What is a Malware? How does a Malware spread?
- Malware is a short form of Malicious software.
- Malware is an umbrella term used to refer to a variety of forms of hostile or intrusive software including Ransom wares, Computer Viruses, Worms, Trojan Horses, Spyware, Adware, Scareware etc.
- Malware can be deployed even remotely and tracking the source of malware is hard.
- It can take the form of executable code, scripts, active content, and other software.
- Malware is typically used to steal information that can be readily monetized, such as login credentials, credit card and bank account numbers etc.
- Spread –
- Malware spreads in computer when you download or install an infected software. They also enter your computer through an email or a link. Once malware enters the computer, it attaches itself to different files and overwrites the data.
- Some malwares are to be executed before it’s activated, but some spread immediately. As malware travels within the network, it infects the computer it moves into.
BlackRock Android Malware
- BlackRock can steal information from smartphone applications, including popular apps like Amazon, Facebook, Gmail, and Tinder, and pose a grave security threat.
- BlackRock is a banking Trojan and said to be an enhanced version of existing Xerxes malware which itself is a variant of the LokiBot Android trojan.
- It collects user information by abusing the Accessibility Service of Android and overlaying a fake screen on top of a genuine app. It uses Android DPC (Device Policy Controller) to provide access to other permissions.
- It appears as a google update.
- It is so powerful that it makes antivirus applications useless.
Consumer Protection Act, 2019 comes into force
- The CCPA will be empowered to conduct investigations into violations of consumer rights and institute complaints / prosecution, order recall of unsafe goods and services, order discontinuance of unfair trade practices and misleading advertisements, impose penalties on manufacturers/endorsers/publishers of misleading advertisements.
- The rules for the prevention of unfair trade practices by the e-commerce platforms will be covered under the Act.
- Every e-commerce entity will be required to provide information regarding the refund, return, warranty and guarantee, exchange, delivery and shipment etc.
- An alternate dispute mechanism of mediation has also been provided.
- Mediation cells will be established.
- There will also be no fee for filing cases up to Rs. 5 lakhs as per the Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission Rules.
- The bill will replace the Consumer Protection Act, 1986
3rd G20 Finance Ministers and Central Bank Governors meeting
- Meeting was held under the Saudi Arabian Presidency through Video Conferencing.
- India was represented by Union Minister for Finance & Corporate Affairs Nirmala Sitharaman in the meeting.
- It discussed the global economic outlook amid evolving Covid-19 pandemic crisis along with other G20 finance track priorities for the year 2020.
- The importance and relevance of the G20 action plan was highlighted.
- During the first G20 FMCBG meet, a plan was laid down by the participants which included health response, economic response, sustainable recovery etc. And the 3rd meet reviewed whether the pan is carried our effectively or not in the G20 nations.
- The Group of Twenty (G20) is the premier forum for international economic cooperation which brings together the leaders of both developed and developing countries from every continent.
- G20 group members are Argentina, Australia, Brazil, Canada, China, France, Germany, India, Indonesia, Italy, Japan, Mexico, Russia, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Republic of Korea, Turkey, the United Kingdom, the United States and the European Union (EU).
Govt allowed contributions from any person or institution NDRF
- The central government has published the guidelines for contributing to the National Disaster Response FUND (NDRF) for the first time.
- Any person or institution can contribute to the National Disaster Response Fund (NDRF) as per Section 46(1)(b) of the Disaster Management (DM) Act, 2005.
- Govt allowed contributions from any person or institution NDRF
- It has been constituted under Section 46 of the Disaster Management Act, 2005.
- It is a fund managed by the Central Government for meeting the expenses for emergency Response, Relief and Rehabilitation due to any threatening disaster situation or disaster.
- Calamities covered – Cyclone, drought, earthquake, fire, flood, tsunami, hailstorm, landslide, avalanche, cloudburst, pest attack, frost and cold waves.
- It supplements the State Disaster Response Fund (SDRF) in case of a disaster of severe nature, provided adequate funds are not available in the SDRF.
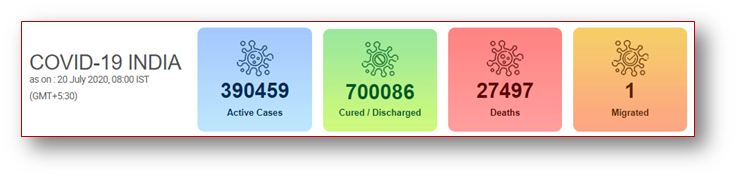
Current COVID19 Situation in India
QUIZ TIME
Consumer Protection Act, 2019 has replaced:
- Consumer Protection Act, 1987
- Consumer Protection Act, 1989
- Consumer Protection Act, 1988
- Consumer Protection Act, 1986
Answer – D
BlackRock Android Malware is a type of:
- Viruses
- worms.
- Banking Trojan
- Adware
Answer – C
Which of the following is not the member of G20 group?
- Germany
- India
- Nepal
- Indonesia
Answer – C
NDRF has been constituted under which of the following act?
- Disaster Management Act, 2005.
- Disaster Management Act, 2006.
- Disaster Management Act, 2007.
- Disaster Management Act, 2008.
Answer – A
Question of the Day
What are Sacred Groves?
Answer in next session…







