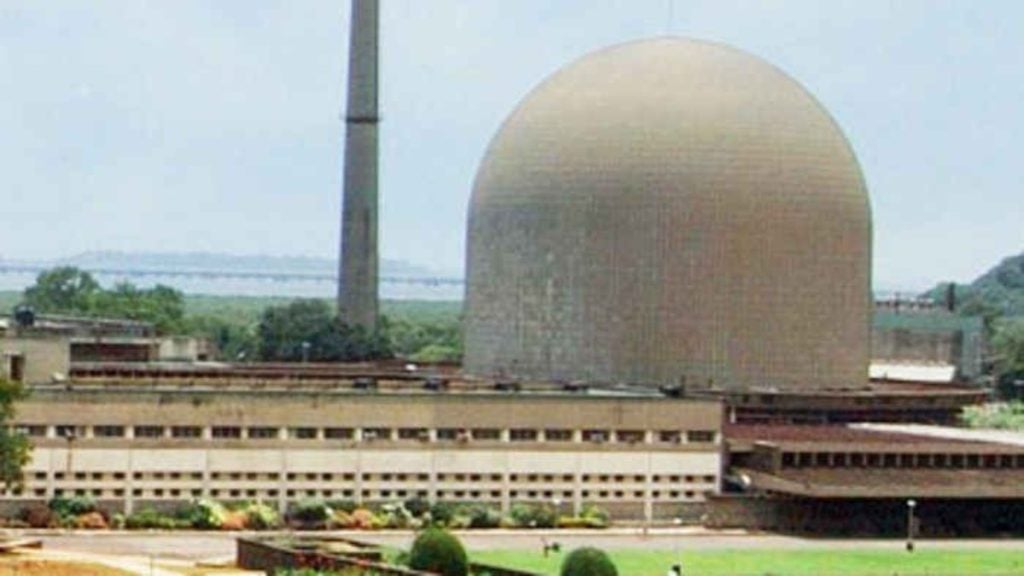
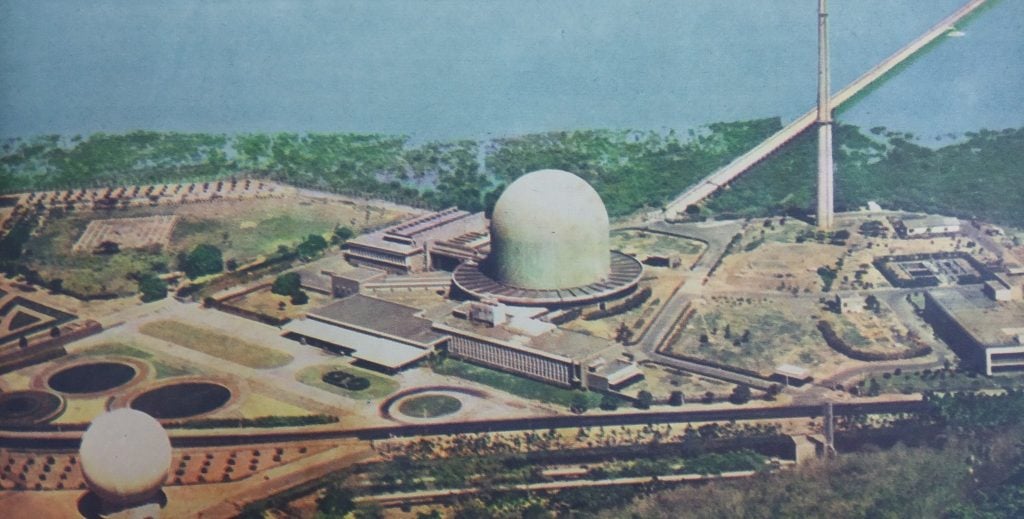
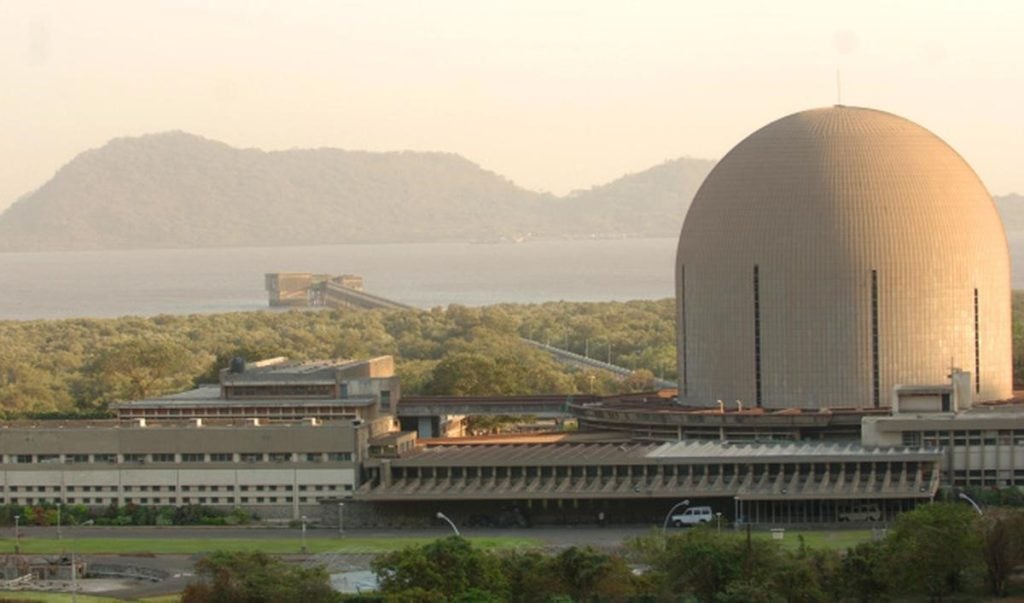
The Bhabha Atomic Research Center (BARC) is a beacon of scientific innovation and development in India, playing a pivotal role in the nation’s nuclear research and energy programs. Established in the mid-20th century, BARC has evolved into a premier institution that not only addresses the country’s energy needs but also contributes significantly to various scientific domains. This article explores the full form of BARC, its history, objectives, and its critical contributions to nuclear science and technology.
