In an era of rapidly evolving global security challenges, India has embarked on a transformative journey to bolster its defense capabilities through the development of cutting-edge indigenous weapon systems. Driven by a steadfast commitment to self-reliance and technological sovereignty, the nation has shifted from being a major arms importer to a rising defense exporter, poised to achieve its ambitious target of $5 billion in defense exports by 2024.
This strategic shift has catalyzed the indigenous design, development, and production of advanced weapon platforms that not only cater to the needs of the Indian Armed Forces but also hold the potential to become global game-changers. From stealthy unmanned combat aerial vehicles (UCAVs) to state-of-the-art surface-to-air missile systems, submarine projects, and next-generation anti-tank guided missiles, India’s defense ecosystem is witnessing a remarkable surge in indigenous capabilities.
In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the 10 Top Indigenous Weapons For Indian Armed Forces that are set to redefine the future of India’s military might, showcasing the nation’s technological prowess and its unwavering commitment to self-reliance in the defense sector.
5 Top Military Aircraft Made By Boeing
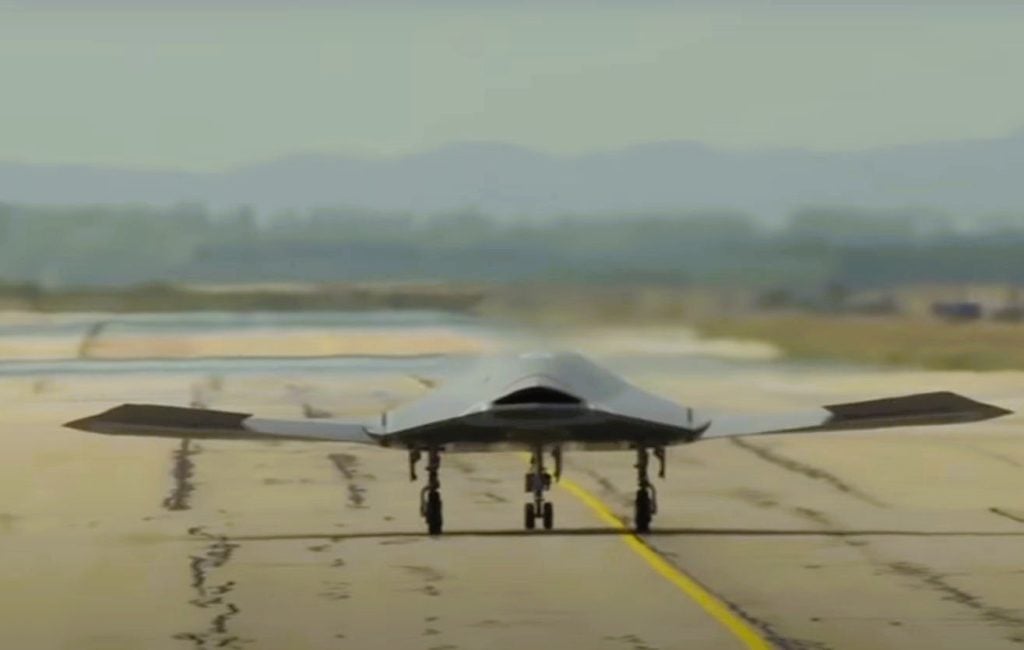
1. Ghatak UCAV
Ghatak, a cutting-edge unmanned combat air vehicle (UCAV) being developed by the Aeronautical Development Establishment (ADE) of the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), represents a significant stride in India’s quest for advanced aerial warfare capabilities. Designed with a focus on stealth and autonomy, the Ghatak UCAV boasts a flying-wing configuration that not only enhances its radar-evading properties but also allows for greater weapons and fuel payload.
Powered by the indigenous GTRE GTX-35VS Kaveri turbofan engine, the Ghatak UCAV is slated to undergo its first full-scale flight by 2025, showcasing India’s indigenous capabilities in the realm of unmanned aerial systems. With the provision of an internal weapon bay and advanced sensors, the Ghatak UCAV will be capable of executing a wide range of missions, from precision strikes to intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) tasks, solidifying India’s position as a emerging global leader in autonomous aerial warfare.
2. Surface-to-Air Missile Systems
India’s indigenous surface-to-air missile (SAM) systems are poised to bolster the nation’s air defense capabilities, providing a multi-layered shield against a diverse array of aerial threats.
