In Current Affairs for 06 May 2025, we will see the latest national and international current affairs news. These important current affairs will be beneficial for your upcoming NDA, CDS, CDS OTA, AFCAT, TA, Agniveer Army, Agniveer Navy, Agniveer Air Force, Women Military Police, INET, MNS, ACC exams, SCO, PCSL, CAPF, and SSB interviews, and direct entries for Army, Navy, and Air Force like SSC Tech, TGC, JAG, NCC, TES, 10+2 Cadet. Download a PDF file about current events at the end of this article. Let us now see the Current Affairs.
Current Affairs 06 May 2025
Digital Access As A Fundamental Right In India
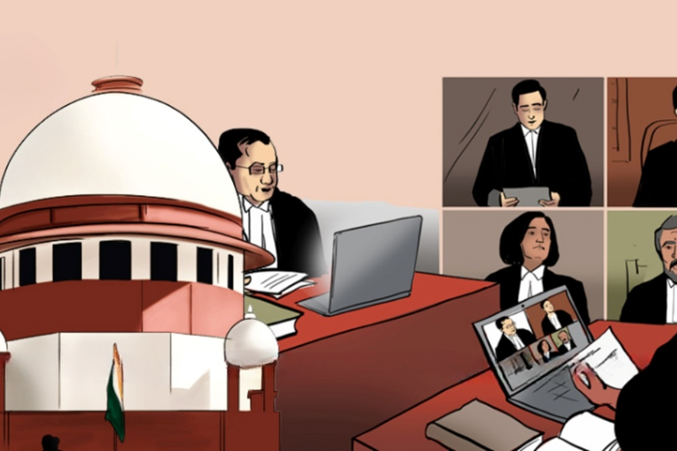
- The Supreme Court of India recognised digital access as a fundamental right under Article 21 of the Constitution. This landmark judgement mandates that the state must provide an inclusive digital ecosystem.
- The Supreme Court ruled that digital access is integral to the right to life and liberty. The judgement arose from petitions by acid attack survivors and visually impaired individuals. They faced barriers in completing digital Know Your Customer (KYC) processes. The court identified these barriers as hindrances to accessing essential services and welfare schemes.
- The court emphasised the need for an inclusive digital ecosystem. It stated that access to services such as healthcare, education, and governance is increasingly digital. Therefore, the state must ensure that all citizens, regardless of their abilities or backgrounds, can participate equally in these digital platforms. The government is constitutionally obligated to build an inclusive digital ecosystem, ensuring access for:
- The marginalised and underprivileged
- Persons with disabilities (PwDs)
- Vulnerable groups
- Historically-excluded communities
- Changes to KYC Processes
- The court directed the government to reform KYC processes to accommodate individuals with disabilities. It mandated that KYC procedures should no longer require visual tasks that are impossible for certain individuals. This includes allowing alternative methods for identity verification, such as video-based KYC processes.
- The ruling reinforced the state’s obligation under various articles of the Constitution.
- Article 21 – Right to life with dignity
- Article 14 – Right to equality
- Article 15 – Protection against discrimination
- Article 38 – State’s duty to promote welfare and reduce inequality
- Recommendations for Government Action
- The Supreme Court issued twenty directives to the government. These directives aim to enhance KYC processes and digital accessibility. The court instructed regulatory authorities to adhere to accessibility standards and ensure that all digital platforms are designed to be inclusive.
