In Current Affairs for 24 May 2025, we will see the latest national and international current affairs news. These important current affairs will be beneficial for your upcoming NDA, CDS, CDS OTA, AFCAT, TA, Agniveer Army, Agniveer Navy, Agniveer Air Force, Women Military Police, INET, MNS, ACC exams, SCO, PCSL, CAPF, and SSB interviews, and direct entries for Army, Navy, and Air Force like SSC Tech, TGC, JAG, NCC, TES, 10+2 Cadet. Download a PDF file about current events at the end of this article. Let us now see the Current Affairs.
Current Affairs 24 May 2025
India Extends Airspace Ban On Pakistani Aircraft
- India has extended NOTAM for Pakistan flights till 23rd of the next month. According to the Ministry of Civil Aviation, Indian airspace is not approved for aircrafts registered in Pakistan and operated, owned and leased by Pakistani airlines including military aircrafts. Talking to the media in New Delhi, Civil Aviation Minister Ram Mohan Naidu Kinjarapu said, the NOTAM has been extended and India is maintaining the status quo.
Konkan Railway Set To Merge With Indian Railways
- The recent decision by the Maharashtra government to merge the Konkan Railway Corporation Limited (KRCL) with Indian Railways marks development in India’s railway infrastructure. This merger follows approvals from Goa, Karnataka, and Kerala, paving the way for the integration of a vital railway line into the national network.
- The Konkan Railway, established in 1990, serves as important link along the scenic western coast of India, connecting Maharashtra, Goa, Karnataka, and Kerala. The Konkan Railway was created as a special purpose vehicle under the Ministry of Railways. Its primary aim was to construct railway lines through the challenging terrain of the Western Ghats.
- Official operations began in January 1998, establishing a 741 km route that reduced travel time and improved connectivity between coastal regions and major cities. KRCL was set up as a joint venture. The Government of India holds a 51% stake, while Maharashtra, Karnataka, Goa, and Kerala hold 22%, 15%, 6%, and 6% respectively. Despite its operational success, KRCL has faced financial challenges, hampering its ability to expand and upgrade infrastructure.
- Reasons for the Merger : The merger is driven by the need for financial sustainability. KRCL’s standalone model has become unviable, with insufficient revenue to support necessary upgrades.
- Chief Minister Devendra Fadnavis brought into light that merging with Indian Railways would allow KRCL to utilise its extensive investment base for future projects and improvements.
- Conditions of the Merger : Maharashtra’s approval was contingent on two main conditions. First, the name “Konkan Railway” must remain post-merger. Second, Indian Railways is to reimburse Maharashtra over Rs 394 crore, reflecting the state’s initial investment in KRCL. The Centre has agreed to these stipulations.
- Implications for Passengers : Once the merger is completed, passengers can expect enhanced services. This includes upgraded infrastructure, increased train frequency, and improved security measures. Additionally, the merger aims to provide competitive fares, seamless booking options through Indian Railways, and a more efficient customer grievance redressal system.
- Future Prospects : The merger process will involve various administrative, financial, and legal steps. The Railway Board will oversee these changes, which may take several months to implement. Ultimately, the integration of KRCL into Indian Railways is expected to benefit local economies, enhance tourism, and create more job opportunities.
Intercrystals
- Recent advancements in material science have led to the discovery of a new class of materials known as intercrystals. Researchers from Rutgers University–New Brunswick have revealed their unique electronic properties, which could influence future technologies. These materials are formed by stacking ultrathin layers of graphene with a slight twist over hexagonal boron nitride, creating moiré patterns that alter electron movement.
- Intercrystals are materials that exhibit both quasicrystalline and crystalline properties. They possess non-repeating atomic patterns like quasicrystals but maintain symmetries found in conventional crystals. This hybrid nature allows for unique electronic behaviours not typically observed in standard materials.
- Role of Twistronics : Twistronics is a modern technique that manipulates the angles of layered materials. By adjusting these angles, researchers can create moiré patterns that dramatically change the electronic structure. This method was very important in discovering intercrystals, as it allows for control over electronic properties through geometric adjustments rather than chemical alterations.
- Unique Electronic Properties: Intercrystals demonstrate varied electronic properties with minor structural changes. This variability can lead to phenomena such as superconductivity and magnetism. Superconductors are particularly valuable as they enable electrical current to flow without resistance, paving the way for efficient electronic applications.
- Potential Applications : The discovery of intercrystals could revolutionise electronic components. They may lead to the development of more efficient transistors and sensors, which traditionally require complex material combinations. Intercrystals could form the foundation of future electronic circuits, where atomic-level geometric tuning controls all functions.
- Environmental Impact : Intercrystals present a sustainable alternative to conventional electronic materials. They can be produced from abundant and non-toxic elements like carbon, boron, and nitrogen. This quality makes them a more environmentally friendly option compared to rare earth materials commonly used in electronics.
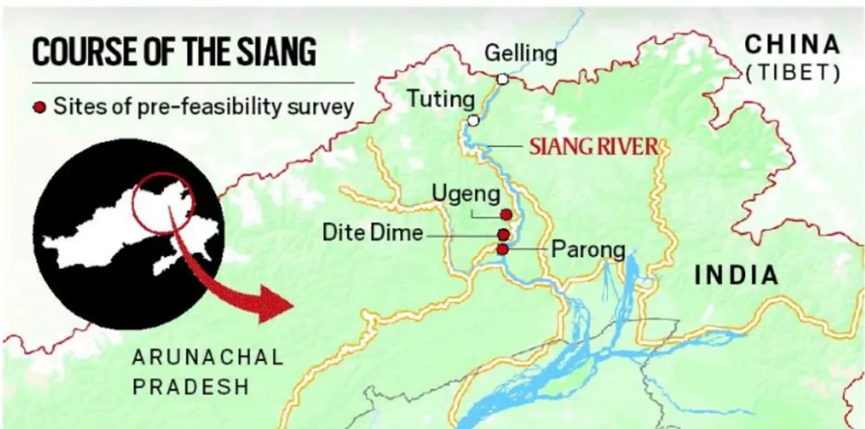
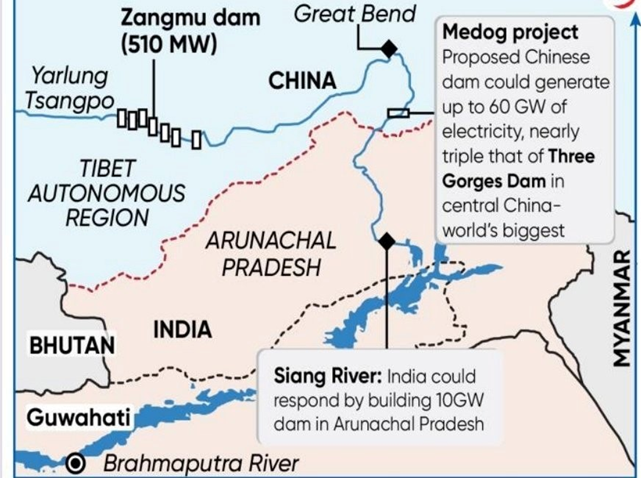
Siang Upper Multipurpose Project
- Siang Upper Multipurpose Project (SUMP) has become a focal point of conflict in Arunachal Pradesh. The project aims to construct an 11.2 GW dam on the Siang River, which is part of the Brahmaputra basin. This initiative has sparked opposition from local communities and student organisations. Residents of over 27 villages along the river express concerns about the potential irreversible impact on their homes and lands.
- The Arunachal government and central authorities argue that the dam is essential for national security, especially in light of China’s construction of the Medog Dam upstream.
- The Siang Upper Multipurpose Project is designed to generate substantial hydroelectric power. The proposed capacity is 11.2 GW, positioning it as contributor to India’s energy needs. The project is also expected to aid in flood control and irrigation. However, the environmental and social implications have raised alarms among local populations.
- The Arunachal Pradesh government, supported by the Centre, maintains that the SUMP is vital for national security. Chief Minister Pema Khandu has stated that the project is necessary to counteract the risks posed by China’s Medog Dam. The government has conducted meetings in the Siang Valley to garner support, framing the dam as a strategic necessity for water security.
- In response to local protests, central armed forces have been deployed in the Siang Valley. This deployment has been met with resistance from residents who feel threatened by the military presence. Protests have erupted over the use of schools and public spaces to house security personnel. Local student bodies have condemned this approach, calling for dialogue rather than force.
- The anticipated impact on communities is deep. Many villagers fear losing their homes and agricultural lands. The social fabric of the region is under strain as differing opinions on the dam create divisions. The situation has prompted calls for more inclusive discussions that address the concerns of affected residents.
- Environmentalists warn that large-scale dam projects can lead to ecological degradation. The Siang River is crucial for the local ecosystem. Concerns include potential changes to water flow, biodiversity loss, and impacts on fisheries. The long-term sustainability of the region’s environment is at stake.
India Plans Integration Of Mission LiFE
- Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC) is evaluating the inclusion of Mission LiFE in the NAPCC, which was originally launched in 2008. The integration seeks to mainstream lifestyle-based climate action within the national framework to accelerate India’s progress towards its climate goals.
- About Mission LiFE
- Launched at COP26 (UNFCCC, 2021) by India.
- Aims to transition from a “use-and-dispose” economy to a circular economy.
- Focuses on behavioural change at the individual and community levels.
- Coordinated nationally by the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC).
