Quick Facts
- It is the naval arm of the Indian Armed Forces.
- The President is the Supreme Commander of the Indian Navy.
- 1612 – East India Company’s Marine was founded protect British merchant shipping in the region.
- 1793 – East India Company established its rule over eastern part of the Indian subcontinent i.e. Bengal
- 1830 – The colonial navy was titled as ‘His Majesty’s Indian Navy’.
- 1934 – Renamed as “Royal Indian Navy”.
- 1950 – Renamed as “Indian Navy”.
- Primary Objective – To safeguard the nation’s maritime borders, and in conjunction with other Armed Forces of the union, act to deter or defeat any threats or aggression against the territory, people or maritime interests of India, both in war and peace.
- Secondary Objective – Through joint exercises, goodwill visits and humanitarian missions, including disaster relief, Indian Navy promotes bilateral relations between nations.
Some Numbers:
- Number of active personnel – 67252
- Number of Reserve Personnel – 55000
- Number of Warships – 137
- Number of Aircrafts – 235
- Number of Aircraft Carriers – 1
- Number of Amphibious Transport Docks – 1
- Number of Landing Ship Tanks – 8
- Number of Destroyers – 11
- Number of Frigates – 14
- Number of nuclear-powered attack submarines – 1
- Number of ballistic missile submarine – 1
- Number of conventionally-powered attack submarines – 15
- Number of corvettes – 22
- Number of mine countermeasure vessel – 1
- Number of fleet tankers – 4
Updates:
The Government of India approved the construction of six new nuclear-powered attack submarines in February 2015. These will be designed by the Navy’s in-house Directorate of Naval Design and indigenously built in the Shipbuilding Center at Visakhapatnam.
Commands:
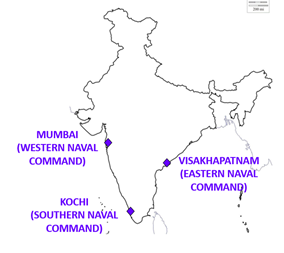
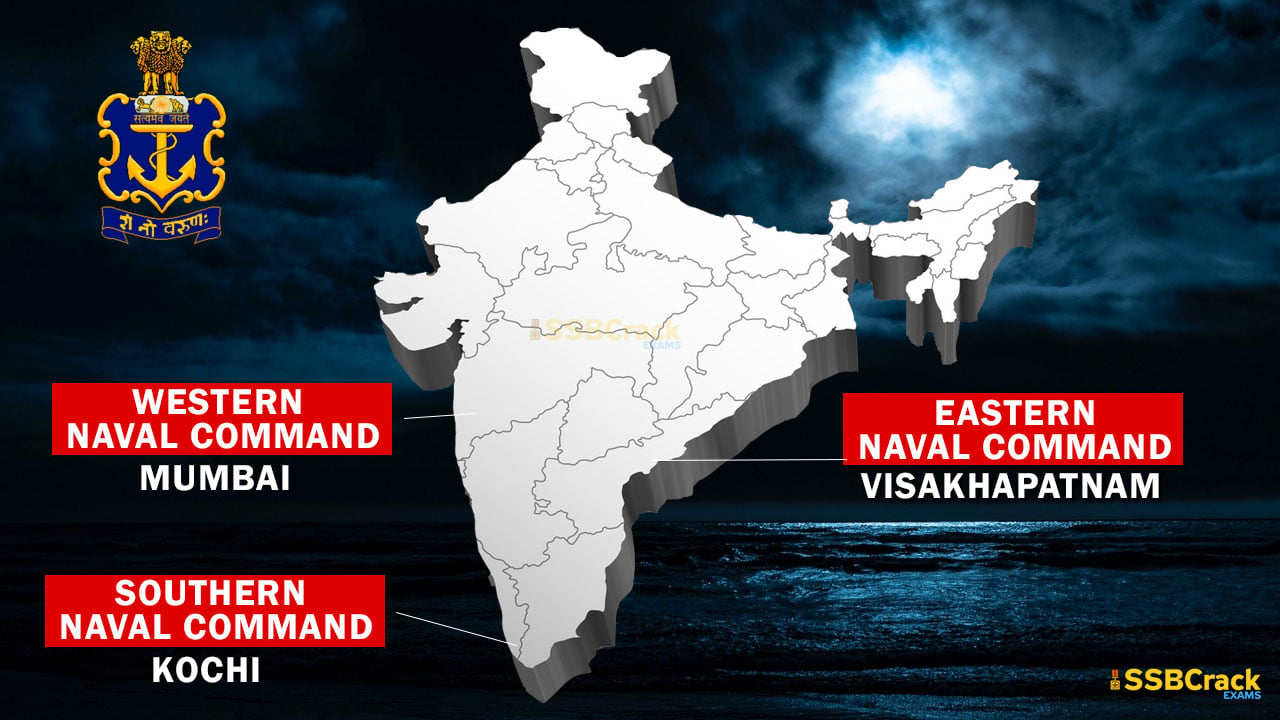
- There are three commands in Indian Navy:
- Eastern Naval Command – Headquartered at Visakhapatnam.
- Western Naval Command – Headquartered at Mumbai.
- Southern Naval Command – Headquartered at Kochi.
- There is also one more Command at the Andaman and Nicobar Islands which is a tri-service command.
- All Commands of the Navy are headed by a “Flag Officer Commanding in Chief” (shortly as FOC-in-C). His rank is of “Vice Admiral”.
- There are also Flotillas of ships, Squadrons of submarines and various types of aircraft operated by the Navy from several Naval Air Stations.
- The major bases of the Indian Navy are located at Mumbai, Goa, Karwar, Kochi, Chennai, Visakhapatnam, Kolkata and Port Blair.
Western Naval Command – Mumbai
- It is responsible for the all naval forces in the Arabian Sea and parts of the Indian Ocean and the naval establishments on the west coast of India.
- The Command was formed on 1 March 1968.
- This command is the sword arm of the Indian Navy and naval operations conducted on the western seaboard would be central to the outcome of any conflict at sea against Pakistan.
- INS Kadamba, a large naval base, was constructed under Project Seabird and completed in 2005. This naval base, at Karwar in Karnataka, is used exclusively by the Indian Navy.
- The Flagship carrier of the Western Fleet is INS Vikramaditya.
- This Command consists of INS Vikramaditya, Delhi class destroyers, Talwar class frigates, Brahmaputra class frigates, INS Kolkata, and Sindhughosh class submarines.
- The Naval Aviation is provided by MiG-29K fighters along with airborne early warning Kamov Ka-31 Helicopters.


