The CH-47 Chinook is a tandem rotor helicopter. A tandem Rotor helicopter has two large horizontal rotor assemblies mounted one in front of the other. It is developed by the American rotorcraft company Vertol and manufactured by Boeing Vertol which is an American aircraft manufacturer. The CH-47 Chinook is a heavy lifter helicopter that is one of the heaviest lifting helicopters yet. It has derived its name Chinook from the Native American Chinook people of Oregon and Washington states.

It is currently functioning in over 19 countries, including the United Kingdom, Japan, the United Arab Emirates, and South Korea.
A fully integrated digital cockpit management system, a Common Aviation Architecture, and sophisticated cargo-handling capabilities are all part of it.
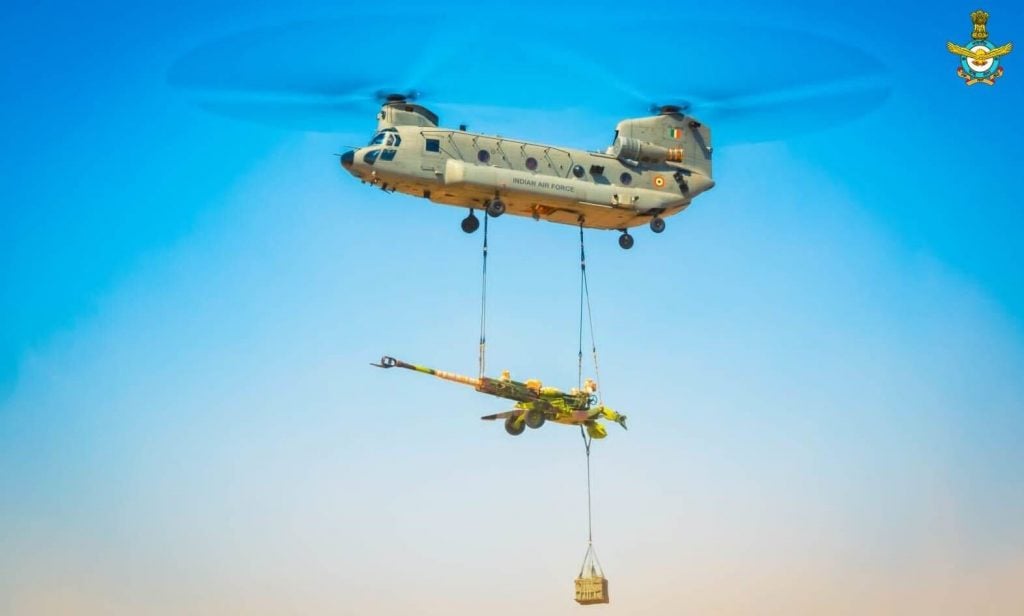
The Chinook can transport up to 45 troops and 11 tonnes of cargo. It also has a load capability of 10 tonnes underslung.
Also Read: List Of Helicopters Used By Indian Air Force
They can also be used for medical evacuation, disaster assistance, and recovery missions. The M-777 ultra howitzers, a towed 155 mm artillery piece, may also be lifted by the helicopters.
Overall, The CH 47 Chinook helicopters are multi-mission heavy-lift transport vehicles that will be employed on the battlefield to deliver troops, artillery, ammunition, supplies, and equipment. Let us know more about the CH-47 chinook Helicopter in the article below!
Design and development
The CH-47 is powered by two Lycoming T55 turbo shaft engines, one on each side of the helicopter’s rear pylon, with drive shafts connecting them to the rotors. The counter-rotating rotors do away with the requirement for an antitorque vertical rotor, allowing all the power to be put to good use for lift and thrust. Because each rotor can modify lift, it is less susceptible to variations in the centre of gravity, which is critical for cargo lifting and dropping. When troops drop from or begin climbing up ropes to the aircraft, or when another cargo is dumped, a twin-rotor helicopter has greater stability over a single-rotor helicopter while hovering over a given place. If one of the engines fails, the other will be able to drive both rotors.