- Approach of Mission LiFE
- Jan Andolan (People’s Movement): Encouraging sustainable daily practices.
- Global Collaboration: Involves ideas from global academia and think tanks.
- Cultural Integration: Promotes climate-friendly practices rooted in local traditions.
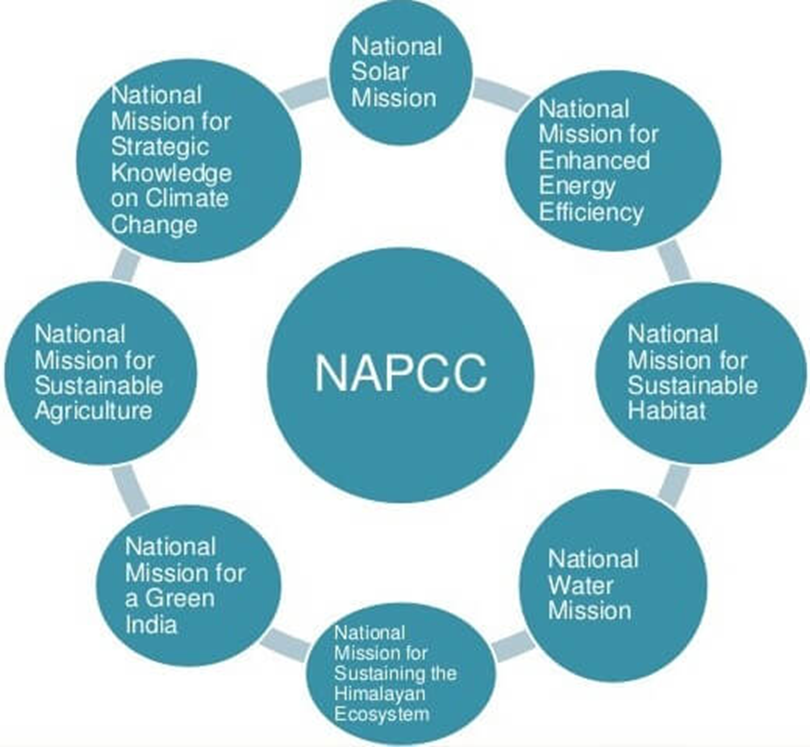
- About the NAPCC
- Launched in 2008 as India’s climate change mitigation and adaptation strategy.
- Consists of 8 Core Missions,
- National Solar Mission
- National Mission for Enhanced Energy Efficiency
- National Mission on Sustainable Habitat
- National Water Mission
- National Mission for Sustaining the Himalayan Ecosystem
- National Mission for a Green India
- National Mission for Sustainable Agriculture
- National Mission on Strategic Knowledge for Climate Change
- Need for Integration
- Quantifiable Impact: Tracks individual and corporate contributions.
- Wider Outreach: Uses NAPCC’s structure to spread Mission LiFE messages.
- Behavioural Change: Promotes low-cost, sustainable actions like waste reduction and energy conservation.
- Bridging Awareness-Action Gap: Converts knowledge into tangible climate action.
- Challenges
- Self-Motivation Required: Unlike incentive-driven schemes, Mission LiFE depends on voluntary participation.
- Lack of Tools: No clear framework for measuring behaviour-led impacts.
- Climate Literacy Gaps: Low public awareness can hinder meaningful engagement.
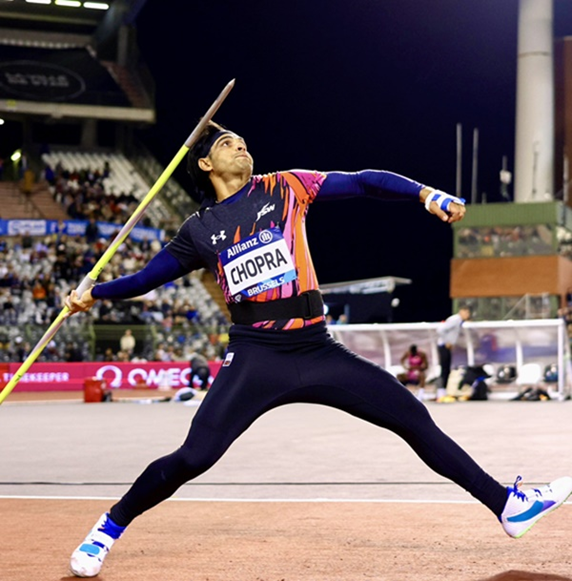
Neeraj Chopra
- Star Indian javelin thrower Neeraj Chopra has clinched the silver medal at the 2025 Janusz Kusociński Memorial meet in Chorzów, Poland.
- The two-time Olympic medallist recorded a throw of 84.14 metres in challenging conditions on his sixth and final attempt. This marked his 22nd consecutive top-two finish since 2021.