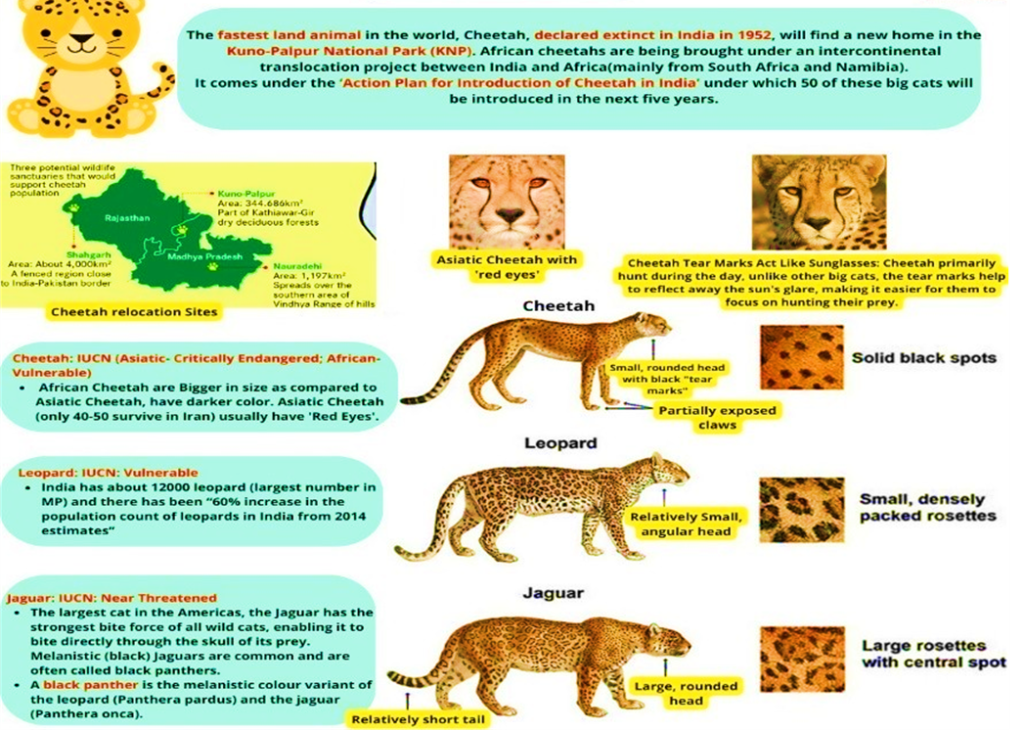
Cheetah Corridor Project
- A Cheetah Corridor is being set up as part of India’s wildlife conservation efforts. The initiative is designed to facilitate the movement of cheetahs across regions, thereby expanding their natural habitat.
- The Cheetah Corridor will cover 17,000 square kilometres. It will stretch across 27 districts in Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, and Madhya Pradesh. This planned corridor includes 13 districts in Rajasthan, 2 in Uttar Pradesh, and 12 in Madhya Pradesh, aiming to create a continuous path for cheetahs to move freely.
- It will interlink several protected areas, including Shahabad Conservation Reserve, Shergarh Wildlife Sanctuary, Mukundra Wildlife Sanctuary, Gandhi Sagar Wildlife Sanctuary, Madhav National Park and Ranthambhore Tiger Reserve. The primary goal of the corridor is to improve genetic diversity among cheetah populations.
- By connecting isolated wildlife reserves, the project aims to reduce habitat fragmentation. This will enable cheetahs to roam freely, find mates, and thrive in their natural environment. Cheetah is a conservation effort launched by the Indian government to bring cheetahs back to the country’s wild landscapes after their extinction in 1952.
- The initiative involves relocating cheetahs from Africa and introducing them into well-suited habitats in India, such as national parks and wildlife sanctuaries. The primary objectives of Project Cheetah are to restore ecological balance, support biodiversity, and boost both conservation initiatives and wildlife tourism in the country.
- The National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) and the Wildlife Institute of India (WII) endorse the project. Their assessments indicate that the Kuno-Gandhi Sagar landscape is ideal for cheetah habitation. This scientific backing reinforces the project’s credibility.
Sahajog Initiative
- Odisha government has launched Sahajog, a groundbreaking initiative aimed at enhancing access to government welfare schemes for the urban poor. Officially inaugurated on May 1, 2025, it seeks to bridge the gap between urban poverty and available state assistance.
- The programme is designed to ensure last-mile delivery of services to eligible beneficiaries in urban communities. Sahajog aims to identify and connect eligible urban poor families with various welfare schemes. It focuses on increasing awareness and facilitating the delivery of essential services directly to the beneficiaries.
- The initiative is a response to the pressing needs of economically weaker sections in urban areas. The programme will operate in a campaign mode from May 1 to June 20, 2025. It will cover 44 Urban Local Bodies (ULBs) across eight districts, benefiting approximately 15 lakh residents.
- The districts selected include Khurda, Cuttack, Ganjam, Sundargarh, Sambalpur, Keonjhar, Mayurbhanj, and Bhadrak. Sahajog will facilitate access to 14 key welfare schemes.
- These include the Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (Urban), ration cards under the National Food Security Act, pipe water supply, Ayushman Cards, and the Subhadra Yojana. The initiative is structured to provide comprehensive support to the urban poor.
- Community volunteers and frontline workers will play important role in the execution of Sahajog. They will receive performance-based incentives to encourage active participation. This grassroots involvement is essential for reaching the most vulnerable populations effectively.
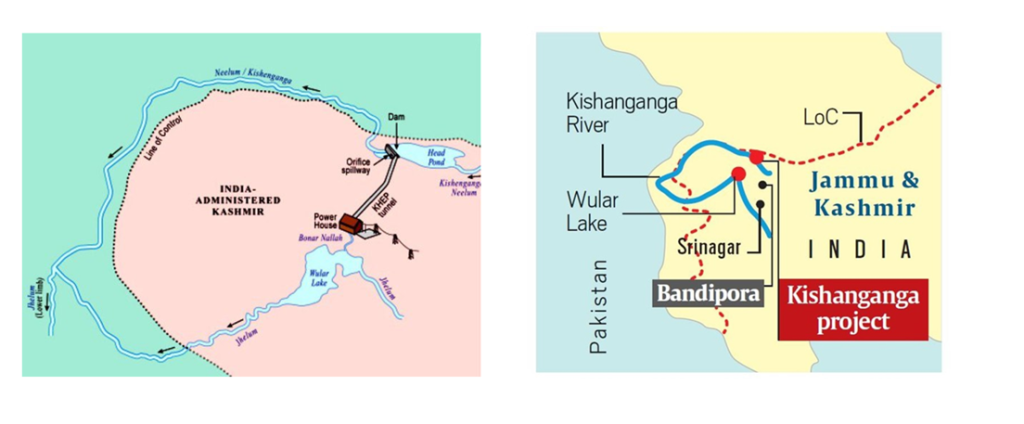
Baglihar Dam
- In yet another strong step against Pakistan in the wake of the Pahalgam terror attack, India has stanched the flow of water through the Baglihar Dam on the Chenab River.
- India has cut off water flow to Pakistan from the Baglihar Dam, following through on its decision not to allow a “single drop” to go to the neighbouring country from the Indus rivers. India is also planning similar measures at the Kishanganga Dam on the Jhelum River.
- The hydroelectric dams Baglihar in Ramban district in Jammu division and Kishanganga in north Kashmir offer India the ability to regulate the timing of water releases. India has lowered sluice gates and initiated de-silting operations.
- Resulted in up to 90% reduction in water flow to Pakistan.
- Official reason: reservoir maintenance and re-filling.
Committee To Appoint CBI Director
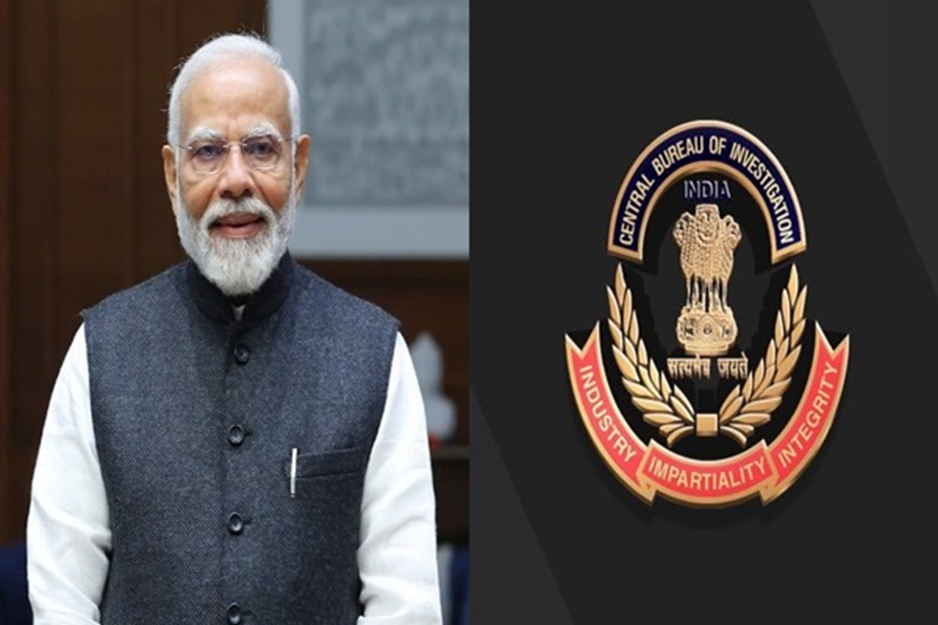
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi chaired a meeting of the Committee for the appointment of the CBI Director at the Prime Minister’s Office in New Delhi. The meeting was attended by the Chief Justice of India, Justice Sanjiv Khanna, and the Leader of the Opposition in the Lok Sabha, Rahul Gandhi.
