Combined Defence Services (CDS) Exam is conducted twice every year by UPSC (Union Public Service Commission) for the aspirants willing to join Indian Armed Forces. CDS Exam consists of two or three papers based on candidate’s eligibility, one of the papers is totally based on elementary mathematics. Objective type questions are asked in this paper, these questions are totally based on basic concepts of mathematics that we have studied in school from class tenth to twelfth (or Metric to intermediate). Most questions are simply direct formula based i.e. you have to put the given data of the question directly into the concept formula and get the answer but ofcourse to do that you have to atleast remember the formula. In this article we will share some very Important formulas for CDS Exam, candidates must revised these formulas before attempting the exam also these formulas can be helpful when preparing for the exam.
CDS Exam Coaching IMA AFA NA
CDS Exam Coaching OTA
CDS Exam Elementary Mathematics Paper Pattern and Syllabus
The objective type question paper includes various topics of elementary mathematics. Candidates should have possessed knowledge about these topics. There are lots of topics to cover which are as following:
Arithmetic
- Number System-Natural numbers, Integers, Rational and Real numbers. Fundamental operations addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, Square roots, Decimal fractions.
- Unitary method-time and distance, time and work, percentages, applications to simple and compound interest, profit and loss, ratio and proportion, variation.
- Elementary Number Theory-Division algorithm. Prime and composite numbers. Tests of divisibility by 2,3,4,5,9 and 11. Multiples and factors. Factorization Theorem. H.C.F. and L.C.M. Euclidean algorithm, Logarithms to base 10, laws of logarithms, use of logarithmic tables.
Algebra
- Basic Operations, simple factors, Remainder Theorem, H.C.F., L.C.M. Theory of polynomials, solutions of quadratic equations, relation between its roots and coefficients (Only real roots to be considered ).
- Simultaneous linear equations in two unknowns-analytical and graphical solutions. Simultaneous linear in-equations in two variables and their solutions. Practical problems leading to two simultaneous linear equations or in-equations in two variables or quadratic equations in one variable & their solutions.
- Set language and set notation, rational expressions and conditional identities, Laws of indices.
Trigonometry
Sine x, cosine x, Tangent x when 0° ≤ x ≤ 90° Values of sin x, cos x and tan x, for x = 0°, 30°, 45°, 60° and 90°. Simple trigonometric identities. Use of trigonometric tables. Simple cases of heights and distances.
Geometry
- Lines and angles, Plane and plane figures, Theorems on
- Properties of angles at a point,
- Parallel lines,
- Sides and angles of a triangle,
- Congruency of triangles,
- Similar triangles,
- Concurrence of medians and altitudes,
- Properties of angles, sides and diagonals of a parallelogram, rectangle and square,
- Circles and its properties including tangents and normals,
- Loci.
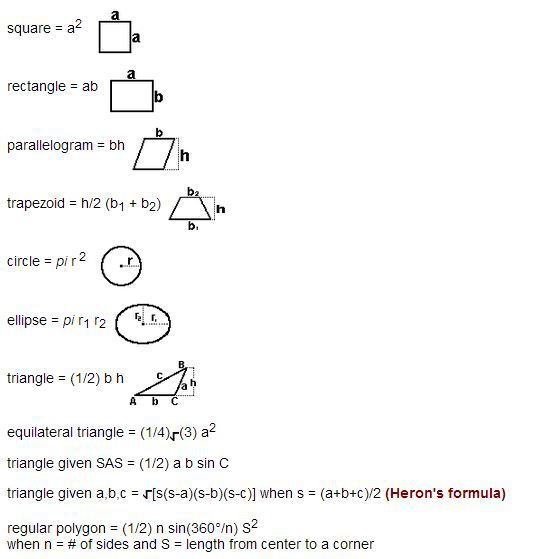
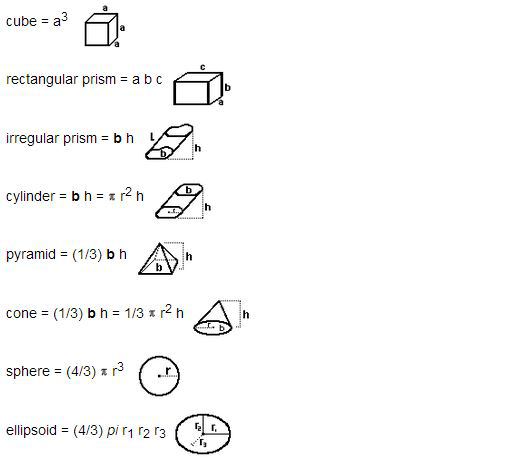
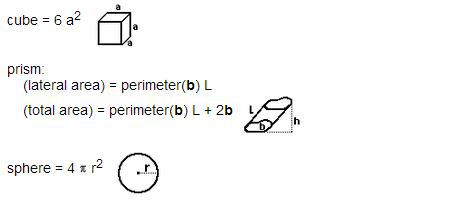
Mensuration: Areas of squares, rectangles, parallelograms, triangle and circle. Areas of figures which can be split up into these figures (Field Book), Surface area and volume of cuboids, lateral surface and volume of right circular cones and cylinders, surface area and volume of spheres.
