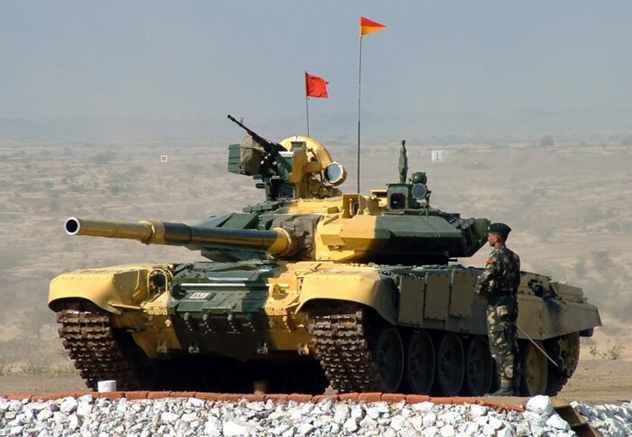
Defence Acquisition Council has reportedly approved the purchase and integration of two technological kinds for T-90 tanks: the Digital Ballistic Computer and Automatic Target Tracker, both of which are a component of the fire control system.
Digital Ballistic Computer & Automatic Target Tracker
In essence, an AoN is the ministry of defense’s approval given at the outset of the procurement procedure. The mainstay of the Indian Army’s armoured capabilities are the T-90 and T-72 tanks, which are manufactured in Russia. Approximately 475 additional T-90 tanks are being developed, and the India Army reportedly has up to 1,200 of them in service.
According to a defence ministry official, the 1,200 tanks that are now in use will be refurbished, but the new tanks will have an integrated ATT, the source continued. The official explained how this technology will benefit the Army, saying that it will “help the T-90s get better sight to spot enemy tanks easily.”
The use of ATT technology facilitates accurate engagement with moving targets. Currently, the T-90 tanks are manually positioned in order to attack a target precisely.
Based on the atmospheric conditions, the DBC, which powers the fire guidance system, determines the round’s course. The temperature inside the tank, the ambient temperature, and the wind’s direction and speed all have an impact on the performance of a round of ammunition. To hit an exact target, the DBC bases its computations on all of these variables.
The tanks’ existing analogue computer is being replaced with a digital one to eliminate the possibility of prejudice and human mistake. The Indian Army also uses over 2,400 T-72 tanks, which are not equipped with the ATT and DBC, in addition to the T-90s. The T-72 tanks will be gradually replaced by 1,700 Future Ready Combat Vehicles (FRCV), which the Indian Army is currently procuring. Battlefield Management System equipment will be installed on the FRCVs (BMS).