Radio waves are used by radar, a type of detection device, to calculate an object’s distance, angle, or speed. It may be used to find terrain, guided missiles, motor vehicles, ships, aeroplanes, and spaceships. Typically, a transmitter that generates an electromagnetic signal and an antenna that emit that signal into space make up a RADAR system. This signal is reflected or reradiated in numerous directions when it encounters an item. The radar antenna picks up this reflected signal and sends it to the receiver, where it is analysed to ascertain the object’s geographic characteristics. Most people still associate radar with the military.
For instance, enemy aircraft or missiles can be spotted using radar antennas deployed at airports or other ground stations. In India, the Defense Research & Development Organization (DRDOElectronics )’s and Radar Development Establishment (LRDE) is the lab in charge of developing radars. This organisation has achieved success as seen by the numerous radar systems it produced that are currently being used extensively by the Indian Armed Forces.
Indra I Radar
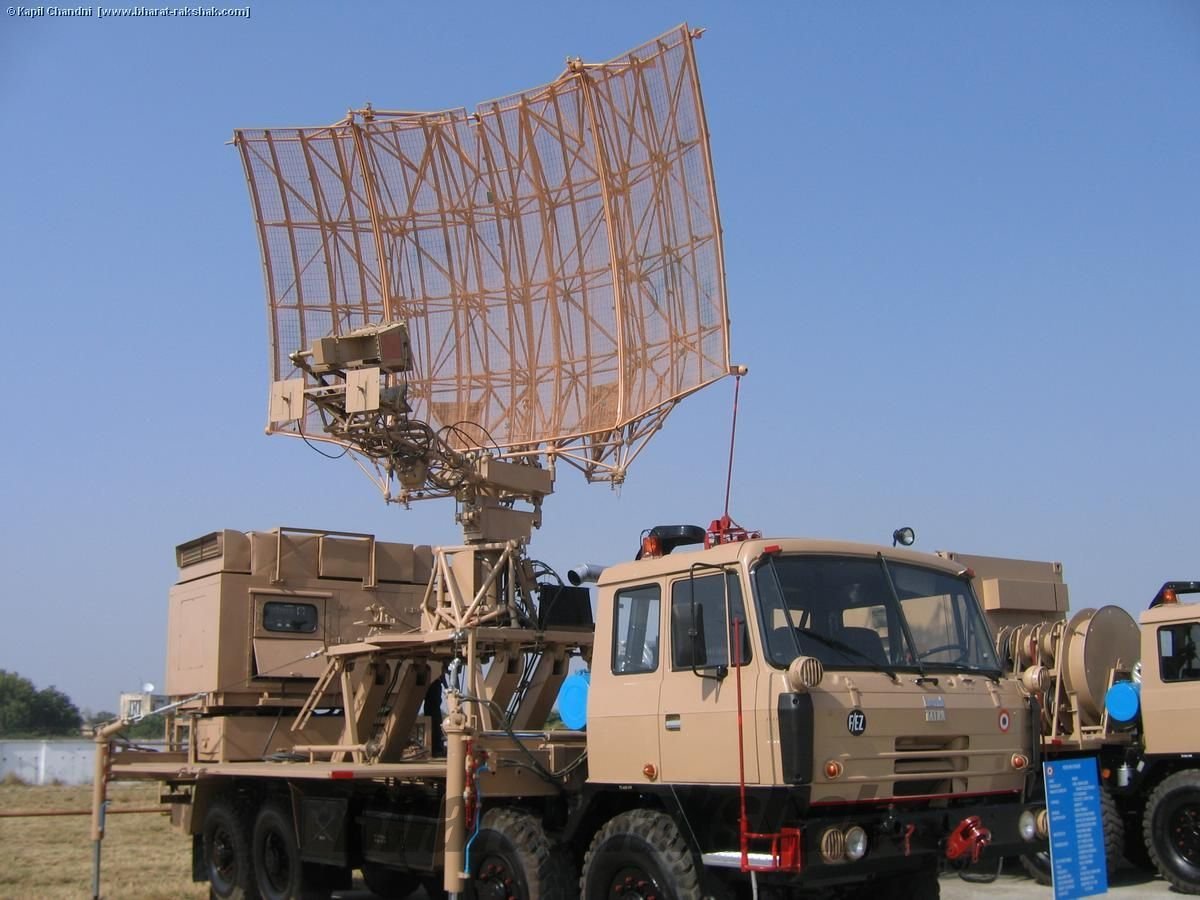
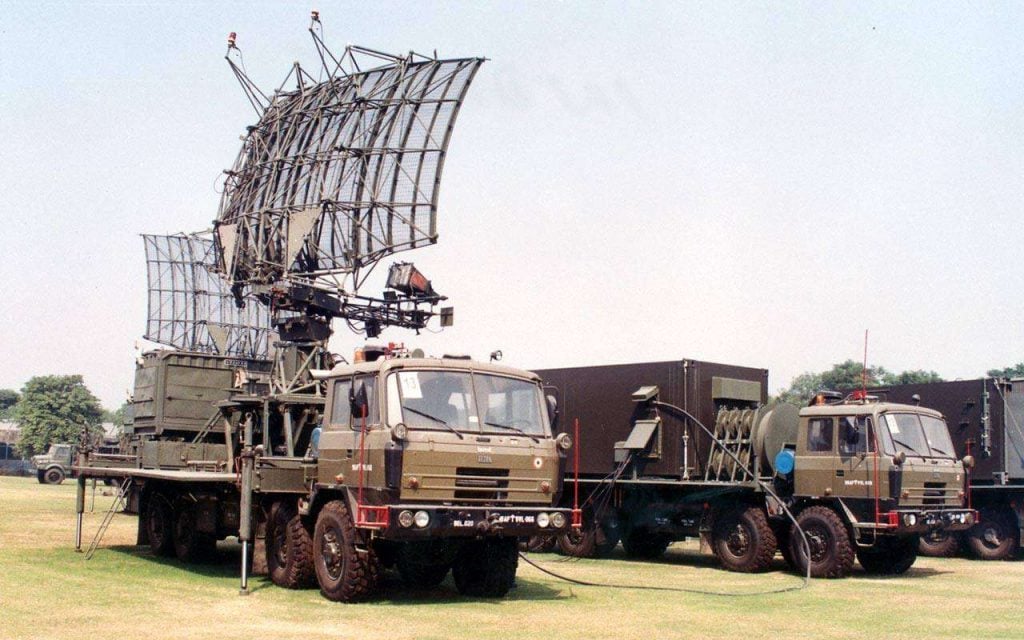
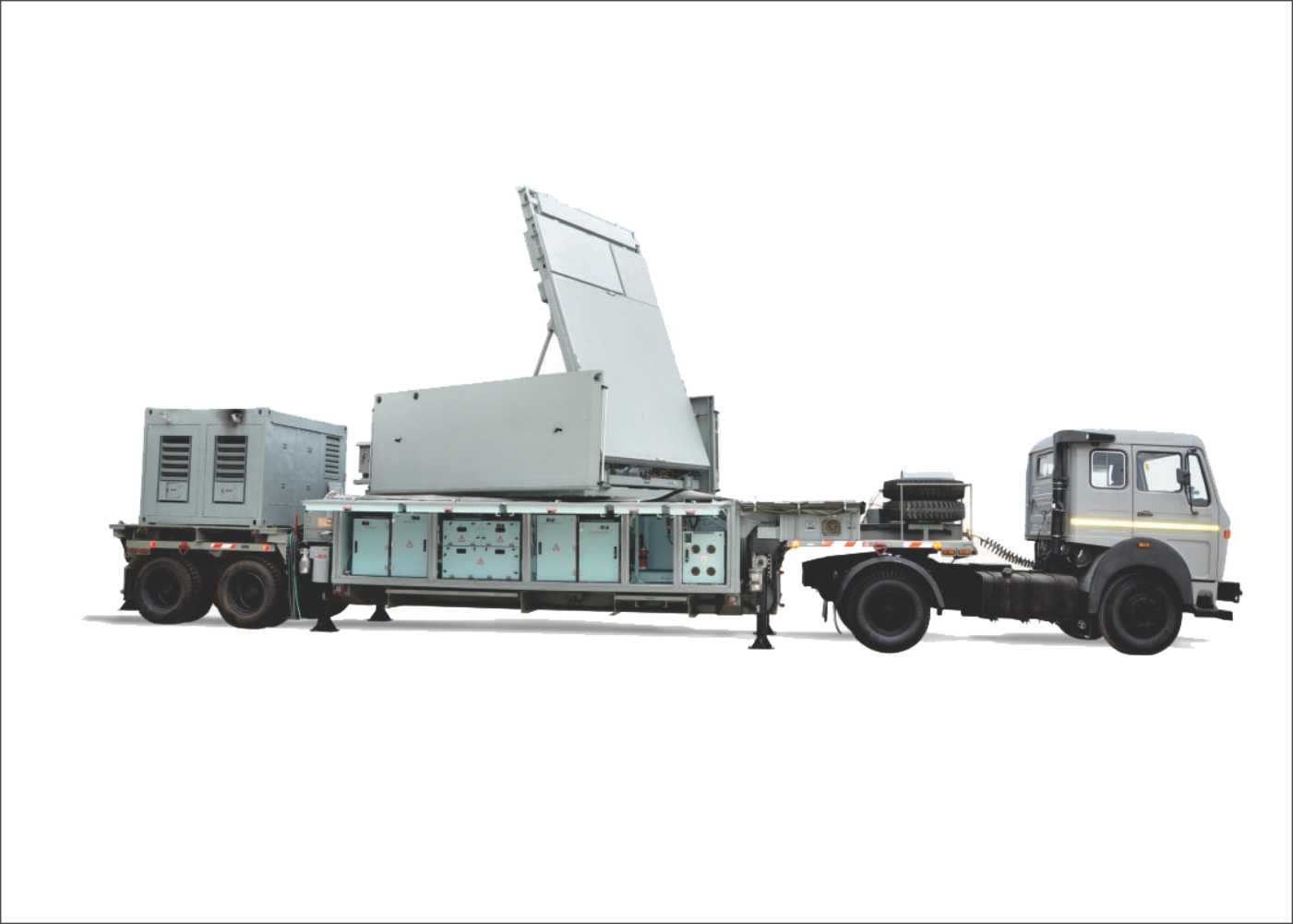
DRDO created the Indian Doppler Radar (INDRA) series of 2D radars for the Army and Air Force. The INDRA-I mobile surveillance radar is used to detect low-level targets, while the INDRA-II is used to intercept targets under ground control.
A 2D mobile surveillance radar called INDRA-I is used to find low-level targets. Two wheeled vehicles are where the radar is housed. Automated Track While Scan (TWS), integrated IFF, and fast scan rate for high speed target detection are a few of the key characteristics. The radar was introduced into service and is made by Bharat Electronics Limited. The INDRA-I was a significant undertaking for the DRDO because it was the first substantial radar system that the company conceptualised and manufactured.
Indra MK2 Radar
It is an INDRA radar type used for ground-based target interception. High range resolution and ECCM capabilities of the radar allow it to detect low-flying aircraft in areas with dense ground clutter. The Indian Army and Air Force use the radar, which was made by Bharat Electronics Limited. The Indian Air Force has ordered seven INDRA-II aircraft.
This radar system is a modification of the INDRA kind used for intercepting targets from the ground. With its great range resolution and ECCM capabilities, the radar is able to detect low-flying aircraft even in dense ground clutter thanks to pulse compression. The radar, manufactured by Bharat Electronics Limited, is in service with the Indian Air Force and Army. In total, the Indian Air Force has placed an order for seven INDRA-IIs.
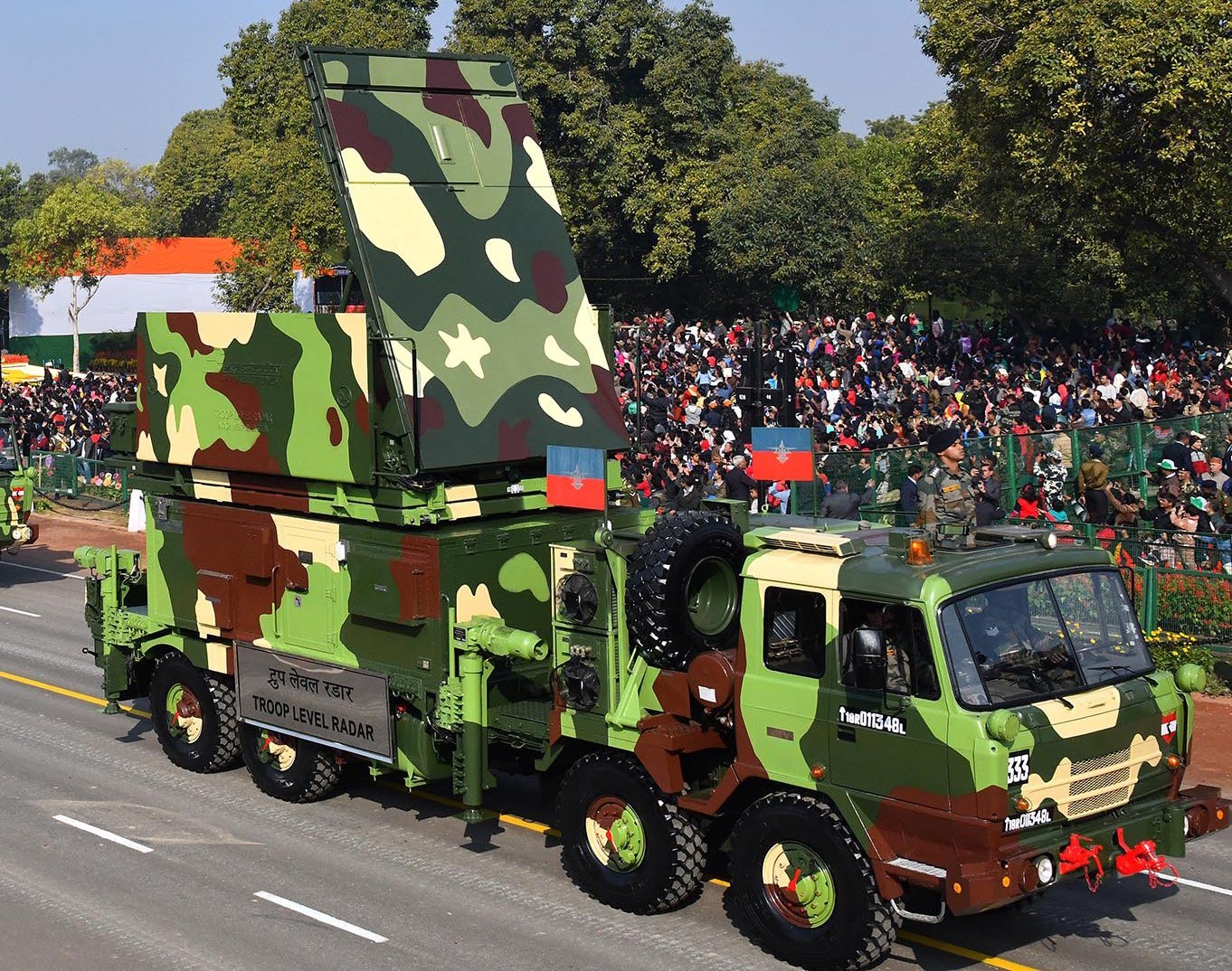
Rajendra Radar (TLR)
The brain of the Aakash Air Defense System, a multifunction electronically scanned phased array radar. It is a passive electronically scanned array (PESA) radar that directs Aakash missiles to their intended targets. It performs numerous radar tasks, including surveillance, tracking, and guidance, when mounted on a two-wheeled vehicle.
It is a multipurpose radar that can monitor low radar cross section objects and engage them. It functions as the main fire control sensor for an Akash battery and is the brain of the Akash surface-to-air missile system.
