NDA’s presidential candidate Droupadi Murmu files her nomination papers today on 24th June 2022. Prime Minister Narendra Modi proposed her name for the nomination, which was seconded by Defence Minister Rajnath Singh. The second set of proposers were the chief ministers of BJP-ruled states, the third proposers were MLAs and MPs from Himachal and Haryana and the fourth set were MLAs and MPs from Gujarat.
Indian Presidential Election Nomination Process Begins
Droupadi Murmu is the first presidential candidate from Odisha of a major political party or alliance. She continues to break barriers and was the first woman governor of Jharkhand. She served as Jharkhand Governor from 2015 to 2021.
Born in a poor tribal family in a village of Mayurbhanj, a backward district in Odisha, Droupadi Murmu completed her studies despite challenging circumstances. She taught at Shri Aurobindo Integral Education Centre, Rairangpur. Born on June 20, 1958, she pursued BA at Ramadevi Women’s College Bhubaneswar. She started her political career as Rairangpur NAC vice-chairman. Droupadi Murmu was a member of the Odisha Legislative Assembly from Rairangpur between 2000 and 2004. As a minister, she held portfolios of Transport and Commerce, Animal Husbandry and Fisheries. She again served as MLA in the Odisha assembly from 2004 to 2009.
In 2007, the Odisha assembly honoured her with the ‘Nilakantha Award’ for best MLA. She served as a junior assistant in Irrigation and Power Department between 1979 and 1983. She has held several organisational posts in BJP and was vice president of state ST Morcha in 1997. Droupadi Murmu was a national executive member of BJP’s ST Morcha from 2013 to 2015 and served as BJP district chief of Mayurbhanj (West) in 2010 and 2013. Between 2006 and 2009, she was chief of BJP’s ST Morcha in Odisha. She was a member of the national executive of BJP ST Morcha from 2002 to 2009.
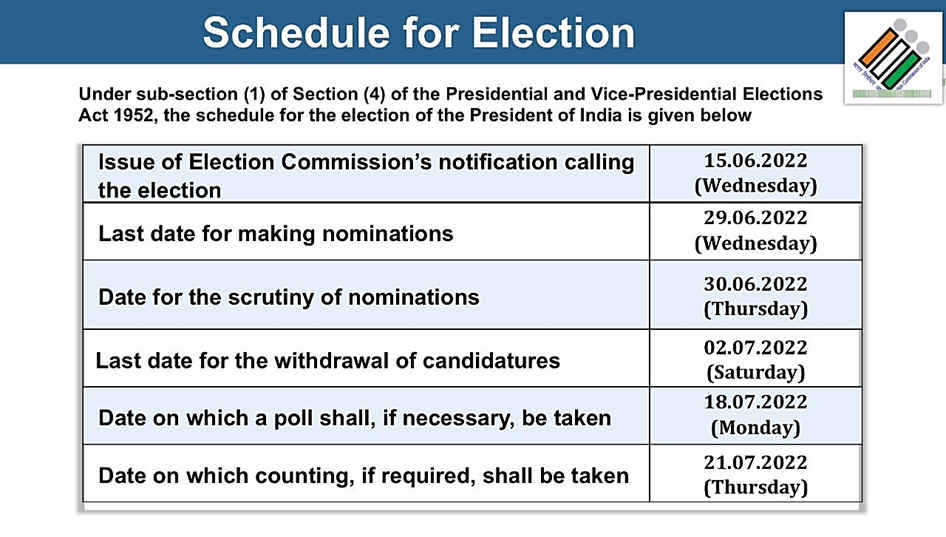
Schedule For 16th President Of India Elections:
President Of India: The First Citizen Of State
- Article 52- 78 Of Part V Of The Indian Constitution Has The Provision Of The Union Executive, Of Which The President Is The Part. The Union Executive Consists Of The President, Prime Minister, Vice President, The Council Of Ministers, And The Attorney General Of India.
Related Constitutional Provisions
- Article 54: Election Of President
- Article 55: Manner Of Election Of President
- Article 56: Term Of Office Of President
- Article 57: Eligibility For Re-election
- Article 58: Qualifications For Election As President
Qualification For The Position
- He Should Be A Citizen Of India
- He Should Have Completed 35 Years Of Age.
- Not Only That But He Should Be Qualified For Election As A Member Of The Lok Sabha.
- He Should Not Hold Any Office Of Profit Under The Union Government Or Any State Government Or Any Local Authority Or Any Other Public Authority.
Condition Of President’s Office
- He Should Not Be A Member Of Either The House Of Parliament Or The House Of The State Legislature. If Any Such Person Is Elected As President, He Is Deemed To Vacate His Seats In That House On The Date He Enters Into His Office As A President. He Should Not Hold Any Other Office Of Profit.
- He Is Entitled, Without Payment Of Rent, To The Use Of His Official Residence Which Is Rashtrapati Bhawan. He Is Entitled To Such Emoluments, Allowances, And Privileges As May Be Determined By The Parliament. His Emoluments And Allowances Cannot Be Diminished During His Term Of Office.
Term Of The President’s Office
- He Is Entitled To Hold The Office For 5 Years From The Start Of His Tenure. He Can Resign From His Office Anytime By Submitting His Resignation Letter To The Vice President Of India.
- He Can Also Be Removed From His Office Before The Completion Of His Tenure By The Process Of Impeachment On Valid Grounds. He Can Also Hold His Office Until The Successor Gets Elected. And He Can Be Selected Any Number Of Times As A President Through The Election Process.
Power To Conduct Elections
- Article 324 Of The Constitution Read With The Presidential And Vice-presidential Elections Act, 1952, And The Presidential And Vice-Presidential Elections Rules, 1974 Vests The Superintendence, Direction And Control Of The Conduct Of Election To The Office Of The President Of India In The ECI.
Conditions For Nomination
- A Candidate Must Be Subscribed By At Least 50 Electors As Proposers And 50 Electors As Seconders. Every Candidate Has To Make A Security Deposit Of Rs. 15000 In The Reserve Bank Of India. The Security Deposit Is Liable To Fortify If The Candidate Fails To Secure ⅙ Of The Votes Polled.
Election Procedure
- The President Is Not Directly Elected By The People. He Is Elected By The Members Of The Electoral College, Comprising:-
- The Elected Members Of Both The Houses Of The Parliament
- The Elected Members Of The Legislative Assemblies Of The State
- The Elected Members Of The Legislative Assemblies Of The Union Territories Of Delhi And Puducherry
- Only The Elected Members Of The Above Posts Can Take Part In The Election Of The President. The Nominated Or The Members Of The Dissolved Assemblies Are Not Entitled To Participate In The Election Process Of The President.
- The Election Will Be Held By Secret Ballot In Accordance With The System Of Proportional Representation By An Electoral College. A Nominated Candidate Does Not Secure Victory Based On A Simple Majority But Through A System Of Bagging A Specific Quota Of Votes.
- While Counting, The EC Totals Up All The Valid Votes Cast By The Electoral College Through Paper Ballots, And To Win, The Candidate Must Secure 50% Of The Total Votes Cast + 1.
- Unlike General Elections, Where Electors Vote For A Single Party’s Candidate, The Voters Of The Electoral College Write The Names Of Candidates On The Ballot Paper In The Order Of Preference.
Value Of Each Vote
- A Vote Cast By Each MP Or MLA Is Not Calculated As One Vote. The Fixed Value Of Each Vote By An MP Of The Rajya Sabha And The Lok Sabha Is 708.
- Meanwhile, The Vote Value Of Each MLA Differs From State To State Based On A Calculation That Factors In Its Population Vis-a-vis The Number Of Members In Its Legislative Assembly.
- As Per The Constitution (84th Amendment) Act 2001, Currently, The Population Of States Is Taken From The Figures Of The 1971 Census. This Will Change When The Figures Of The Census Taken After The Year 2026 Are Published.
- The Total Number Of Electors Will Be 4,809 Including 776 Members Of Parliament And 4,033 Members Of Legislative Assemblies. The Total Value Of The Votes Will Be 10,86,431.
Impeachment Of The President Of India
- According To Article 61, The President Can Be Removed From His Office Before The Expiry Of His Term Only On The Grounds Of Violation Of The Constitution. However, The Constitution Does Not Define The Meaning Of The Phrase.
- The Impeachment Process Can Be Started From Any House Of The Parliament By Levelling Charges Against Him. The Notice Bearing The Charges Against The President Must Be Signed By At Least A Quarter Of Members Of The House.
- The Resolution To Impeach The President Must Be Passed By A Special Majority (Two-thirds) In The Originating House. Next, It Is Sent To The Other House For Consideration. The Other House Acts As The Investigating House.
- A Select Committee Is Formed To Investigate The Charges Labelled Against The President. During The Process, The President Of India Has The Right To Defend Himself Through Authorised Counsel. He Can Choose To Defend Himself Or Appoint Any Person/Lawyer Or Attorney General Of India To Do So.
- If The Select Committee Finds The Charges Appropriate, The Resolution To Impeach The President Again Must Be Passed By A Special Majority (Two-thirds) In The Other House. If Resolution Is Passed The President Of India Will Automatically Stand Impeached.
REVIEW QUESTIONS
- Procedure Of Impeachment Of The President Of India Is
- Judicial Procedure
- Quasi-Judicial Procedure
- Legislative Procedure
- Executive Procedure
ANSWER: B
- Only Condition For Impeachment Of The Indian President
- Proved Misbehaviour
- Declared Insolvent
- Criminal Charges
- Violation Of The Constitution
ANSWER: D
- The Impeachment Process Of President Shall Be Introduced In
- Lok Sabha Only
- Rajya Sabha Only
- Lok Sabha Or Rajya Sabha
- Supreme Court
ANSWER: C
- President Of India Is Appointed By
- Chief Justice Of India
- Vice President Of India
- Electoral College
- None Of The Above
ANSWER: D
- The President Of India Submits His Resignation To
- Chief Justice Of India
- Vice President Of India
- Prime Minister Of India
- Lok Sabha
ANSWER: B
- President Of India Has The Power Of Pardoning Under
- Article 72
- Article 73
- Article 74
- Article 76
ANSWER: A
- Article 74 States About ____
- The Extent Of The Executive Power Of The Union
- Council Of Ministers Shall Aid The President
- Attorney General Of India
- Conduct Of Business Of The Government Of India
ANSWER: B
- Minimum Age To Contest Elections For President Of India
- 18
- 25
- 35
- 65
ANSWER: C
- Odd One Out: Qualification For President Of India
- He Shall Be A Citizen Of India.
- He Holds Office For A Period Of 5 Years.
- He Should Have Not Completed 65 Years Of Age.
- He Should Be Qualified To Be Elected As A Member Of Lok Sabha.
ANSWER: C
- The Electoral College For President’s Election Does Not consist Of
- Elected Members Of Lok Sabha
- Nominated Members Of Rajya Sabha
- Elected Members Of States Assemblies
- Elected Members Of Delhi And Puducherry Assemblies
ANSWER: B
To crack the SSB interview, You can join our SSB interview live classes batch and we recommend you to Enroll SSB INTERVIEW ONLINE COURSE. Trusted by thousands of defence aspirants.
Also Read:
- 16th Presidential Election: Voting, Result, Dates, And 10 Key Take Aways
- The President Of India: Indian Polity Notes For Defence Exams
- Complete List Of Presidents Of India