- During the meeting, the appointment of the next CBI Director was discussed. The meeting comes ahead of the end of the two-year term of incumbent CBI Director Praveen Sood on the 25th of this month. The appointment of the CBI Director is done by the Central Government on the recommendation of a three-member appointment committee, which is headed by the Prime Minister and comprises the Leader of Opposition in Lok Sabha and the Chief Justice of India.
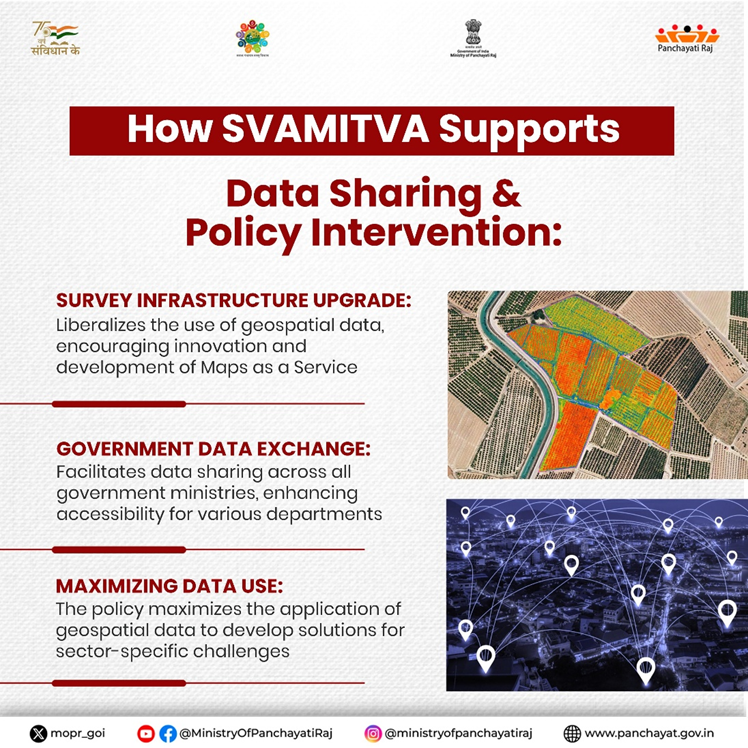
World Bank Land Conference 2025
- India is poised to play a crucial role at the 2025 World Bank Land Conference, set to take place from May 5th to 8th at the World Bank Headquarters in Washington, D.C. A high-level Indian delegation, led by Shri Vivek Bharadwaj, Secretary, Ministry of Panchayati Raj (MoPR), will present India’s transformative SVAMITVA Scheme, alongside the Gram Manchitra platform.
- These initiatives, which harness advanced geospatial technologies and drones, aim to revolutionize rural land governance and contribute to climate action and sustainable development.
- India’s leadership at this global forum underscores its commitment to digital land reforms and climate-responsive governance. 2025 World Bank Land Conference is drawing attention for its focus on securing land tenure and fostering climate action through effective land governance. As a part of this, India’s SVAMITVA Scheme and Gram Manchitra platform are gaining global recognition for their innovative approach to land mapping and rural empowerment.
- Aim of India’s Participation at the World Bank Land Conference 2025
- To showcase the success and potential of the SVAMITVA Scheme and Gram Manchitra platform as models of digital land governance.
- To highlight India’s efforts in empowering rural populations, particularly women, through secure land tenure and digital mapping technologies.
- To contribute to global discussions on scaling land governance reforms and integrating geospatial technologies for climate action.
- SVAMITVA Scheme Overview : To provide legal ownership of rural properties through drone mapping and high-resolution geospatial data. Impact Over 24.4 million households across 1.6 lakh villages have received property cards, unlocking a land value of approximately $1.162 trillion. SVAMITVA exemplifies inclusive, tech-driven governance by improving land rights, tax administration, and infrastructure planning.
- Gram Manchitra Platform : A tool that utilizes SVAMITVA’s geospatial data to support village-level planning, including land use, disaster preparedness, and solar energy site selection. It serves as a catalyst for rural development by ensuring that local governance is informed by accurate, up-to-date geospatial information.
- India’s participation at the World Bank conference emphasizes its growing role in global land governance discussions.
- The country is committed to promoting South-South cooperation, where developing nations can share knowledge and best practices for land administration and sustainable development.
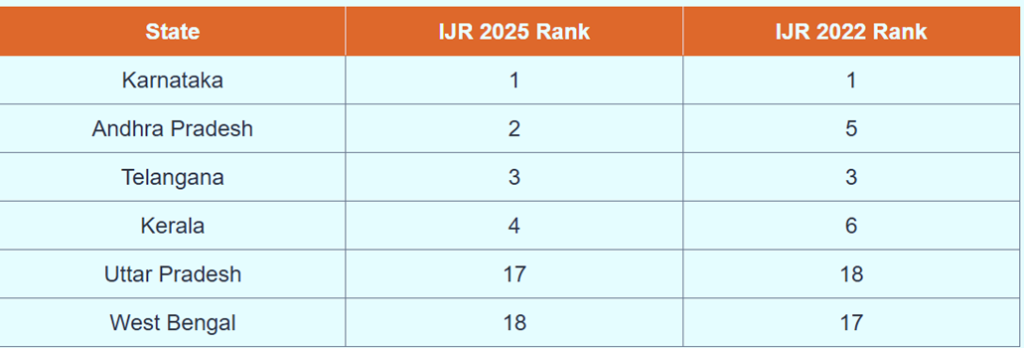
India Justice Report 2025
- India Justice Report (IJR) 2025, published earlier this year, delivers a comprehensive analysis of the institutional capacity of the justice delivery system in India. Now in its fourth edition, the IJR has become the only quantitative index of its kind in India, relying entirely on government data to assess how well states are equipped to deliver justice to their citizens.
- Launched first in 2019 with the support of Tata Trusts, the 2025 report has been jointly produced in partnership with DAKSH, Commonwealth Human Rights Initiative, Common Cause, Centre for Social Justice, Vidhi Centre for Legal Policy, and TISS-Prayas.
- IJR 2025 evaluates the justice system using five key pillars: police, prisons, judiciary, legal aid, and human rights commissions. These pillars are measured using a mix of indicators related to human resources, infrastructure, budgetary allocations, workload, and diversity.
- The report notes a continued concentration of police infrastructure in urban areas, with a decline in the number of rural police stations between 2017 and 2023. This urban bias results in weakened law enforcement in rural regions, where crimes often go unreported or are poorly investigated.
- The police-to-population ratio in India stands at 155 per lakh, significantly below the sanctioned strength of 197 per lakh. Bihar exemplifies this challenge, with just 81 police personnel per lakh population, one of the lowest in the country.
- Such shortages lead to delayed investigations, poor community policing, and compromised public safety. highlights an alarming overcrowding rate in Indian prisons, with the average occupancy standing at 131%. In some facilities, this number exceeds 400%, putting a severe strain on infrastructure, safety, and human dignity.
- Even more troubling is the statistic that 76% of all prisoners are undertrials, many of whom remain behind bars for extended periods without conviction. About 25% of undertrials have spent between one to three years in detention awaiting trial. the legal aid network consists of 41,553 panel lawyers and 43,050 paralegal volunteers, yet their outreach remains limited. The lack of community-based legal support undermines access to justice, especially for the poor and marginalised.
- India’s criminal justice system ranks 89th, indicating weak mechanisms to prosecute offenses and deliver fair outcomes. Its civil justice system performs even worse, at 111th, largely due to issues such as accessibility, delays, corruption, and lack of impartial dispute resolution.
Padma Shri K.V. Rabia
- Won Padma Shri K.V. Rabia, An Inspirational Literacy Activist From Kerala, Passed Away At The Age Of 59 While Undergoing Treatment. Despite Battling Severe Health Conditions Such As Polio, Cancer, And Spinal Injury, Rabia Dedicated Her Life To Social Service And Women’s Education.
- Her Commitment To Empowering Marginalized Communities Through Literacy Earned Her Several Accolades, Including The Prestigious Padma Shri In 2022.
- Padma Shri (2022) – For Contributions To Social Service.
- National Youth Award (1993).
- Kannaki Stree Shakti Puraskar (1999).
- Seethi Sahib Memorial Award (2010).
- Vanitha Ratnam Award (2014) – State Recognition.
Current Affairs 06 May 2025 Question
- K.V. Rabia, who passed away in May 2025, was a notable figure in which field
A. Environmental conservation
B. Literacy movement
C. Space research
D. Political activism
ANSWER: B - What significant step was taken under the Namami Gange Mission
A. Construction of new dams
B. Release of dolphins into the Ganga
C. Reintroduction of the Red-Crowned Roofed Turtle
D. Ban on industrial fishing in Ganga
ANSWER: C - Where was the Red Admiral butterfly spotted for the first time in India
A. Aravalli Hills
B. Dhauladhar mountain range
C. Western Ghats
D. Sundarbans
ANSWER: B - According to IMF’s World Economic Outlook India is expected to become __
largest economy in 2025.
A. Second
B. Third
C. Fourth
D. Fifth
ANSWER: C - Koraput Kalajeera Rice Got GI Status, Is Cultivated In Which State
A. Punjab
B. Odisha
C. Andhra Pradesh
D. Uttar Pradesh
ANSWER: B - What is India’s projected nominal GDP for FY2025-26, as per IMF
A. $3,980.123 billion
B. $4,100.000 billion
C. $4,187.017 billion
D. $4,300.000 billion
ANSWER: C - Which international event is highlighting India’s SVAMITVA Scheme, Gram
Manchitra platform
A. UN Climate Conference 2025
B. World Economic Forum
C. World Bank Land Conference 2025
D. G20 Summit 2025
ANSWER: C - What is the primary focus of Operation Hawk 2025 launched by the CBI
A. Financial fraud detection
B. Wildlife trafficking
C. Cyber terrorism
D. Online child sexual exploitation
ANSWER: D - Kirkuk Which Was Seen In The News, Is Located In Which Country
A. Israel
B. Iraq
C. Australia
D. Greece
ANSWER: B - Umiam Lake Seen In The News, Is Located In Which State
A. West Bengal
B. Arunachal Pradesh
C. Sikkim
D. Meghalaya
ANSWER: D - Which operations preceded Operation Hawk in combating child exploitation
A. Operation Sea wave and Operation Panther
B. Operation Carbon and Operation Megh Chakra
C. Operation Raksha and Operation Suraksha
D. Operation Lotus and Operation Trinetra
ANSWER: B - India’s recent reduction of water flow to Pakistan from Baglihar and
Kishanganga projects is linked to which of the following
A. Flood control
B. Drought in India
C. Breakdown of the Indus Waters Treaty
D. Power generation expansion
ANSWER: C - Mount Makalu, Lies On The Border Between Which Two Regions
A. India and Nepal
B. Nepal and Tibet
C. India and Bhutan
D. Bhutan and China
ANSWER: B - Where Was The First National Mediation Conference 2025 Inaugurated
A. New Delhi
B. Mumbai
C. Hyderabad
D. Chennai
ANSWER: A - Solar Energy Corporation Of India Is Under The Administrative Control Of
Which Ministry
A. Ministry of Power
B. Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change
C. Ministry of Science and Technology
D. Ministry of New and Renewable Energy
ANSWER: D - Which Insecticide Did India Oppose Banning Under The Stockholm Convention
During The 2025 BRS Conventions In Geneva
A. Endosulfan
B. Chlorpyrifos
C. Atrazine
D. DDT
ANSWER: B - Ramman Festival Is Celebrated In Which State
A. Uttarakhand
B. Assam
C. Odisha
D. Himachal Pradesh
ANSWER: A - In Which Country’s Trench Is Emden Deep, World’s 3rd deepest Point, Located
A. Indonesia
B. Japan
C. Philippines
D. Papua New Guinea
ANSWER: C - Which Organization Brokered Indus Waters Treaty Between India & Pakistan
A. United Nations
B. International Court of Justice
C. Asian Development Bank
D. World Bank
ANSWER: D - Which Insecticide Did India Oppose Banning Under The Stockholm Convention
During The 2025 BRS Conventions In Geneva
A. Endosulfan
B. Chlorpyrifos
C. Atrazine
D. DDT
ANSWER: B