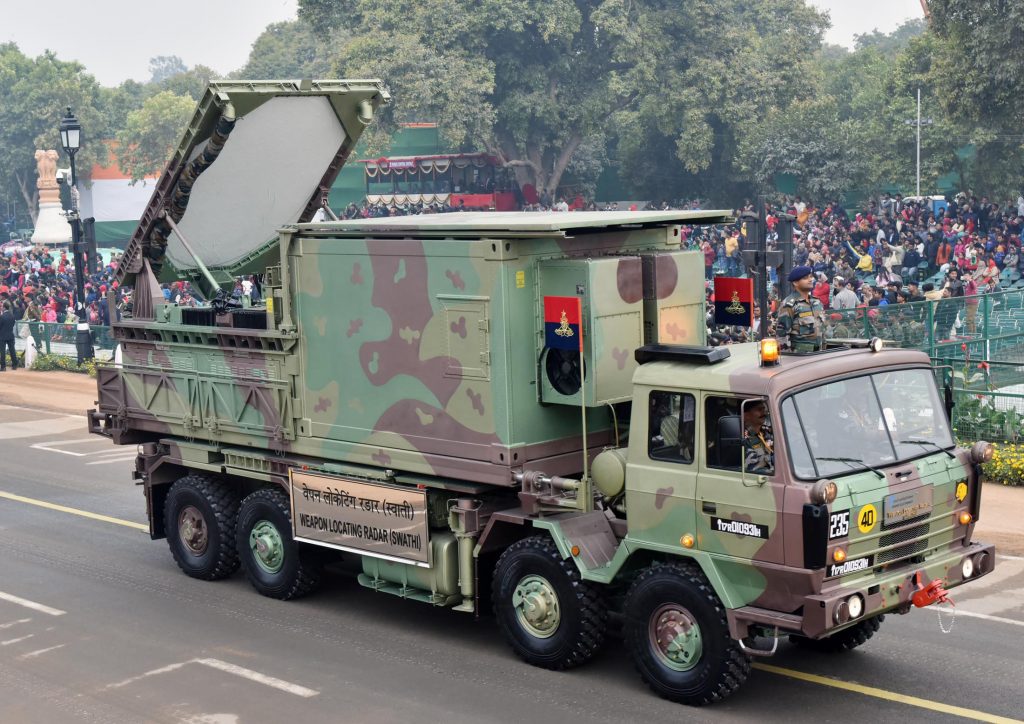
Swathi Weapon Locating Radar (WLR)
India developed the Swathi Weapon Locating Radar, a mobile phased array radar for locating artillery. It is a counter-battery radar made to find the site of origin of counter-battery fire by detecting and tracking incoming artillery and rocket fire.
It was created by the government-owned Bharat Electronics Limited, LRDE, and the DRDO’s Bangalore base laboratory (BEL). It helps the Indian Army find Pakistani artillery locations along the LOC and can track seven targets at once.
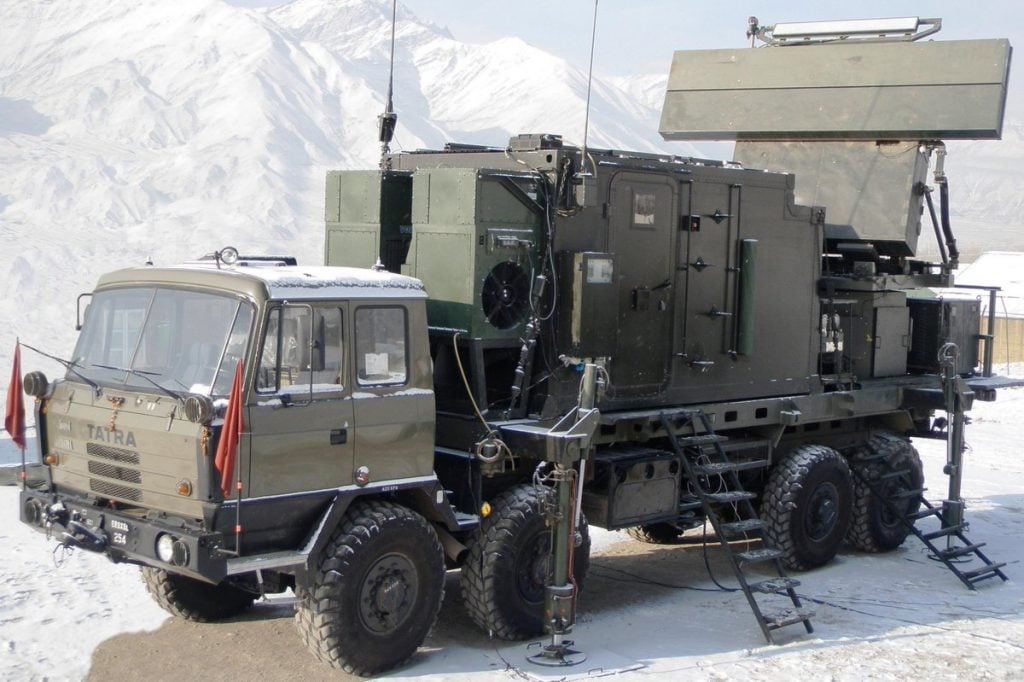
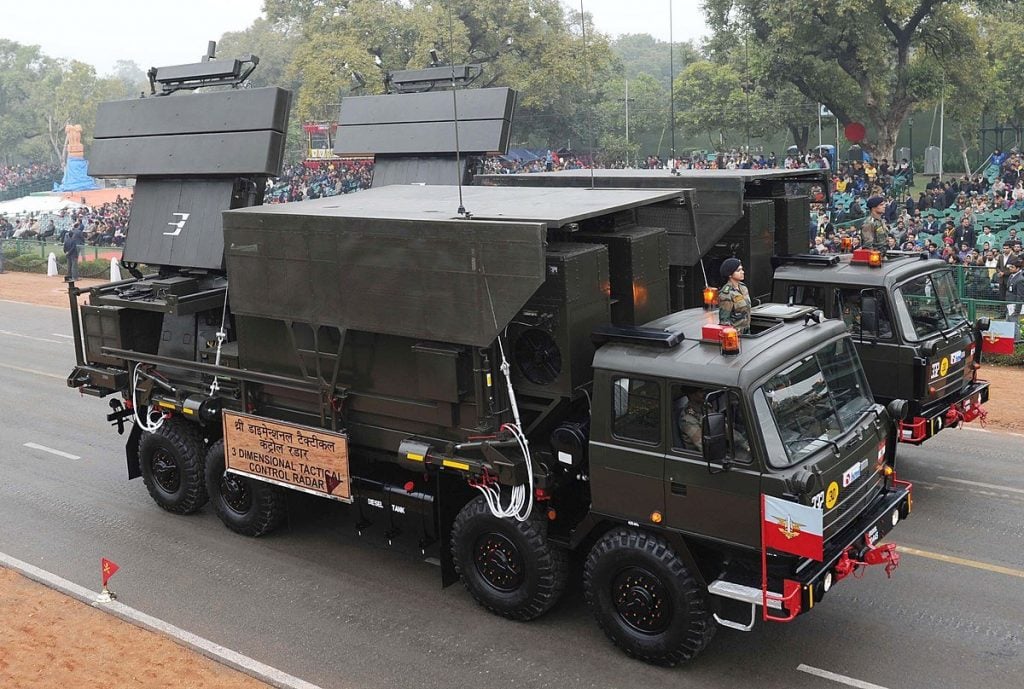
Central Acquisition Radar (3D-CAR)
The DRDO created a 3D S-Band Radar for the Indian Army and Indian Air Force. Air Force employs the Revathi variant, whereas the Army uses the Rohini variant. It can identify low-altitude objects, as well as supersonic aircraft travelling at above Mach 3 speed, and track targets out to a range of more than 180 km.
High resolution, precision, responsiveness, and information availability are provided by the radar’s digital receiver and programmable signal processor. To suit operational and tactical mobility requirements, the radar is mounted on two high mobility TATRA vehicles.