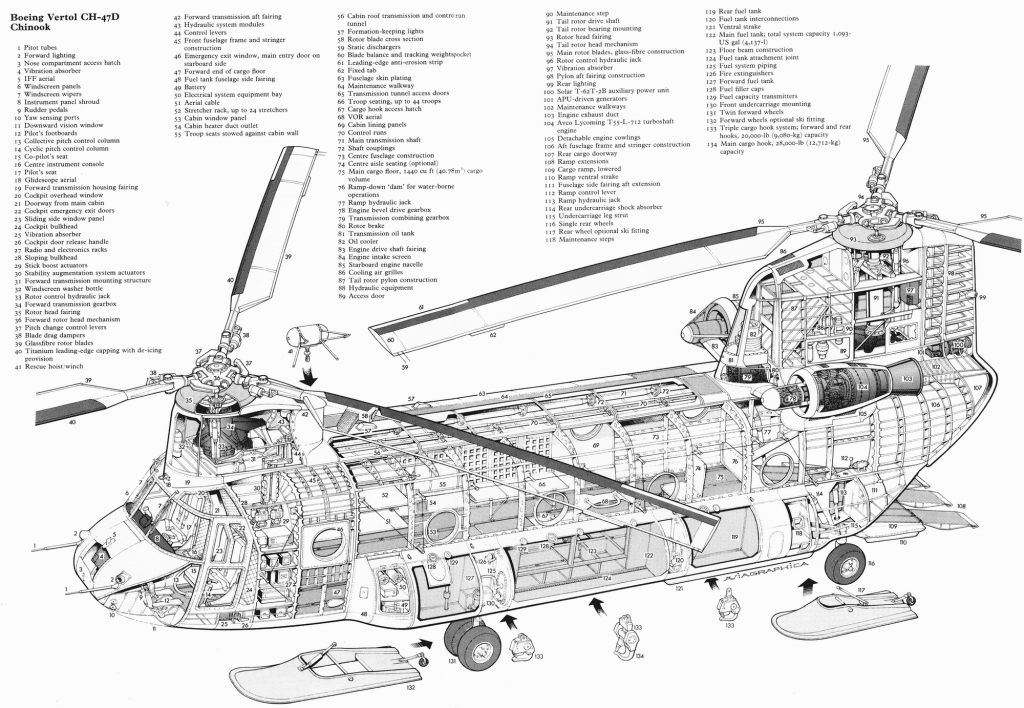
Since the CH-47’s introduction into service, improved and more powerful versions have been developed. The now-common CH-47D, which entered service in 1982, was the US Army’s first major design leap. Upgraded engines, composite rotor blades, a redesigned cockpit to reduce pilot effort, enhanced and redundant electrical systems, a sophisticated flight control system and improved avionics were among the changes from the CH-47C. The CH-47F is the most recent mainstream model, with various substantial changes to minimise maintenance, computerised flying controls, and two Honeywell engines producing 4,733 horsepower (3,529 kW).
Operational history
The CH-47 has a long working experience in wars and war trodden areas. It has participated in Vietnam War, Libya wars, Falklands war, Afghanistan and Iraq wars. It also serves in Iran air Force., during the Iran-Iraq war, Iran made heavy use of CH-47 chinook helicopters. Furthermore, it has also played an important role in other areas apart from wars, such as disaster relief.
According to experts, the Chinook’s ability to carry large, underslung loads has been of significant value in relief operations in the aftermath of natural disasters. The 2004 Asian Tsunami led the Republic of Singapore air force to use the Chinook helicopters for relief purposes. Similarly, after the 2005 Kashmir earthquake, the Royal Air Force dispatched several Chinooks to Northern Pakistan to assist in recovery efforts. Six CH-47D helicopters were deployed from Fort Bragg in North Carolina in August 1992 to provide relief in the aftermath of Hurricane Andrew, in what was one of the first major helicopter disaster relief operations on US soil.


Following the 9.0 earthquake in 2011, three Japanese CH-47s were used to cool reactors 3 and 4 of the Fukushima Nuclear Power Plant; they were used to collecting seawater from the nearby ocean and drop it over the affected areas. The Chinook has served in a variety of secondary missions since its inception, including medical evacuation, disaster relief, search and rescue, aircraft recovery, fire fighting, and heavy construction assistance. So, there has been a very vivid use of the CH-47 Chinook helicopter because of its lifting capacity. In February 2020, the Indian Air Force started using Chinooks at theatres such as Ladakh and Siachen Glacier to assist Indian forces deployed at the Indian borders with China and Pakistan.