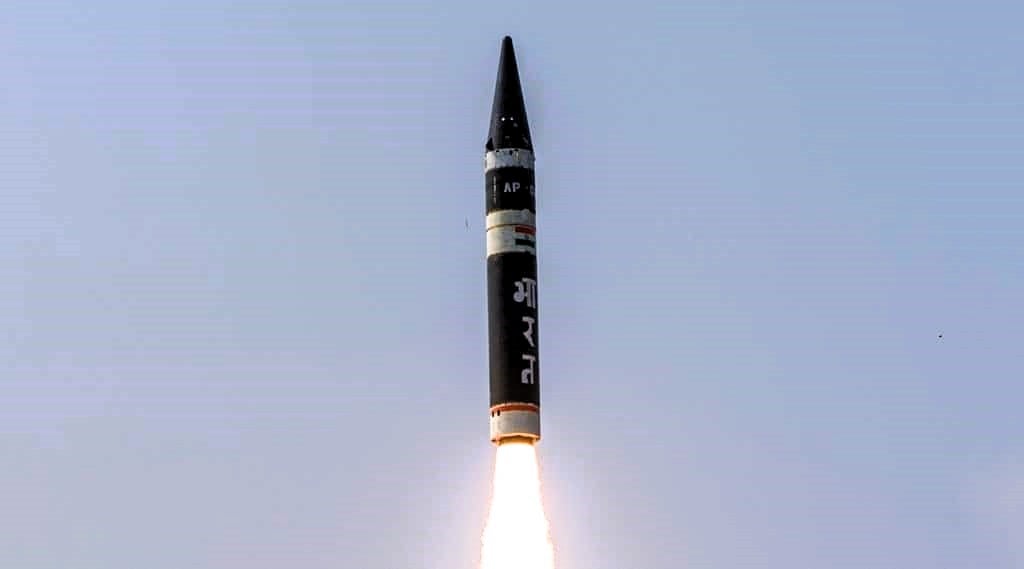
Agni-P
The Agni-P, or Agni-Prime, is a medium-range ballistic missile that represents a significant upgrade over the previous Agni-series missiles. Designed by the DRDO, the Agni-P boasts enhanced features, including a maneuverable re-entry vehicle (MaRV), improved propellants, navigation, and guidance systems.
Equipped with a multiple independently targetable reentry vehicle (MIRV) capability, the Agni-P can carry a heavier payload of warheads, further strengthening India’s strategic deterrence.
XRSAM
The XRSAM, or extra-long-range surface-to-air missile, is a DRDO-developed system designed to bridge the gap between the medium-range MR-SAM (70 km) and the long-range S-400 (400 km) systems. With a formidable range of 250 km, the XRSAM will be capable of neutralizing a wide array of aerial threats, including fighter jets, cruise missiles, and even ballistic missiles in the terminal stage.
The integration of advanced features, such as fragmentation warheads and optical proximity fuzes, will enhance the XRSAM’s lethality and versatility, making it a crucial asset for India’s air defense.
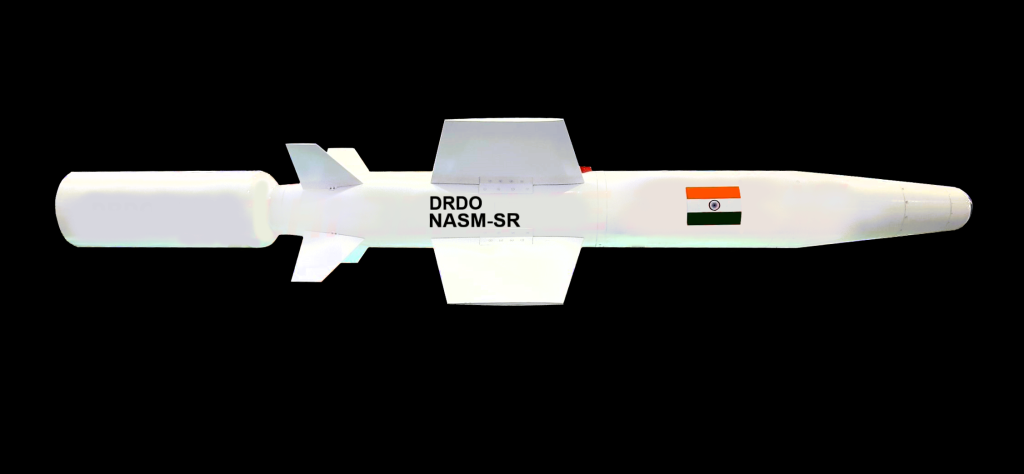
3. NASM-SR
The NASM-SR, or naval anti-ship missile-short range, is the second indigenous air-launched anti-ship cruise missile developed by the DRDO for the Indian Navy. Designed to be launched from naval helicopters, the NASM-SR employs a 100 kg multi-explosively formed penetrator (MEFP) warhead and a radio proximity fuze for precise target engagement.
The successful maiden test of the NASM-SR, which demonstrated its sea-skimming capabilities and precision strike accuracy, marks a significant milestone in India’s quest for self-reliance in naval warfare. With the integration of advanced avionics and navigation systems, the NASM-SR will bolster the Indian Navy’s ability to neutralize surface threats with enhanced lethality and range.
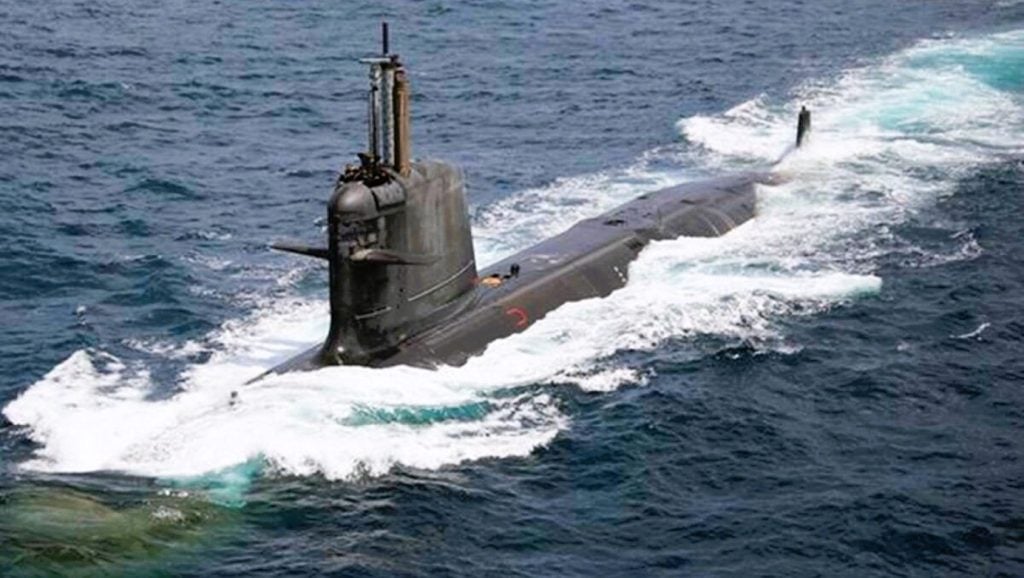
4. Submarine Projects
India’s indigenous submarine development programs are poised to reinforce the nation’s maritime prowess and strategic deterrence capabilities.
Project 75 Alpha
Under Project 75A, the Indian Navy is set to acquire a fleet of nuclear-powered attack submarines (SSNs) that will be designed and manufactured in-house at the Navy Shipbuilding Center in Visakhapatnam. These advanced SSNs will be equipped with the CLWR-B2 Compact Light-water Reactor, providing them with the power and endurance to undertake extended underwater missions. Capable of carrying a diverse array of armaments, including heavyweight torpedoes, the Nirbhay cruise missile, and the BrahMos supersonic cruise missile, these indigenous SSNs will bolster India’s underwater dominance.
S5-Class Submarines
The S5-class submarine project, codenamed S5, is a strategic initiative to develop nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarines (SSBNs) for the Indian Navy. These submarines, with their increased payload and reactor capacity compared to the Arihant-class, will be armed with the formidable K-6 submarine-launched ballistic missiles, further enhancing India’s nuclear deterrence capabilities and completing the country’s nuclear triad.
5. MPATGM
The MPATGM, or man-portable anti-tank guided missile, is a third-generation missile developed by the DRDO in partnership with the Indian defense contractor VEM Technologies. Designed to replace the aging Milan and Konkurs anti-tank missiles, the MPATGM boasts a dual-charge high-explosive anti-tank (HEAT) warhead capable of penetrating advanced reactive armor.
Equipped with an advanced imaging infrared (IIR) sensor and integrated avionics, the MPATGM offers top-attack capability and an effective firing range of 200 meters to 4,000 meters. The missile’s lightweight, collapsible tripod launch tube, weighing just 14.24 kg, ensures enhanced mobility and ease of deployment for infantry and special forces units, further strengthening India’s ground-based anti-armor capabilities.