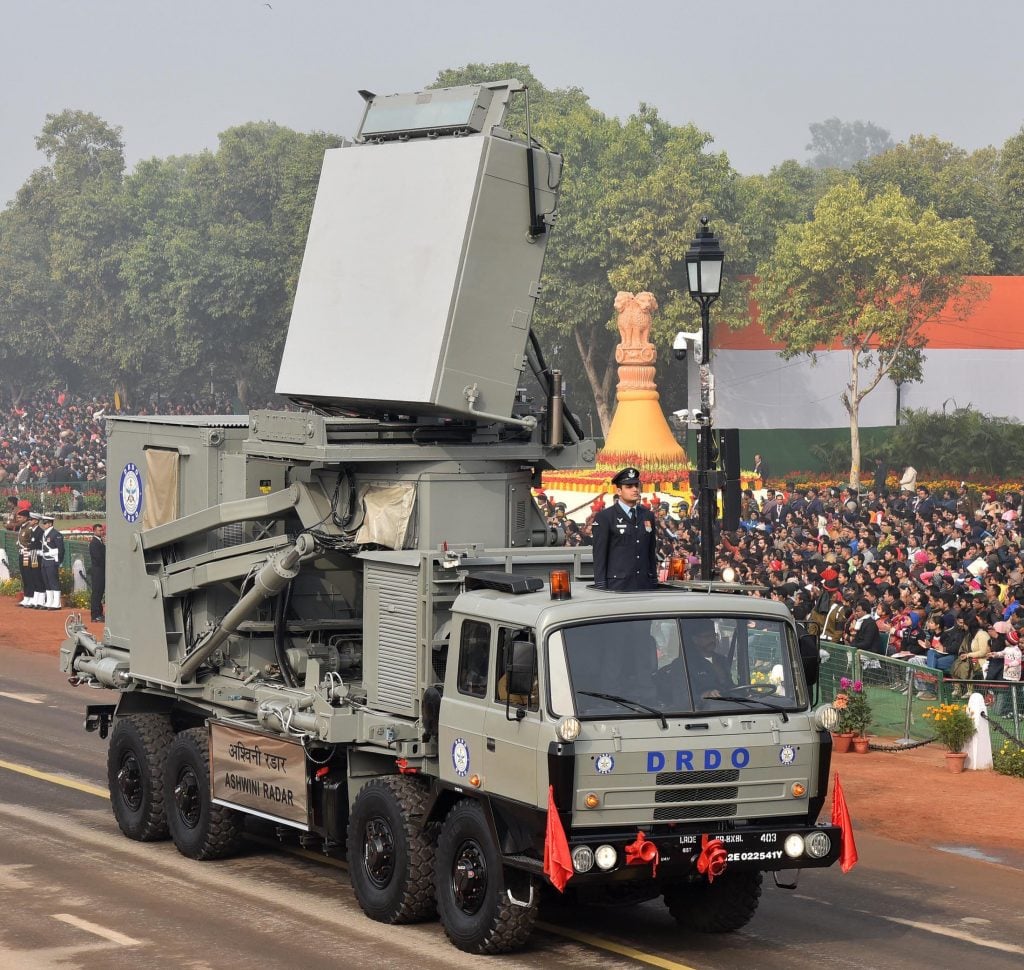
Ashwini Radar
Its 4D Low Level Transportable Radar technology was created to track hostile targets with absolute precision. It has a detection range of up to 200 kilometres and can identify fast-moving targets. Being conveniently transportable, it is an active phased array.
4D radars can measure distance, azimuth, height, and velocity vector as well. It is designed to be quickly deployable and serves as a substitute for the tested Rohini system.
Either the rotating or scanning modes of the radar are in use. With 360° of azimuth and 40° of elevation of surveillance coverage when in rotation mode, the antenna rotates at 7.5/15 rpm. The antenna stares in the designated azimuth while providing surveillance coverage of 60° in azimuth and 40° in elevation.