Vice Admiral Ajit Kumar PVSM AVSM VSM ADC is the current Flag Officer Commanding in Chief of the Western Naval Command.
Eastern Naval Command – Visakhapatnam
- The command is responsible for the all naval forces in the Bay of Bengal and parts of the Indian Ocean and the naval establishments on the east coast of India.
- The Command was established on 1 March 1968.
- The headquarters at Visakhapatnam is also a strategically important dockyard for two nuclear-powered submarines.
- Due to congestion and heavy shipping traffic, a new 20 square km base INS Varsha is being developed for exclusive naval use about 50 km south of Visakhapatnam.
- The Navy has opened its latest naval air base, INS Baaz, at the southernmost tip of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands to secure the strategically important Straits of Malacca, and another naval air station in Kolkata to base an unmanned aerial vehicle squadron.


Vice Admiral Atul Kumar Jain PVSM AVSM VSM is the current Flag Officer Commanding in Chief of the Eastern Naval Command.
Southern Naval Command – Kochi
- It is the Training Command of the Indian Navy and is responsible for the training of all its personnel, both officers as well as sailors, from basic to advance stages.
- The Southern Naval Command consists of a Flag Officer Sea Training (FOST), a training squadron, training establishments and bases, and land forces and survey ships. It has a naval air station, and a ship repair yard.


Vice Admiral Anil Kumar Chawla PVSM AVSM NM VSM ADC is the current Flag Officer Commanding in Chief of the Southern Naval Command.
Andaman and Nicobar Command
Consists of 6 Naval Bases:
- INS Kardip
- INS Jarawa
- INS Utkrosh – jointly administered by IN & IAF
- INS Baaz – Naval Air Station
- INS Kohassa – Naval Air Station
Also Read: