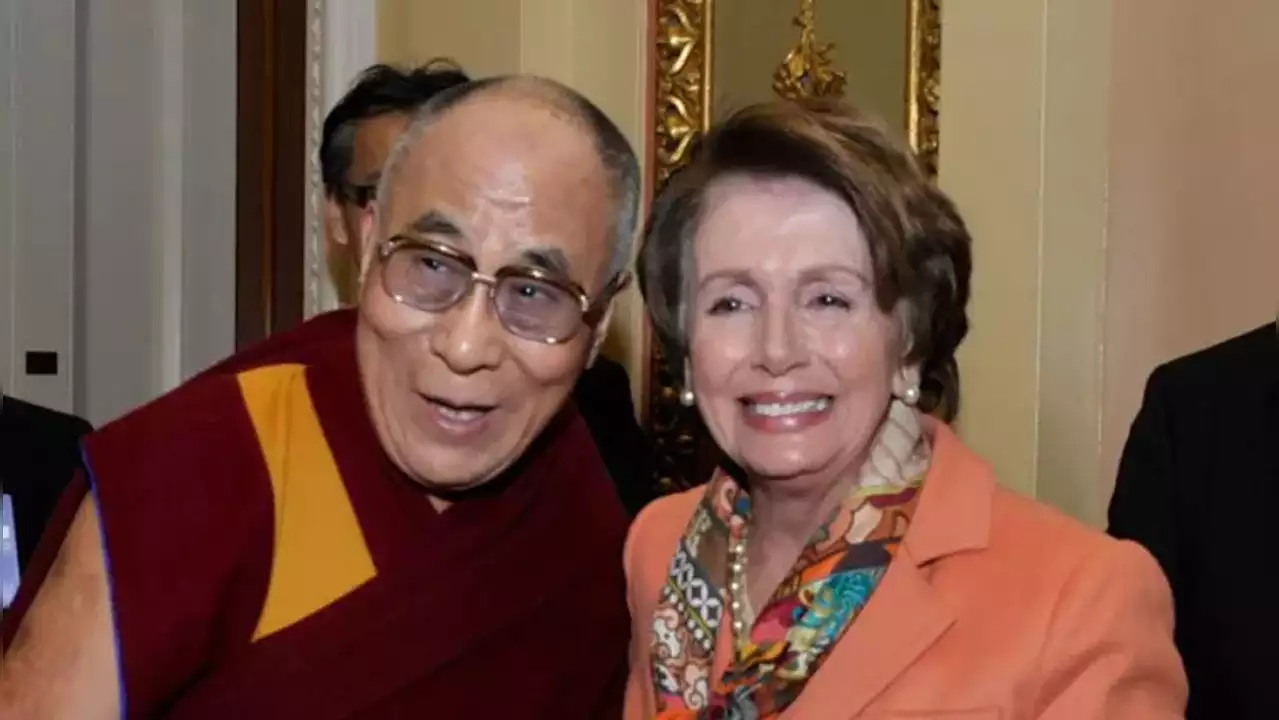
A bipartisan delegation from the US House of Representatives, which includes Speaker Emerita Nancy Pelosi and House Foreign Affairs Committee chairperson Michael McCaul arrived in Dharamshala on Tuesday and will meet His Holiness the Dalai Lama on Wednesday.
US lawmakers To Meet Dalai Lama
Why In News
- A bipartisan delegation from the US House of Representatives, which includes Speaker Emerita Nancy Pelosi and House Foreign Affairs Committee chairperson Michael McCaul arrived in Dharamshala on Tuesday and will meet His Holiness the Dalai Lama on Wednesday.
- Tibet’s government-in-exile is based in Dharamshala and it represents over one lakh Tibetans living in around 30 countries.
- The US has strongly been supporting the Tibetan cause and condemning all oppression and coercion of Tibetans by China.
- The US House of Representatives voted 391-26 last Wednesday to approve the Promoting and Resolution to the Tibet-China Dispute Act, which was passed by the Senate, a media report said, adding, that the bill would direct funds to counter what it calls “disinformation” from Beijing about Tibet’s history, people and institutions.