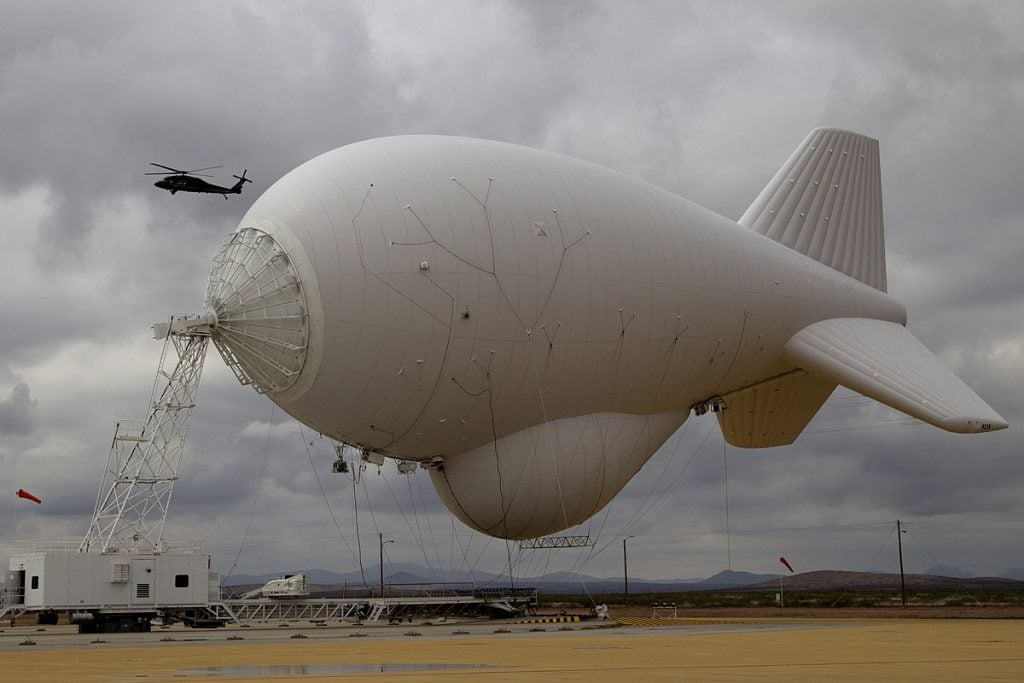
AEROSTAT Radar
The aerostats, which are substantial cloth bags filled with helium, can soar up to a height of 15,000 feet (4,600 metres) while being attached to a single cable.
The largest can hoist a cargo of 1,000 kg to a working altitude that offers radar coverage at ground level and to the downward side. In December 1980, the United States Air Force received its first aerostats at Cudjoe Key, Florida. In order to combat illegal drug trafficking, the U.S. Customs Service ran a network of aerostats during the 1980s.
Swordfish Radar (LRTR)
An Indian long-range tracking radar called Swordfish was created primarily to address the threat of ballistic missiles. It will be a component of the ballistic missile programme of India. This radar underwent its initial testing in March 2009. The primary goal of the test was to verify the performance of the locally created Swordfish Long Range Tracking Radar (LRTR). The missile that will be hit will be launched from a greater distance than in the previous test.
According to a project participant, the DRDO evaluated whether or not the radar could monitor the approaching missile from that distance. Swordfish is a recognised descendant of the crucial element of Israel’s Arrow missile defence system, the long-range Green Pine radar. Although it uses Indian Transmit Receive modules, signal processing, computers, and power sources, it is different from the Israeli system in this regard. It was created to satisfy India’s unique BMD requirements and is more potent than the original Green Pine system.
Around July 2002 and August 2005, India bought two Green Pine radars and put them into service. An official descendant of the original Green Pine is the Swordfish Long Range Tracking Radar produced by the Indian Defence Research and Development Organization.
PJT-531 Battle Field Surveillance Radar
It is a man portable 2D short-range battlefield and perimeter surveillance radar. This radar has been a boon to Indian forces at LOC. It is used by Indian Army and BSF along with foreign customers like Indonesia and Sudan. It operates in J Band in 21 frequencies, and can detect crawling men, group of men, Armored Vehicles and Heavy Vehicles at varying distance.


I hope you liked the article. If you are preparing for defence exams and SSB Interview, SSBCrackExams is providing a number of courses and study material. Join today and boost up your preparation.
To join the Indian Armed Forces as an officer and crack SSB Interview, You can join our SSB interview live classes batch and we recommend you to Enroll SSB INTERVIEW ONLINE COURSE. Trusted by thousands of defence aspirants.
Also Read: