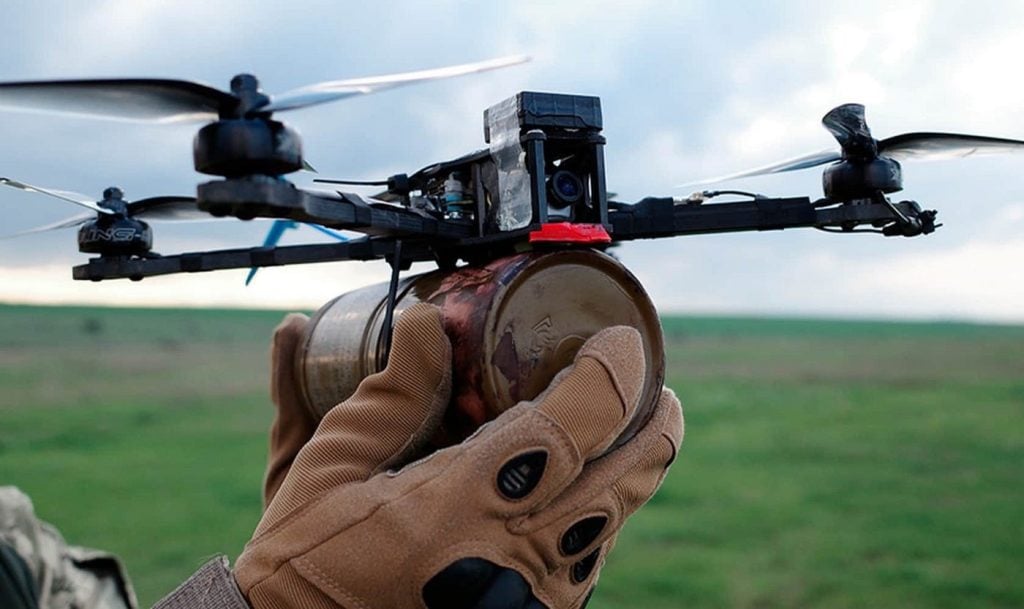
Another key advantage of FPV drones is their versatility and cost-effectiveness. These platforms can be rapidly assembled, customized, and deployed, often at a fraction of the cost of larger, more sophisticated unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). This scalability and accessibility make FPV drones an attractive option for a wide range of military applications, from tactical strikes and surveillance to counterterrorism and urban warfare operations. Furthermore, the modular design of FPV drones allows for easy integration of various payloads, sensors, and weaponry, further expanding their operational capabilities.
5 Best Military Drones by General Atomics
The Evolution of FPV Drones in Modern Warfare
The integration of FPV drones into modern military operations has been a transformative process, marked by a continuous cycle of innovation, adaptation, and strategic deployment. As the ongoing Russia-Ukraine conflict has vividly demonstrated, these agile, high-speed platforms have become a crucial component of the military’s arsenal, challenging traditional notions of warfare and reshaping the tactical landscape.