China’s Statement
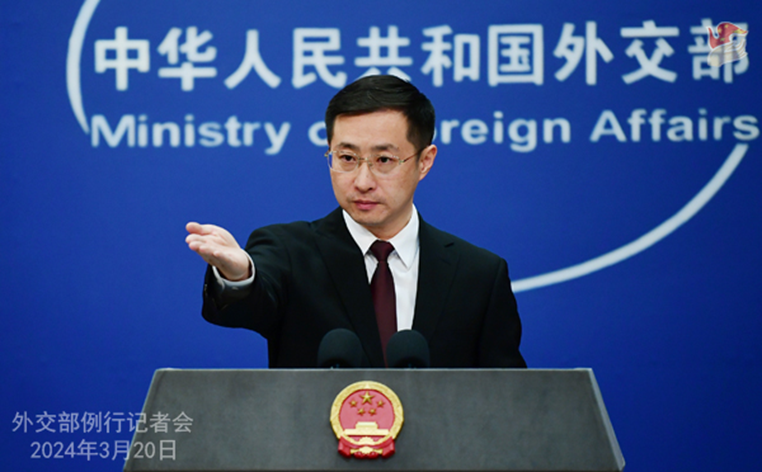
- Chinese Foreign Ministry spokesperson, Lin Jian, while reacting to the US delegation visit, told a media briefing here: “The 14th Dalai Lama is not a pure religious figure, but a political exile engaged in anti-China separatist activities under the cloak of religion.”
- “We are gravely concerned over the relevant reports and urge the US side to fully recognise the anti-China separatist nature of the Dalai group, honour the commitments the US has made to China on issues related to Xizang, have no contact with the Dalai group in any form, and stop sending the wrong signal to the world”, he said.
- Lin also urged Biden not to sign the bipartisan Tibet policy bill adopted by both the US Senate and the House of Representatives. The bill awaits Biden’s signature to make it into a law, according to media reports in Washington.
- The bill seeks to counter China’s narrative about its control over Tibet and promote dialogue between the Chinese government and the Dalai Lama.
- Claiming that Tibet has been part of China since ancient times, Lin said it always remained China’s territory and “Tibet related affairs are purely China’s internal affairs that brook no external interference.”
- “No one and no force should ever attempt to destabilise Tibet to contain and suppress China. Such attempts will never succeed,” he said.
- “We urge the US side to adhere to its commitments of recognising Xizang as part of China and not supporting ‘Xizang independence.
Tibet Issue
- Detailing the Tibet Bill, reported earlier that it refutes the Chinese government’s claim that Tibet has been part of China since ancient times, and would make it US policy that the dispute over Tibet’s status is unresolved.
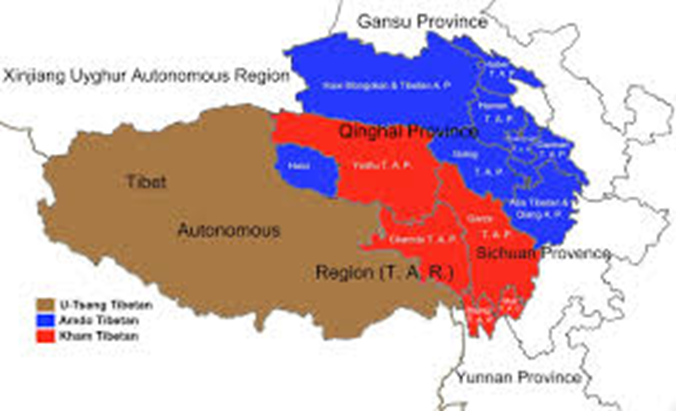
- It would also make it US policy that “Tibet” refers not only to the Tibet autonomous region as defined by the Chinese government but also to Tibetan areChina in April this year said it would talk only with the representatives of the Dalai Lama and not the officials of the Tibetan government in exile based in India.
- At the same time, China ruled out dialogue on the Dalai Lama’s long-pending demand for autonomy for his remote Himalayan homeland.
- In its talks with China between 2002 and 2010, the Tibetan side pitched genuine autonomy for the Tibetan people in line with the middle-way policy as proposed by the Dalai Lama, who has said he does not seek political independence for Tibet but seeks autonomy for all Tibetan areas which included Gansu, Qinghai, Sichuan and Yunnan provinces besides the current official Tibet Autonomous Region, a truncated version of Tibet before it was annexed by China.
- After a failed anti-Chinese uprising in 1959, the 14th Dalai Lama fled Tibet and came to India where he set up the government-in-exile.
- Relations between the two sides strained further due to protests against China in Tibetan areas in 2008.