The acronym BARC stands for the Bhabha Atomic Research Center. Named after Dr. Homi Jehangir Bhabha, a renowned physicist and the architect of India’s nuclear program, BARC symbolizes India’s commitment to harnessing nuclear energy for peaceful applications. As the institution continues to evolve, it remains at the forefront of nuclear research, ensuring that India maintains its position in the global scientific community.
An Overview of BARC
The Role of BARC in Nuclear Research
Founded in 1954, BARC operates under the Department of Atomic Energy (DAE) and is headquartered in Trombay, Mumbai. The center is instrumental in advancing nuclear science and technology, focusing on several key areas:
- Nuclear Science: BARC conducts extensive research in nuclear physics, contributing to the development of nuclear reactors and fuel cycles.
- Chemical Engineering: The center plays a vital role in the chemical processes involved in nuclear energy production.
- Biotechnology: BARC is involved in applying nuclear techniques in healthcare and agriculture, enhancing food safety and medical diagnostics.
- Materials Science: Research in this area focuses on developing advanced materials for nuclear applications.
Multidisciplinary Approach
BARC’s multidisciplinary approach is crucial for addressing the complexities of nuclear research. Its diverse fields of study include:
- High-Energy Physics: Investigating the fundamental particles and forces that constitute the universe.
- Plasma Physics: Exploring the behavior of ionized gases, which has implications for nuclear fusion research.
- Supercomputing: Utilizing advanced computational techniques to model nuclear reactions and reactor behavior.
This comprehensive focus enables BARC to contribute significantly to India’s strategic and sustainable development goals.
Also Read | 8 Top Tips to Crack the Rashtriya Military School Interview
Historical Background of BARC
The Genesis of Nuclear Research in India
India’s journey into nuclear science began shortly after independence in 1947. Recognizing the importance of nuclear technology for national development, Dr. Homi Bhabha established the Atomic Energy Establishment, Trombay (AEET) in 1954. This institution laid the groundwork for what would become BARC.
Evolution and Milestones
- 1954: The establishment of AEET marked the beginning of organized nuclear research in India.
- 1967: Following Dr. Bhabha’s untimely demise, AEET was renamed the Bhabha Atomic Research Center to honor his legacy.
- 1970s and 1980s: BARC made significant strides in developing indigenous nuclear reactors and fuel cycles, enhancing India’s energy security.
These milestones illustrate BARC’s evolution into a leading research institution, integral to India’s nuclear ambitions.
BARC’s Motto and Mission
Atoms in the Service of the Nation
BARC’s motto, “Atoms in the Service of the Nation,” encapsulates its mission to harness nuclear energy for the benefit of society. This guiding principle reflects BARC’s commitment to using atomic science for:
- Energy Production: Developing sustainable nuclear power solutions to meet the nation’s energy demands.
- Healthcare: Applying nuclear techniques in medical diagnostics and treatment.
- Agriculture: Enhancing food security through nuclear technologies.
This motto emphasizes the institution’s dedication to ensuring that nuclear science serves the greater good.
Key Roles and Objectives of BARC
Promoting Peaceful Applications of Nuclear Energy
One of BARC’s primary goals is to advocate for the peaceful use of nuclear technology. This includes:
- Nuclear Power Generation: Developing safe and efficient nuclear reactors for energy production.
- Medical Applications: Utilizing isotopes in medical imaging and cancer treatment.
