What is Samarth Scheme?
- Samarth Scheme, also known as Scheme for Capacity Building in the Textile Sector (SCBTS).
- Ministry: Skill Development Scheme of Ministry Of Textiles.
- This scheme is about providing skill development to the youth for gainful and sustainable employment in the textile sector covering the entire value chain of textiles excluding spinning and weaving.
- Objectives:
- Provide demand driven, placement oriented NSQF (National Skills Qualification Framework) Compliant skilling programme to incentivize organized textile and related sectors excluding Spinning and Weaving.
- Promote skilling and skill up-gradation in the traditional sectors of handlooms, handicrafts, sericulture and jute.
- Provide Sustainable livelihood to all sections of the society across the country
CAG Report: 40% of toilets in Government schools unused
- The Comptroller and Audit General submitted its report to both the houses.
- The report was titled “Construction of Toilets in Schools by the CPSEs”.
- CPSEs are Central Public Sector Enterprises.
- Public sector units claimed to have constructed 1.4 lakh toilets in government schools as part of a Right to Education project, but almost 40% of those surveyed were found to be non-existent, partially constructed, or unused.
- Over 70% did not have running water facilities in the toilets, while 75% were not being maintained hygienically.
- Swachh Vidyalaya Abhiyan
- Launched in 2014 by the then Ministry of HRD (now Ministry of Education).
- Aim: to meet the Right to Education Act’s mandate that all schools must have separate toilets for boys and girls.
- Under the programme the CPSEs to build toilets with running water and hand washing facilities.
CAG Report on Indian Railways
- The Comptroller and Auditor General of India submitted its report on Indian Railways in the Parliament.
- The report was titled “Assessment and Utilisation of Locomotives and Production and Maintenance of LHB coaches in Indian Railways”.
- The number of diesel locos has been increased by 20 per cent between 2012 and 2018.
- Reason: The Indian Railway Board failed to assess the requirement of electric locos.
- This also highlights the gap in the implementation of the Mission Electrification and De-Carbonisation
- Mission 100% Electrification
- Indian Railways aims to achieve 100% electrification of its railway network by 2023 through its ‘Mission Electrification’ plan.
- 63% of railway lines have been electrified in the country.
- Around 23,765 routes are yet to be electrified.
- Comptroller and Auditor-General of India
- It is an independent office.
- He is the head of the Indian audit & account department and chief Guardian of Public purse.
- Constitutional provisions: Article 148 – 151.
- His duty is to uphold the Constitution of India and the laws of Parliament in the field of financial administration.
- He submits his audit reports relating to the accounts of the Centre and State to the President and Governor, who shall, in turn, place them before both the houses of Parliament and the state legislature respectively.
G4 Foreign Ministers Meeting
- Group of 4 (G4), consisting of India, Brazil, Japan and Germany.
- Highlighted the urgency of reforming the United Nations and updating its main decision-making bodies, in order to better reflect contemporary realities.
- G4 is a group of countries that are seeking permanent membership of the UNSC.
- India in January will commence a two-year non-permanent term on the UNSC.
- India is proponent of other UNSC reforms — such as
- Increasing the number of permanent (currently five) and non-permanent (currently 10) seats
- Ensuring greater representation for Africa.
Plastic Parks Scheme
- Government has come up with a scheme of Setting up of Plastic Parks with an state-of-the-art infrastructure through cluster development approach.
- The Ministry of Chemicals & Fertilizers has approved setting up of 10 Plastic Parks in the country.
- The Parks are being set up in the states of Assam, Madhya Pradesh, Odisha, Tamil Nadu, Jharkhand, Uttarakhand and Chhattisgarh.
- Plastic Park is an industrial zone, developed in cluster approach for establishing units for plastic enterprises and its allied.
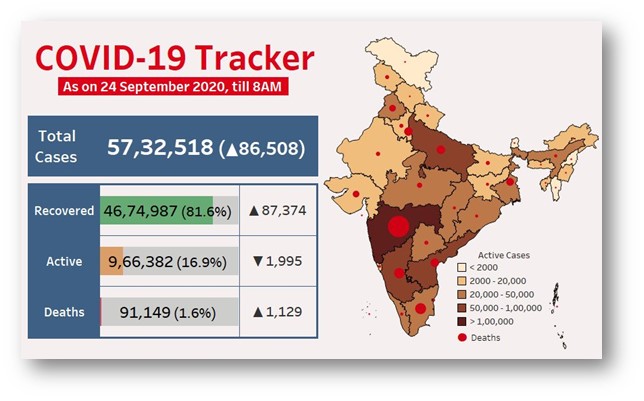
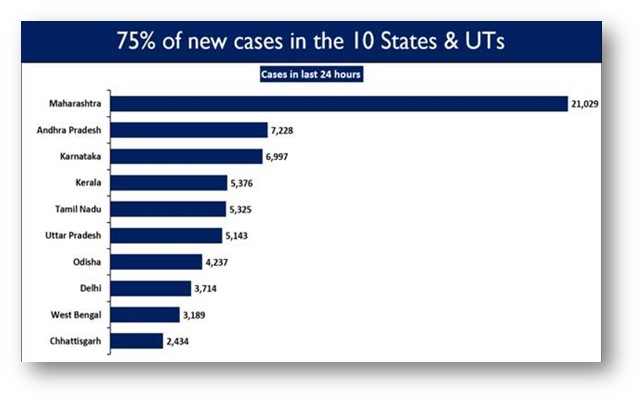
Current COVID19 Situation in India
QUIZ TIME
Who is the head of the Indian audit & account department?
- Finance Minister
- President
- Prime Minister
- CAG
Answer – D
Who is the chief Guardian of Public purse?
- Finance Minister
- President
- Prime Minister
- CAG
Answer – D
Comptroller and Auditor-General of India submits its reports to:
- President
- Prime Minister
- Finance minister
- None of these
Answer – A
Question of the Day
What are the key features of Major Port Authorities Bill, 2020?
Answer in next session…