5 Top Ballistic Missile Submarines in the World 2024
6. Anti-Tank Guided Missiles
India’s indigenous anti-tank guided missile (ATGM) programs are poised to provide the armed forces with a formidable array of precision-guided munitions to counter the evolving threat landscape.
SANT Missile
The SANT, or standoff anti-tank guided missile, is an upgraded version of the HELINA helicopter-launched anti-tank missile. Featuring a new nose-mounted millimeter-wave active radar homing (MMW ARH) seeker and an extended electro-optical/infrared (EO/IR) range of up to 20 km, the SANT empowers airborne platforms to engage armored targets from standoff distances with enhanced accuracy and lethality.
The SANT’s lock-on-after-launch and lock-on-before-launch capabilities further bolster its operational flexibility, allowing the missile to track and engage moving targets even after launch. As the SANT nears its final testing phase, it will equip the Indian Army Aviation Corps and Air Force with a formidable anti-armor solution.
SAMHO
The SAMHO, or gun-launched anti-tank guided missile, is an indigenous development by the Armament Research and Development Establishment (ARDE), a subsidiary of the DRDO. Designed to be fired from the 120 mm gun of the Arjun main battle tank and the 125 mm smoothbore gun of the T-90 tank, the SAMHO employs a tandem high-explosive anti-tank (HEAT) warhead to defeat modern armored vehicles and their explosive reactive armor (ERA) protection.
Utilizing semi-active laser homing or laser guidance, the SAMHO provides the Indian Army with a versatile anti-armor solution that can engage both ground targets and low-flying attack helicopters, further enhancing the firepower and lethality of the nation’s mechanized forces.
7. DRDO ATAGS
The ATAGS, or Advanced Towed Artillery Gun System, is a 155 mm/52 caliber howitzer developed by the DRDO’s Armament Research and Development Establishment (ARDE). Manufactured by Bharat Forge and Tata Power SED, the ATAGS boasts an effective firing range of 48 km, which can be further extended to 52 km with the use of high-explosive base-bleed (HE-BB) ammunition.
Equipped with an all-electric drive, advanced communication systems, and an automated command and control interface, the ATAGS offers enhanced mobility, quick deployability, and improved accuracy and range compared to its contemporaries. The successful completion of field trials and the planned induction of 150 ATAGS units into the Indian Army underscore the critical role this indigenous howitzer will play in modernizing the nation’s artillery capabilities.
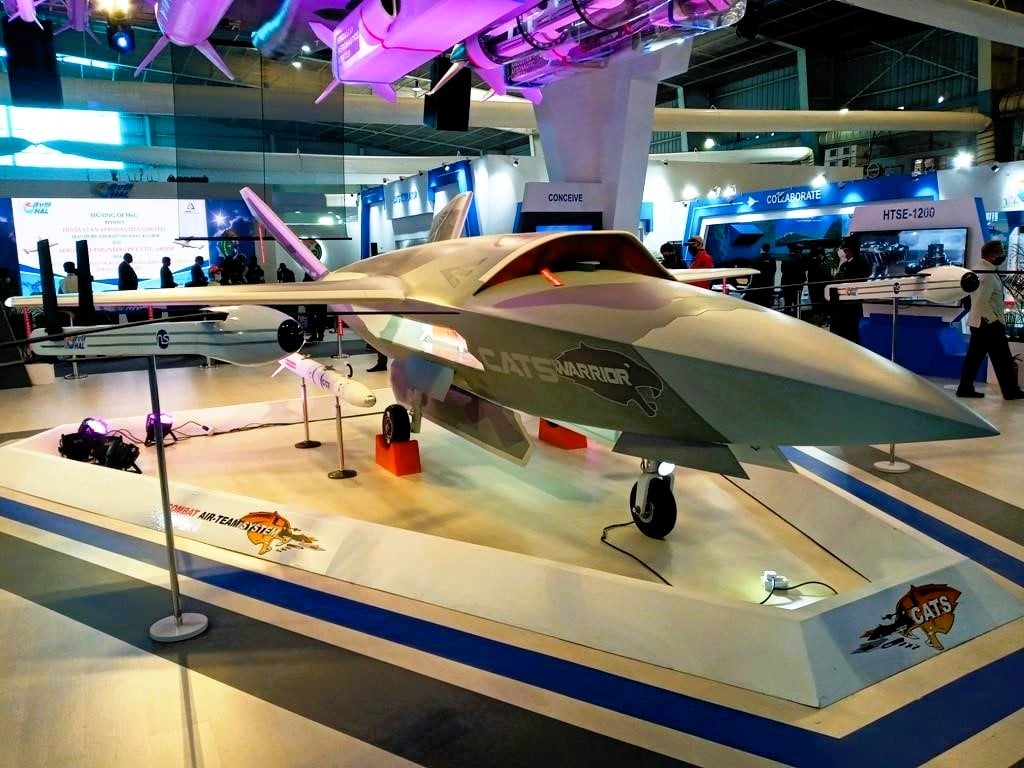
8. HAL CATS
The HAL Combat Air Teaming System (CATS) is a manned-unmanned combat aircraft system being developed by Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) in collaboration with the DRDO, National Aerospace Laboratories, and Newspace Research & Technologies.
CATS Warrior
The CATS Warrior is an autonomous UCAV designed to operate as a wingman to a manned fighter aircraft, potentially a modified twin-seat variant of the LCA Tejas. Featuring a composite structure with a hybrid design, the CATS Warrior will be powered by a modified HAL PTAE-7 or HAL HTFE-25 turbofan engine and equipped with an internal weapon bay, electro-optic/infrared sensors, active electronically scanned array (AESA) radar, and advanced electronic warfare capabilities.
CATS Hunter
The CATS Hunter, on the other hand, is envisioned as a low-observable, standoff air-launched cruise missile that can carry a 250 kg warhead with a range of 200-300 km. Equipped with terrain-contour matching (TERCOM) guidance and multiple global navigation satellite systems (GNSS), the CATS Hunter will be capable of autonomous target acquisition during the terminal phase, further enhancing the precision and lethality of India’s air-to-ground strike capabilities.
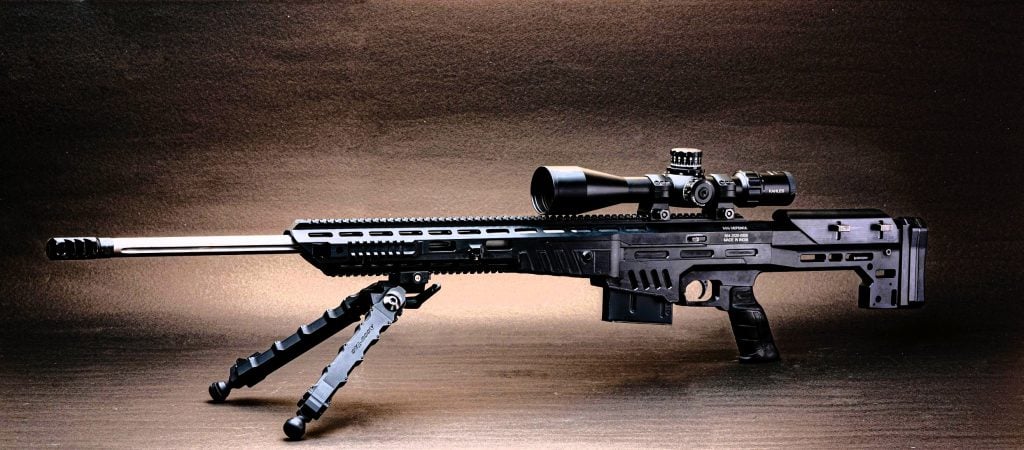
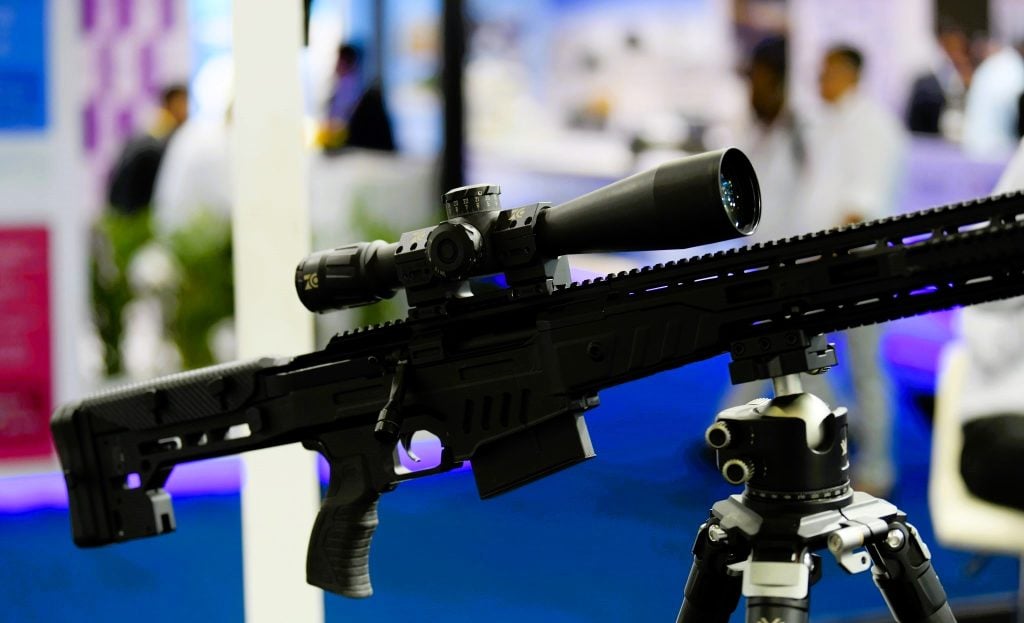
9. SSS Defence Sniper Rifles
SSS Defence, an Indian defense manufacturer, has developed a range of indigenous sniper rifles tailored to the specific requirements of the Indian armed forces, particularly the special forces units.
The Viper, a sub-MOA sniper rifle chambered for the 7.62×51 mm or .308 cartridge, boasts a proven range of over 1,000 meters, providing exceptional long-range precision. The Saber, on the other hand, is a .338 Lapua Magnum-chambered sniper rifle with an adjustable stock and a range of around 1,500 meters. Both rifles feature Picatinny rail systems, ambidextrous magazine releases, and lightweight, durable construction, ensuring optimal performance and seamless integration with the Indian soldiers’ physique and operational needs.
10. SSS Defence Assault Rifles
Complementing its sniper rifle offerings, SSS Defence has also developed the P-72 family of assault rifles, designed with a philosophy similar to the ACR, FN SCAR, and CZ Bren 2 platforms. This modular rifle system includes the P-72 Rapid Engagement Combat Rifle (RECR), the P-72 Recon Carbine, and the P-72 Designated Marksman Rifle (DMR), catering to the diverse requirements of infantry, special operations, and designated marksman roles.
Chambered for 7.62×39 mm or 7.62×51 mm cartridges, the P-72 series rifles leverage gas-piston operation and a range of barrel lengths to provide the Indian Armed Forces with a versatile and reliable small arms platform, further strengthening the nation’s self-reliance in the field of small arms development.
Top 5 Guns For Any Police Officer
Conclusion
India’s unwavering commitment to self-reliance in the defense sector has ushered in a new era of indigenous weapon development, positioning the country as a rising global power in the field of military technology. The top 10 fully indigenous weapon systems highlighted in this article showcase the breadth and depth of India’s defense capabilities, from stealthy UCAVs and advanced surface-to-air missile systems to cutting-edge submarine projects and precision-guided anti-tank and assault rifles.
As the Indian Armed Forces prepare to induct these indigenous marvels, the nation’s defense ecosystem is poised to witness a transformative shift, bolstering its strategic deterrence, operational readiness, and technological superiority. This journey of self-reliance not only strengthens India’s national security but also serves as a testament to the country’s engineering prowess and its ability to innovate and develop world-class defense solutions.
Through the continued development and integration of these indigenous weapon systems, India is solidifying its position as a formidable military power, ready to safeguard its interests and contribute to regional and global stability in the years to come.
FAQs
1. What is the most powerful weapon in India?
Brahmos warhead
2. Which is the indigenously developed guided weapon system of India?
The Prithvi series of short-range ballistic missiles, the Trishul low-altitude, short-range surface-to-air missile, the Akash medium-range surface-to-air missile, and the Nag third-generation anti-tank guided missile were succeeded by the Agni series of medium and long-range ballistic missiles.
3. Which indigenous tanks are used by Indian Army?
The Vijayanta marked the debut of indigenous tank production for the Indian Army. Its prototype was finalized in 1963, with the tank officially commissioned into service on December 29, 1965.
4. What is the indigenous ballistic missile in India?
Agni-V
5. What is the indigenous rifle of India?
The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) has introduced ‘Ugram’, a domestically developed assault rifle designed to fulfill the operational needs of armed forces, paramilitary units, and state police forces.