Comprehensive Management of Nuclear Power
BARC oversees the entire lifecycle of nuclear power generation, which includes:
- Reactor Design: Innovating new reactor designs that prioritize safety and efficiency.
- Simulation and Modeling: Using advanced computational tools to predict reactor behavior and performance.
Safety and Risk Management
BARC places a strong emphasis on safety and risk management in nuclear operations:
- Research and Development: Conducting studies to improve reactor safety and fuel efficiency.
- Waste Management: Ensuring the responsible disposal of nuclear waste materials.
Industrial Applications of Isotopes
The center also focuses on the industrial applications of isotopes, which include:
- Radiation Technologies: Applying radiation techniques in sectors such as agriculture, food safety, and environmental monitoring.
- Material Testing: Utilizing isotopes for non-destructive testing and quality assurance in various industries.
Through these initiatives, BARC demonstrates its commitment to advancing nuclear technology for national development.
BARC’s Research Reactors
A Legacy of Innovation
India’s nuclear journey is marked by the establishment of several pioneering reactors. These reactors have significantly contributed to the country’s research capabilities and energy independence.
APSARA-U Reactor
- Description: The APSARA-U is a modern reactor that employs domestically developed depleted uranium fuel in the form of uranium silicide.
- Milestone: In September 2018, it achieved criticality, marking a significant advancement in nuclear research safety.
APSARA Reactor
- Historical Significance: Launched in 1956, the APSARA reactor was India’s first nuclear reactor to achieve criticality.
- Specifications: Operating at a capacity of 1 megawatt, it utilizes light water as both coolant and moderator.
ZERLINA Reactor
- Operational History: The ZERLINA reactor, which achieved criticality in January 1961, was primarily focused on reactor research.
- Decommissioning: It was decommissioned in 1983 after fulfilling its research objectives.
CIRUS Reactor
- Collaboration: Developed in partnership with a Canadian research organization, the CIRUS reactor began operations in 1960.
- Applications: It is utilized for fuel testing, material irradiation, and producing radioisotopes for medical uses.
These reactors have played a crucial role in shaping India’s nuclear landscape, each contributing unique innovations to the field of nuclear science.
Establishing a Foundation for Nuclear Science in India
The Visionary Leadership of Dr. Bhabha
Dr. Homi Jehangir Bhabha’s vision was instrumental in laying the foundation for nuclear science in India. In 1945, he established the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research (TIFR), which became a cornerstone for future nuclear research initiatives.
The Birth of BARC
In 1954, Dr. Bhabha founded the Atomic Energy Establishment, Trombay, which later became BARC. This institution has since evolved into a leading research center, driving advancements in nuclear technology and energy.
Also Read | A Day In The Life Of An RMS Student
BARC’s Contributions to Global Nuclear Research
International Collaborations
BARC actively engages in international collaborations to enhance its research capabilities. These partnerships facilitate knowledge exchange and technological advancements in nuclear science.
- Joint Research Initiatives: Collaborating with global institutions on nuclear safety and reactor technology.
- Training Programs: Offering training and educational programs for international scientists and engineers.
Contributions to Nuclear Safety
BARC plays a crucial role in promoting nuclear safety standards globally. Its research in safety protocols and risk management contributes to the international community’s efforts to ensure safe nuclear practices.
Future Directions for BARC
Embracing Innovation
As technology evolves, BARC is committed to embracing innovation in nuclear research. This includes:
- Advanced Reactor Designs: Developing next-generation reactors that prioritize sustainability and safety.
- Fusion Research: Exploring nuclear fusion as a potential energy source for the future.
Commitment to Sustainable Development
BARC is dedicated to aligning its research objectives with sustainable development goals. This involves:
- Renewable Energy Integration: Exploring synergies between nuclear power and renewable energy sources.
- Environmental Stewardship: Ensuring that nuclear practices are environmentally responsible and sustainable.
Also Read | How Military School Prepares You For Tough Challenges
Conclusion
The Bhabha Atomic Research Center stands as a testament to India’s commitment to nuclear science and technology. With its rich history, diverse research initiatives, and unwavering dedication to safety and sustainability, BARC continues to play a vital role in shaping the future of nuclear energy. As India moves forward, BARC will remain at the forefront of innovation, ensuring that atomic science serves the nation and the world.
FAQs
1. What is the full form of BARC?
The full form of BARC is the Bhabha Atomic Research Center.
2. When was BARC established?
BARC was established in 1954.
3. Who founded BARC?
BARC was founded by Dr. Homi Jehangir Bhabha.
4. What are the primary objectives of BARC?
BARC aims to promote the peaceful use of nuclear energy, ensure nuclear safety, and advance research in various scientific fields.
5. Where is BARC located?
BARC is headquartered in Trombay, Mumbai, India.