Statistics: Collection and tabulation of statistical data, Graphical representation frequency polygons, histograms, bar charts, pie charts etc. Measures of central tendency.
List of Important formulas for CDS Exam
Geometry:
- Equal chords of circle subtends equal angle at center and vice versa. If AB =CD in figure then
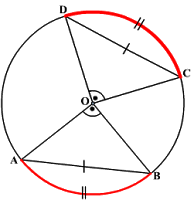
- Perpendicular from the center of the circle to a chord bisects the chord. If
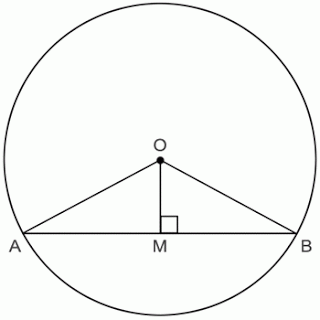
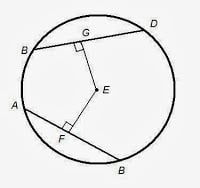
- Equal chords of the circle are equidistant from Center. If AB=BD then GE=EF
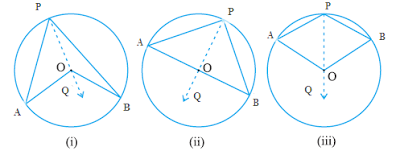
- The angle subtended by an arc at the center is double the angle subtended by it at any point on the remaining part of the circle. In each case
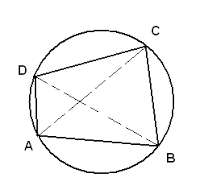
- The sum of the either pair of opposite angles of cyclic quadrilateral is 180.a quadrilateral is cyclic if all the four vertices of it lie on a circle. Here
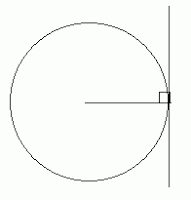
- The tangent at any point of a circle is perpendicular to the radius through the point of contact.
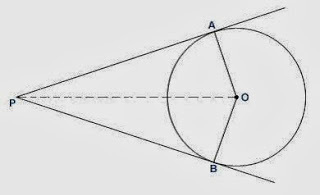
- The lengths of the tangents drawn from external point on circle are equal. Here PA=PB
Speed Distance and Time
- Speed = Distance/Time, Time = Distance/Speed, Distance = Speed * Time
- Km/hr to m/sec conversion: x Km/hr = [x * (5/18)] m/sec
- m/sec to Km/hr conversion: x m/sec = [x*(18/5)] Km/hr
- Suppose a man covers a certain distance at x Km/hr and equal at y Km/hr then, the average speed during the whole journey is [2xy/(x+y)] Km/hr
CDSE Train Problems Tips
- Time taken by a train of length l metres to pass a pole or standing man or a signal post is equal to the time taken by the train to cover l metres.
- Time taken by a train of length l metres to pass a stationery object of length b metres is the time taken by the train to cover (l + b) metres.
- Suppose two trains or two objects bodies are moving in the same direction at u m/s and v m/s, where u > v, then their relative speed is = (u – v) m/s.
- Suppose two trains or two objects bodies are moving in opposite directions at u m/s and v m/s, then their relative speed is = (u + v) m/s.
- If two trains of length a metres and b metres are moving in opposite directions at u m/s and v m/s, then, the time taken by the trains to cross each other = (a+b)/(u + v) sec.
- If two trains of length a metres and b metres are moving in the same direction at u m/s and v m/s, then, the time taken by the faster train to cross the slower train = (a + b)/(u – v) sec.
CDSE Boat and Stream Formula
- Downstream/Upstream: In water, the direction along the stream is called downstream. And, the direction against the stream is called upstream.
- If the speed of a boat in still water is u km/hr and the speed of the stream is v km/hr, then: Speed downstream = (u + v) km/hr. Speed upstream = (u – v) km/hr.
- If the speed downstream is a km/hr and the speed upstream is b km/hr, then: Speed in still water = ½ (a + b) km/hr; Rate of stream = ½ (a – b) km/hr.
Algebra
- (a + b)(a – b) = (a2 – b2)
- (a + b)2 = (a2 + b2 + 2ab)
- (a – b)2 = (a2 + b2 – 2ab)
- (a + b + c)2 = a2 + b2 + c2 + 2(ab + bc + ca)
- (a3 + b3) = (a + b)(a2 – ab + b2)
- (a3 – b3) = (a – b)(a2 + ab + b2)
- (a3 + b3 + c3 – 3abc) = (a + b + c)(a2 + b2 + c2 – ab – bc – ac)