Variants of Chinook helicopter
Many variants have been developed for the CH-47 Chinook helicopter. Every version holds some specific and better qualities than before. some extra features are added in every latest version of CH-47 Chinook helicopters. The variants of CH-47 Chinook helicopters are given below:-
- HC-1B
- CH-47 A
- CH-47 B
- CH-47 C
- CH-47 D
- MH-47 D
- MH-47 E
- CH-47 F
- MH-47 G
- CH-47J
- HH-47
- Sea Chinook
Specifications of CH – 47 Chinook Helicopter
The CH-47 Chinook helicopter has many variants, with few advancements in all the variants. The following specification is related to the CH-47F Chinook helicopter. Go through the following specifications to get an idea about the Chinook helicopters.
| Rotor Diameter | 18.29 m (60 ft) |
| Length with Rotors Operating | 30.14 m (98 ft, 10.7 in) |
| Fuselage | 15.46 m (50 ft, 9 in) |
| Height | 5.68 m (18 ft, 7.8 in) |
| Fuselage Width | 3.78 m (12 ft, 5 in) |
| Fuel Capacity | 3914 liters (1034 gallons) |
| Maximum Speed | 302 km/h (170 KTAS) |
| Cruise Speed | 291 km/h (157 KTAS) |
| Mission Radius | 200 nm (370.4km) |
| Service Ceiling | 6,096 m (20,000 ft) |
| Max Gross Weight | 22,680 kg (50,000 lbs) |
| Useful Load | 24,000 lbs (10,886 kg) |
General Characteristics
- Crew: 3 (pilot, copilot, flight engineer or loadmaster)
- Capacity:
- 33–55 troops or
- 24 stretchers and 3 attendants or
- 24,000 lb (10,886 kg) payload
- Length: 98 ft (30 m)
- Fuselage length: 52 ft (16 m)
- Width: 12 ft 5 in (3.78 m) (fuselage)
- Height: 18 ft 11 in (5.77 m)
- Empty weight: 24,578 lb (11,148 kg)
- Max takeoff weight: 50,000 lb (22,680 kg)
- Powerplant: 2 × Lycoming T55-GA-714A turboshaft engines, 4,733 shp (3,529 kW) each
- Main rotor diameter: 2× 60 ft (18 m)
- Main rotor area: 5,600 sq ft (520 m2)
- Blade section: root: Boeing VR-7 ; tip: Boeing VR-8
Performance
- Maximum speed: 170 kn (200 mph, 310 km/h)
- Cruise speed: 160 kn (180 mph, 300 km/h)
- Range: 400 nmi (460 mi, 740 km)
- Combat range: 200 nmi (230 mi, 370 km)
- Ferry range: 1,216 nmi (1,399 mi, 2,252 km)
- Service ceiling: 20,000 ft (6,100 m)
- Rate of climb: 1,522 ft/min (7.73 m/s)
- Disk loading: 9.5 lb/sq ft (46 kg/m2)
- Power/mass: 0.28 hp/lb (0.46 kW/kg)
Armament
- Up to 3 pintle-mounted medium machine guns (1 on loading ramp and 2 at shoulder windows), generally 7.62 mm (0.308 in) M240/FN MAG machine guns, and can be armed with the 7.62 mm M134 Minigun rotary machine gun.
Avionics
- Rockwell Collins Common Avionics Architecture System (CAAS) (MH-47G/CH-47F)
In the context of the Indian Defence system
The Indian air force has already received 15 deadly and heavyweight lifter Chinook helicopters from the US. it certainly means that the Chinook helicopters will help and strengthen the Indian Armed forces in the areas of high altitudes such as Northeastern states. It also means that strategically, the Chinook helicopters will help the Indian armed focus to counter China’s increasing aggression in the Ladakh region.
Conclusion
The CH-47 Chinook is a heavyweight helicopter which has been developed by American rotorcraft company Vertol and manufactured by Boeing Vertol. It is the most advanced tandem rotor helicopter yet. India has already acquired 25 of the CH-47F Chinook helicopters, which have been placed towards the Northeastern birders to counter the common undiplomatic territorial aggression of China. Being versatile with high attitudes with the capability to lift heavy weights will help in strengthening India’s defence forces.
To crack the SSB Interview, You can join our SSB interview live classes batch and we recommend you to Enroll SSB INTERVIEW ONLINE COURSE. Trusted by thousands of defence aspirants.
Also Read: All You Need To Know About Indian Air Force Fighter Aircraft







