The Indian Army is one of the largest and most formidable military forces in the world, renowned for its rich history, diverse regiments, and strategic prowess. Each regiment within the army plays a vital role in maintaining national security and executing various operations.
This article delves into the different categories of Indian Army Regiments, their functions, histories, and significance.
The Indian Army is structured into several regiments, each specializing in specific combat roles. The primary classifications include:
- Artillery Regiments
- Armoured Regiments
- Infantry Regiments
- National Cadet Corps (NCC)
Understanding these regiments is crucial for anyone interested in military operations and the organizational framework of the Indian Army.
1. Artillery Regiments
Artillery regiments form a critical component of the Indian Army, providing essential firepower to support ground operations. They are responsible for delivering devastating artillery strikes that can dominate the battlefield.
Structure and Organization
The artillery branch is one of the largest arms of the Indian Army, accounting for approximately one-sixth of its total personnel. Units within this branch are organized at both corps and divisional levels. This structure allows for efficient deployment and utilization of artillery in various combat scenarios.
Historical Background
Historically, artillery was viewed as a support arm, but its role has evolved into a combat arm, emphasizing both direct support and counter-bombardment capabilities. The largest artillery training center is situated in Nashik, Maharashtra, which has been pivotal in shaping artillery strategies and training.
Notable Regiments
Some prominent artillery regiments include:
- 9th Parachute Field Regiment
- 11th Field Regiment
- 861 Regiment (equipped with BrahMos missiles)
- 170 Medium Regiment (Veer Rajput)
These regiments have played significant roles in various military operations, showcasing the importance of artillery in modern warfare.
Also Read | The Moment Every Defence Aspirant Aspires For
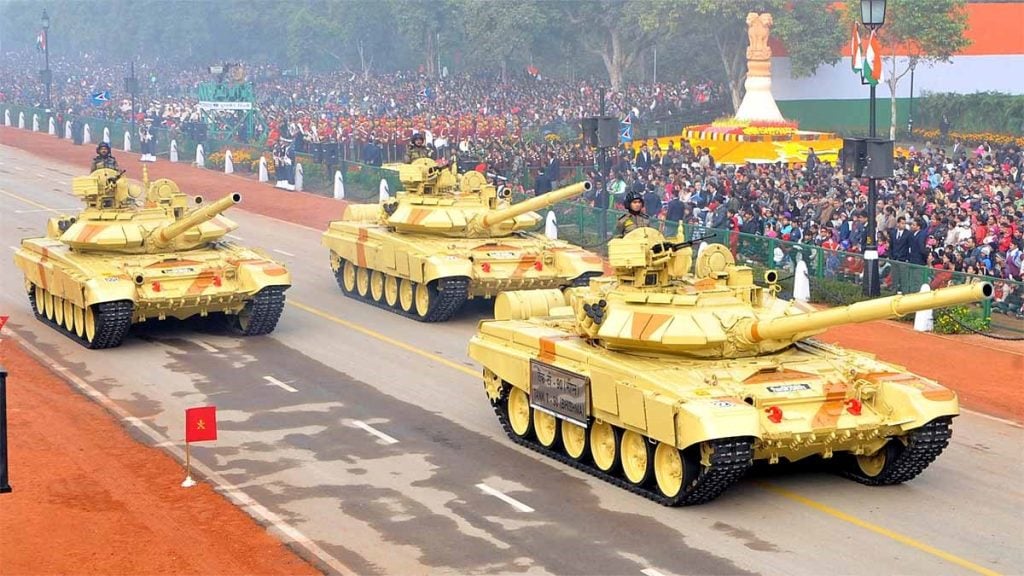
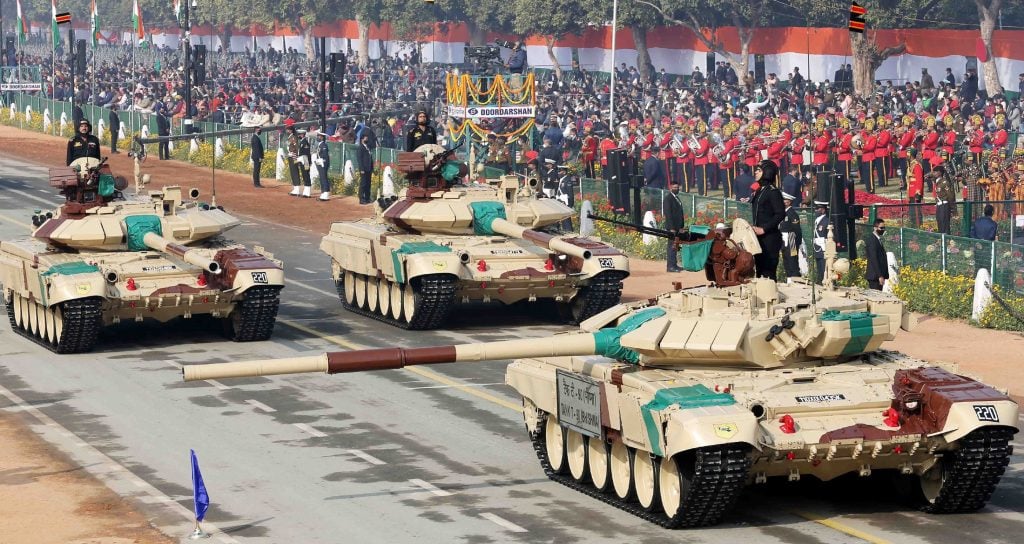
2. Armoured Regiments
Armoured regiments are crucial for mechanized warfare, providing mobility and firepower on the battlefield. They utilize tanks and other armored vehicles to execute rapid assaults and reconnaissance missions.
Composition and Functionality
The Indian Army comprises around 93 armoured regiments, each equipped with advanced tanks and armored vehicles. These regiments often have independent reconnaissance squadrons consisting of tanks and infantry, allowing for versatile operational capabilities.
Historical Development
The terminology surrounding armoured regiments has evolved, with terms like ‘Cavalry’ and ‘Lancer’ being phased out since the 65th Armoured Regiment. This change reflects a shift in focus towards modern mechanized warfare.
Key Armoured Regiments
Some of the notable armoured regiments include:
- President’s Bodyguards
- 1st Skinned Horse
- 2nd Lancers
- 4th Hodson’s Horse
- 7th Cavalry
- 21st Central India Horse
These regiments are equipped to engage in both offensive and defensive operations, making them integral to the Indian Army’s tactical framework.
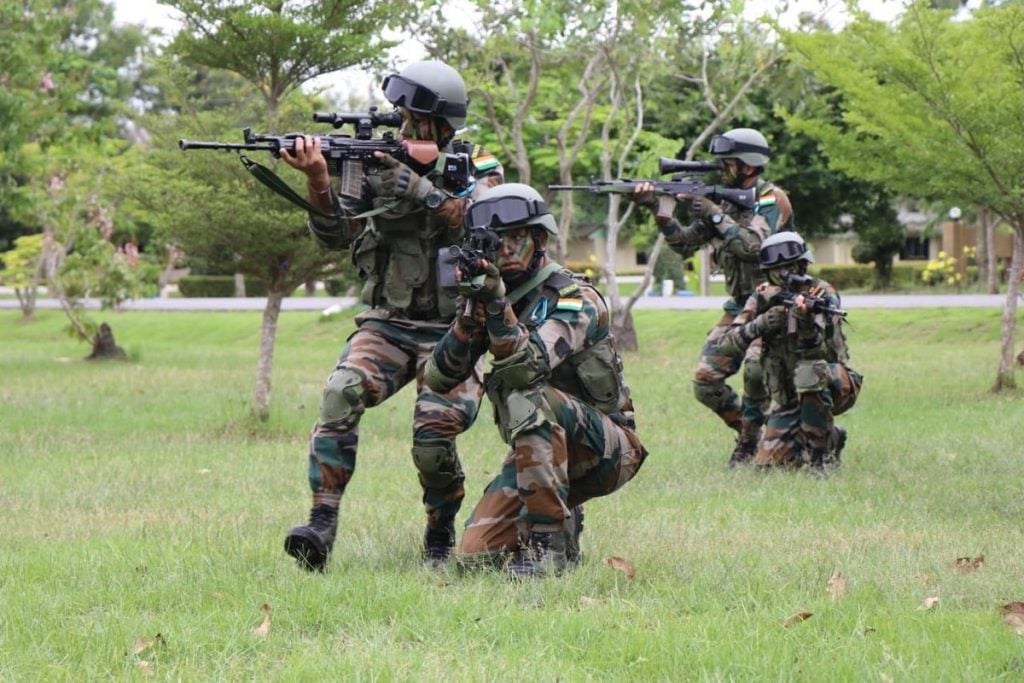
3. Infantry Regiments
The infantry is often regarded as the backbone of the Indian Army. Infantry regiments are responsible for ground combat operations, engaging the enemy in close quarters and holding strategic positions.
Structure and Deployment
Infantry regiments are organized into battalions, which are then deployed across various formations such as brigades and divisions. This decentralized structure allows for flexibility and rapid response to changing battlefield dynamics.
Combat Role and Training
Infantry soldiers are trained for a range of combat scenarios, from urban warfare to mountainous terrain. They are equipped with a variety of weapons designed for close combat, including rifles, machine guns, and grenades.
Prominent Infantry Regiments
Some of the distinguished infantry regiments in the Indian Army include:
- Gorkha Rifles
- Garhwal Rifles
- Brigade of the Guards
- Bihar Regiment
- Parachute Regiment
- Punjab Regiment
- Madras Regiment
- Maratha Light Infantry
- Rajputana Rifles
- Rajput Regiment
- Jat Regiment
- Sikh Regiment
These regiments have a storied history and have participated in numerous conflicts, demonstrating valor and resilience.
Also Read | What Does the Baton Represent for Indian Army Officers?
4. National Cadet Corps (NCC)
Established in 1948, the National Cadet Corps (NCC) aims to foster a sense of discipline, commitment, and patriotism among the youth of India. The NCC provides young individuals with training and exposure to military life, preparing them for potential careers in the armed forces.
Structure and Components
The NCC comprises three main wings:
- Army Wing
- Naval Wing
- Air Wing
Each wing focuses on specific training relevant to its domain, ensuring comprehensive development for cadets.
Divisional Organization
The NCC is divided into three divisions:
- Senior Division
- Junior Division
- Girls Division
This structure allows for tailored training programs that cater to the diverse needs of cadets, promoting inclusivity and engagement.
The Role of Regiments in Modern Warfare
The various regiments of the Indian Army play an indispensable role in contemporary military strategies. Each regiment is designed to complement the others, creating a cohesive force capable of addressing multiple challenges.
Integrated Operations
Modern warfare often involves joint operations among different branches of the military. Artillery, armoured, and infantry regiments must work in unison to achieve strategic objectives. This integration enhances operational effectiveness and ensures a comprehensive approach to combat.
Technological Advancements
The Indian Army continually adapts to technological advancements, incorporating modern weaponry and equipment into its regiments. This evolution is crucial for maintaining a competitive edge in a rapidly changing global landscape.
Training and Preparedness
Rigorous training programs are essential for all regiments, ensuring that personnel are well-prepared for the complexities of modern warfare. Continuous drills, simulations, and exercises help maintain high levels of readiness.
Also Read | How to Overcome Nervousness in SSB Interview Screening Tests
Conclusion
The regiments of the Indian Army represent a blend of tradition, valor, and modernity. Each regiment has its unique identity, history, and operational role, contributing to the overall strength of the armed forces. Understanding the structure and function of these regiments is vital for anyone aspiring to join the military or seeking to comprehend the dynamics of national defense.
FAQs
1. What are the main types of regiments in the Indian Army?
The Indian Army primarily consists of artillery, armoured, infantry regiments, and the National Cadet Corps (NCC).
2. How are artillery regiments organized?
Artillery regiments are structured at both corps and divisional levels, allowing for efficient deployment and support in combat operations.
3. What is the role of infantry regiments?
Infantry regiments engage in ground combat, holding strategic positions and engaging the enemy in close quarters.
4. How does the NCC contribute to the Indian Army?
The NCC trains youth in military discipline and skills, preparing them for potential careers in the armed forces while promoting patriotism and leadership.
5. Why is the integration of regiments important in modern warfare?
Integrated operations among different regiments enhance operational effectiveness and ensure a comprehensive approach to combat challenges.