The Rise of FPV Drones in the Russia-Ukraine Conflict
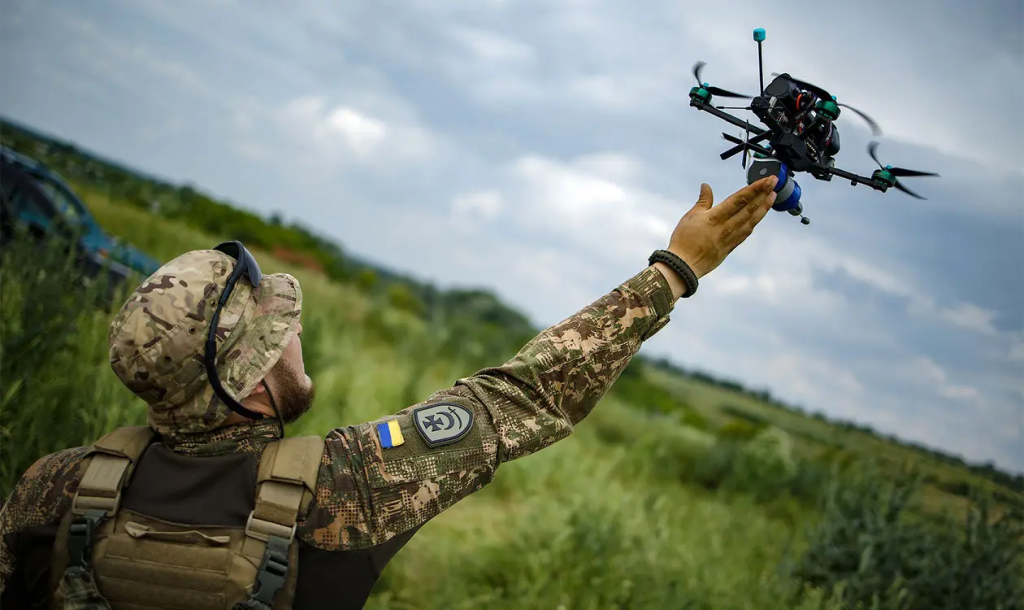
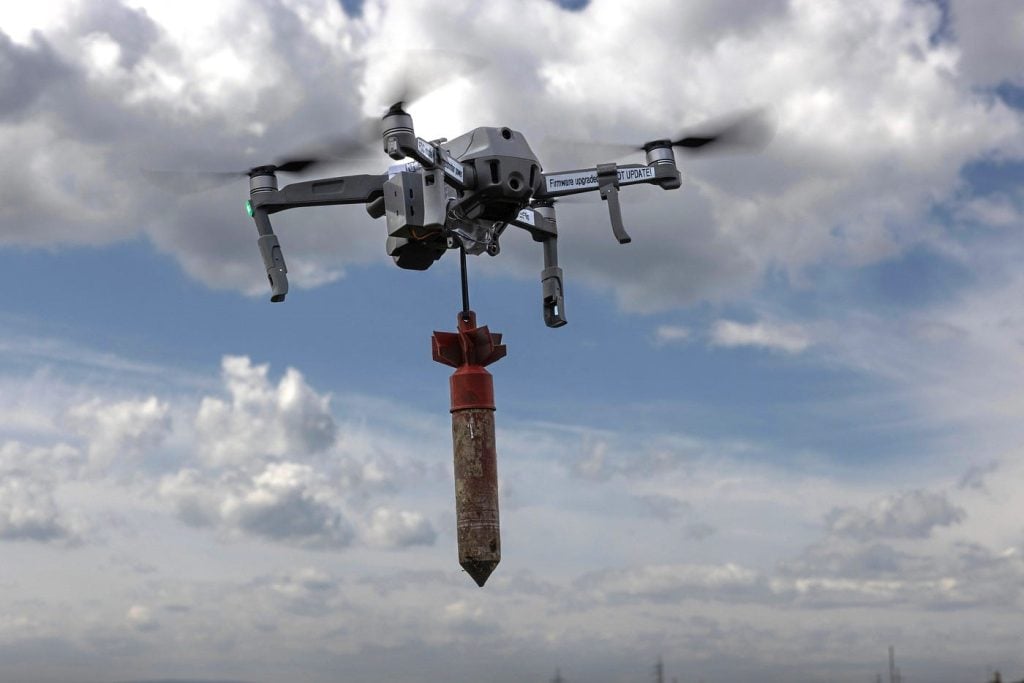
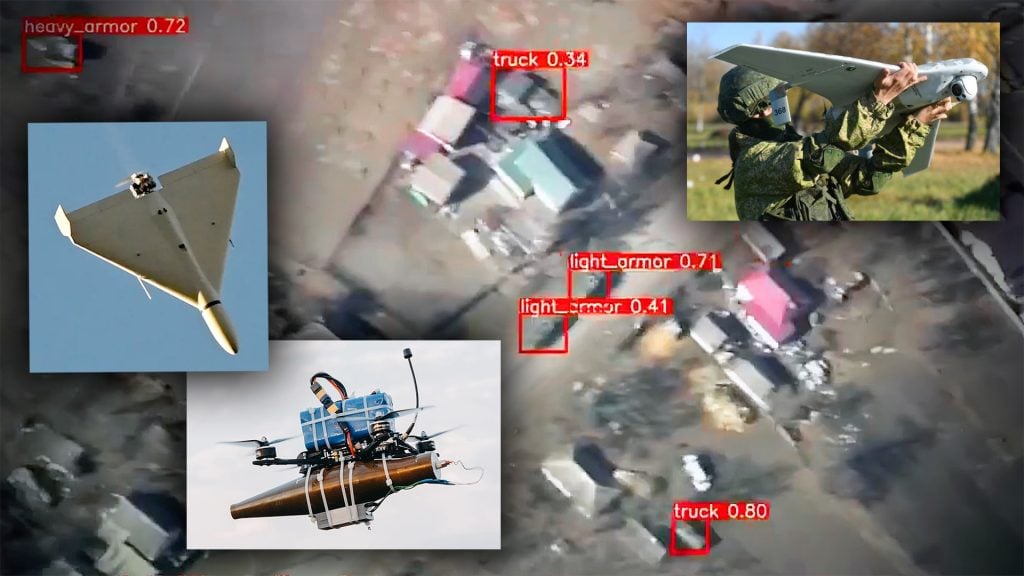
The Russia-Ukraine conflict has served as a crucible for the rapid development and widespread adoption of FPV drones. Both sides have leveraged these platforms to gain tactical advantages, with the Ukrainians pioneering the use of FPV drones for targeted strikes and the Russians responding with their own innovations in AI-enabled and kamikaze variants.
The success of FPV drones in this conflict has been driven by their ability to overcome the limitations of larger, more sophisticated UAVs. As Russia’s air defense and electronic warfare (EW) capabilities have grown, the Ukrainians have increasingly turned to smaller, more maneuverable FPV drones to penetrate enemy airspace, conduct reconnaissance, and deliver precision strikes. Conversely, the Russians have responded by developing their own FPV drone arsenal, including AI-enabled platforms capable of autonomous target acquisition and engagement.
Collaborative Innovation and Rapid Prototyping
The rapid evolution of FPV drones in the Russia-Ukraine conflict has been fueled by a unique blend of collaborative innovation and rapid prototyping. In both countries, volunteer communities with strong technical backgrounds have played a pivotal role in developing and iterating on FPV drone designs, often in close collaboration with military and defense entities.
This grassroots approach has enabled the rapid development and deployment of FPV drones, as these communities can quickly adapt to battlefield conditions and incorporate user feedback. The modular, COTS-based (commercial off-the-shelf) nature of FPV drone components has further accelerated this process, allowing for rapid assembly, customization, and deployment of these platforms.
Strategic Implications and Operational Adaptations
The widespread adoption of FPV drones in the Russia-Ukraine conflict has had far-reaching strategic implications, challenging traditional notions of warfare and military capabilities. These agile, cost-effective platforms have disrupted the conventional balance of power, empowering smaller, nimbler actors to engage in asymmetric warfare and overcome the technological superiority of larger, more sophisticated military forces.
As a result, both Russia and Ukraine have been forced to adapt their operational strategies to account for the growing threat posed by FPV drones. This has led to the development of countermeasures, such as enhanced electronic warfare and air defense systems, as well as the integration of FPV drones into combined-arms operations, where they work in tandem with other military assets to achieve strategic objectives.
Know the 5 Types of Drones Used by the US Military
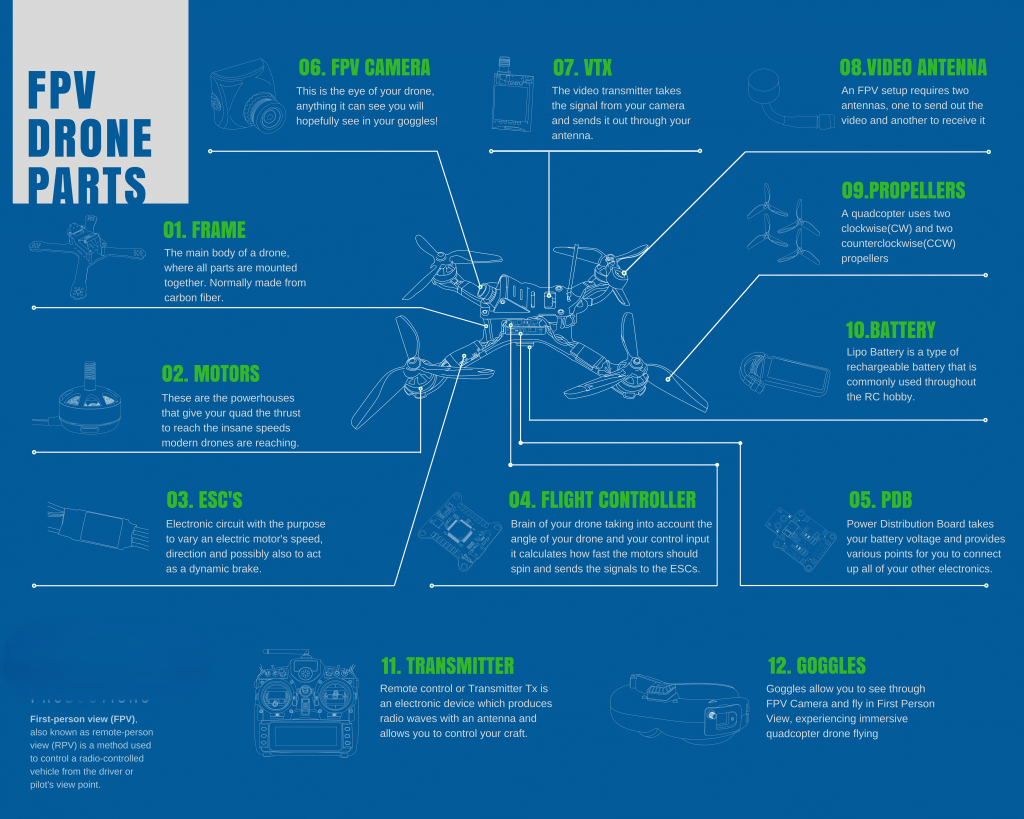
Anatomy of an FPV Drone
At the core of the FPV drone revolution lies a intricate interplay of specialized components, each contributing to the overall performance and capabilities of these high-tech platforms. From the frame and flight systems to the power source and FPV-specific equipment, the design and integration of these elements are crucial in shaping the drone’s agility, endurance, and precision.
Frame and Structural Components
The frame of an FPV drone serves as the foundation upon which all other components are built. Typically constructed from lightweight, durable materials like carbon fiber, the frame’s design is a crucial factor in determining the drone’s maneuverability and aerodynamic performance. Factors such as frame shape, wheelbase, and mounting points all play a vital role in optimizing the drone’s flight characteristics.
Flight Systems and Propulsion
At the heart of an FPV drone’s flight capabilities are its advanced flight systems and propulsion components. This includes the flight controller, which acts as the “brain” of the drone, managing sensors, stabilization, and autonomous features. Electronic speed controllers (ESCs) and brushless motors work in tandem to provide the necessary thrust and control, while specialized propellers are designed to maximize efficiency and agility.
Power Systems and Battery Management
Powering the FPV drone’s flight and onboard systems is a critical consideration. Lithium-polymer (LiPo) batteries are the prevalent choice, offering a favorable balance of energy density, discharge rate, and weight. Efficient power distribution boards (PDBs) ensure the reliable delivery of power to the various components, while advanced battery management systems monitor and optimize the drone’s power consumption.
FPV-Specific Equipment
The defining feature of an FPV drone is its specialized equipment for providing the immersive first-person view experience. This includes the onboard camera, which is often positioned for a forward-facing, unobstructed view, and the video transmitter (VTX) module that converts the camera’s output into a compatible video signal for transmission. The operator’s FPV goggles or display device completes the loop, allowing them to see the drone’s perspective in real-time.
Customization and Modularity
One of the key advantages of FPV drones is their inherent customization and modularity. The modular design of these platforms allows for easy integration of various payloads, sensors, and even specialized weaponry, expanding their operational capabilities to suit a wide range of military applications. This flexibility, coupled with the availability of commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) components, enables rapid prototyping, iterative improvements, and seamless adaptation to evolving operational requirements.
IAF & Indian Navy To Acquire 10 Tapas Drones
The Transformative Impact of FPV Drones
The integration of FPV drones into modern military operations has had a profound and far-reaching impact, challenging traditional notions of warfare and redefining the strategic landscape. From the cost-effectiveness and scalability of these platforms to their ability to overcome technological superiority, the transformative impact of FPV drones is undeniable.
Disrupting the Cost-Capability Paradigm
One of the most significant impacts of FPV drones is their ability to disrupt the traditional cost-capability paradigm in military technology. Compared to larger, more sophisticated UAVs, FPV drones offer a compelling value proposition. Their modular, COTS-based design and rapid prototyping capabilities allow for the development and deployment of these platforms at a fraction of the cost of their more complex counterparts.
This cost-effectiveness, combined with their impressive performance and versatility, has enabled smaller, resource-constrained actors to leverage FPV drones as a force multiplier, challenging the technological dominance of larger military powers. This shift has profound implications for the future of warfare, as it empowers a wider range of stakeholders to engage in asymmetric conflicts and potentially offset the advantages of more conventional military assets.
Overcoming Technological Superiority
The Russia-Ukraine conflict has vividly demonstrated the ability of FPV drones to overcome technological superiority. As Russia’s air defense and electronic warfare capabilities have grown, the Ukrainians have increasingly turned to these agile, high-speed platforms to penetrate enemy airspace, conduct reconnaissance, and deliver precision strikes.
The adaptability and resilience of FPV drones have been crucial in this context. Their modular design allows for rapid integration of countermeasures, such as electronic warfare suites and autonomous navigation algorithms, enabling them to operate effectively even in the face of advanced adversarial capabilities. This ability to adapt and evolve has allowed FPV drones to become a formidable asset in the face of technological superiority, redefining the dynamics of modern warfare.
Collaborative Innovation and Decentralized Warfare
The rise of FPV drones in modern warfare has been fueled by a unique blend of collaborative innovation and decentralized warfare. In both Russia and Ukraine, volunteer communities with strong technical backgrounds have played a pivotal role in developing and iterating on FPV drone designs, often in close collaboration with military and defense entities.
This grassroots approach to innovation has enabled the rapid development and deployment of FPV drones, as these communities can quickly adapt to battlefield conditions and incorporate user feedback. The modular, COTS-based nature of FPV drone components has further accelerated this process, allowing for rapid assembly, customization, and deployment of these platforms.
The decentralized nature of this innovation ecosystem has profound implications for the future of warfare, as it empowers smaller, nimbler actors to engage in asymmetric conflicts and challenge the traditional dominance of larger military powers. This shift towards a more collaborative and adaptive approach to military technology development has the potential to reshape the strategic landscape, fostering a more dynamic and unpredictable battlefield environment.
Top 10 Anti-Drone Technologies to Counter Drones
Navigating the Ethical Considerations
As the adoption of FPV drones in military operations continues to grow, it is essential to consider the ethical implications and potential challenges associated with this transformative technology. The increased accessibility and scalability of these platforms raise important questions about the responsible use of force, the protection of civilian populations, and the need for robust governance frameworks.
Civilian Harm and Collateral Damage
One of the primary ethical concerns surrounding FPV drones is the potential for civilian harm and collateral damage. The agility and precision of these platforms, combined with their ability to operate in complex, urban environments, heighten the risk of unintended consequences. Robust target identification, discrimination, and engagement protocols are crucial to mitigate the impact on non-combatants and ensure compliance with international humanitarian law.
Autonomous Capabilities and Meaningful Human Control
The integration of autonomous features and AI-enabled decision-making into FPV drones raises complex ethical questions about the appropriate level of human control and oversight. As these platforms become increasingly capable of independent target acquisition and engagement, there is a need to ensure that meaningful human control is maintained, and that accountability mechanisms are in place to address potential misuse or unintended outcomes.
Proliferation and Accessibility
The cost-effectiveness and scalability of FPV drones have led to concerns about their potential proliferation and accessibility to non-state actors, including terrorist organizations and criminal networks. Effective governance frameworks, export controls, and international cooperation are essential to mitigate the risks of these platforms falling into the wrong hands and being used for malicious purposes.
Transparency and Accountability
Addressing the ethical challenges posed by FPV drones requires a commitment to transparency and accountability. Military and defense organizations must engage in open dialogues with civil society, policymakers, and the international community to establish clear guidelines, rules of engagement, and oversight mechanisms. This collaborative approach is crucial in building public trust and ensuring the responsible use of these transformative technologies.
10 Best Military Drones In The World
Conclusion
The rise of first-person view (FPV) drones has ushered in a new era of modern warfare, redefining the strategic landscape and challenging traditional notions of military capabilities. These agile, high-speed platforms have emerged as a game-changer, offering unparalleled levels of immersion, precision, and tactical advantage to both state and non-state actors.
The ongoing Russia-Ukraine conflict has served as a crucible for the rapid development and widespread adoption of FPV drones, with both sides leveraging these platforms to gain crucial advantages on the battlefield. The collaborative innovation and rapid prototyping that have driven this evolution have profound implications for the future of warfare, empowering smaller, nimbler actors to engage in asymmetric conflicts and overcome the technological superiority of larger military forces.
As the integration of FPV drones continues to transform the military landscape, it is essential to navigate the ethical considerations and ensure the responsible use of these transformative technologies. Addressing concerns about civilian harm, autonomous capabilities, proliferation, and transparency will be crucial in shaping the future of warfare and maintaining the delicate balance between military necessity and humanitarian principles.
In the years to come, the impact of FPV drones is poised to grow exponentially, as these platforms continue to evolve, adapt, and integrate with other emerging technologies. The defense sector’s ability to harness the power of FPV drones, while upholding ethical and legal standards, will be a defining factor in the future of modern warfare.
FAQs
1. What does FPV mean for a drone?
An FPV drone is an unmanned aerial vehicle equipped with a camera that sends video feed wirelessly to goggles, a headset, a mobile device, or another display. This allows the user to experience a first-person view (FPV) of the drone’s surroundings and capture both video and still images.
2. What is the difference between FPV and regular drones?
FPV drones differ from regular camera drones in that they offer a first-person view; this means the camera feed is displayed through the operator’s video goggles or VR headset rather than on a phone screen. Unlike standard drones, FPV drones typically lack a gimbal, so the camera is fixed in place.
3. Why do people use FPV drones?
These compact, highly maneuverable drones have captivated the drone community, allowing pilots to participate in thrilling racing events and produce stunning cinematic footage previously unattainable on screen.
4. How fast can FPV fly?
FPV racing quadcopters can achieve speeds of up to 120 mph (193 km/h). The maximum speed is influenced by the motor power, battery capacity, and overall design of the quadcopter.
5. Do FPV drones use WIFI?
Operate your drone without concern for internet connectivity, as most drones generate their own Wi-Fi network for direct connection with your phone. This allows you to control your drone and view live FPV (First Person View) footage on your phone, even in remote locations with no internet access.