- Germany’s Julian Weber won the Gold with a throw of 86.12 metres, while Anderson Peters of Grenada secured third place with a throw of 83.24 metres.
- Chopra’s next appearance will be at the Ostrava Golden Spike meeting in the Czech Republic on June 24.
Shooting
- In Shooting, Olympian Raiza Dhillon bagged a silver medal in the women’s skeet event at the ongoing ISSF Junior World Cup in Germany. Dhillon hit 51 targets in the 60-shot final. She finished just behind Great Britain’s Phoebe Bodley-Scott, who clinched gold with a score of 53.
- Home favourite, Annabella Hettmer, took the bronze. India now tops the medals tally with one gold and two silver medals. Kanak claimed gold in the women’s 10m air pistol event, while Adriyan Karmakar earned silver in the men’s 50m rifle prone category.
- Shooter Kanak has bagged India’s first gold medal at the ongoing International Shooting Sport Federation (ISSF) Junior World Cup in Suhl, Germany. Kanak, the silver medalist at the junior world championship in Lima last year, scored 239 in the Women’s 10 metre Air Pistol final to claim the yellow metal.
- She outperformed Anna Dulce of Moldova, a two-time Olympian and reigning European Champion, by 1.7 points. Chen Yen-Ching of Chinese Taipei won the bronze medal. Meanwhile, another Indian shooter, Prachi, finished fifth. Earlier, Adriyan Karmakar opened India’s medal account with a silver in 50 metre rifle prone event.
Current Affairs 24 May 2025 Question
- SPICED Scheme Is Implemented Under Which Ministry
A. Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare
B. Ministry of Food Processing Industries
C. Ministry of Commerce and Industry
D. Ministry of Rural Development
ANSWER: C - Polavaram Project Is A Multi-purpose Irrigation Initiative Built On Which River
A. Godavari
B. Krishna
C. Narmada
D. Kaveri
ANSWER: A - International Day For Biological Diversity Is Observed On Which Day
A. May 21
B. May 22
C. May 23
D. May 24
ANSWER: B - Where Was The 67th Governing Body Meeting Of The Asian Productivity
Organization Held
A. Tokyo
B. Singapore
C. Jakarta
D. Bangkok
ANSWER: C - Koraput Kalajeera Rice Got GI Status, Is Cultivated In Which State
A. Punjab
B. Odisha
C. Andhra Pradesh
D. Uttar Pradesh
ANSWER: B - Who Won The Silver Medal In The 50m Rifle Prone Event At The ISSF Junior
World Cup In Suhl, Germany
A. Adriyan Karmakar
B. Jesper Johansson
C. Saurabh Chaudhary
D. Manu Bhaker
ANSWER: A - Who Became The First Kannada Writer To Win The International Booker Prize
A. Kuvempu
B. U.R. Ananthamurthy
C. Girish Karnad
D. Banu Mushtaq
ANSWER: D - Which Indian City’s Airport Recorded A 7.7% Passenger Growth In 2024-25
A. Guwahati
B. Mumbai
C. Delhi
D. Bengaluru
ANSWER: A - Kirkuk Which Was Seen In The News, Is Located In Which Country
A. Israel
B. Iraq
C. Australia
D. Greece
ANSWER: B - On Which Date Is National Anti- Terrorism Day Observed In India
A. January 30
B. May 21
C. August 15
D. October 2
ANSWER: B - In Which Indian State Were 891 Asiatic Lions Recorded Across 11 Districts
During The 16th Lion Population Census
A. Gujarat
B. Rajasthan
C. Madhya Pradesh
D. Maharashtra
ANSWER: A - Who launched the e-Zero FIR initiative aimed at fast-tracking the registration
of FIRs in cyber financial fraud cases
A. Narendra Modi
B. Rajnath Singh
C. Piyush Goyal
D. Amit Shah
ANSWER: D - Which Country Hosted The Second Blue Talks Ahead Of The United Nations
Ocean Conference 2025
A. France
B. Costa Rica
C. India
D. Brazil
ANSWER: C - Surface Water And Ocean Topography (SWOT) Satellite Is A Joint Mission Of
Which Two Space Agencies
A. European Space Agency (ESA) and Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO)
B. China National Space Administration (CNSA) and Japan Aerospace Exploration
Agency (JAXA)
C. European Space Agency (ESA) and China National Space Administration (CNSA)
D. NASA and Centre National d’Études Spatiales (CNES) French Space Agency
ANSWER: D - Kakapo, Is The Flightless Parrot Native To Which Country
A. China
B. Russia
C. New Zealand
D. Australia
ANSWER: C - When did the Government of India begin rolling out chip-based e-passports
A. January 26, 2024
B. March 31, 2024
C. April 1, 2024
D. May 1, 2024
ANSWER: C - What is a major benefit of the chip-based e-passports
A. Free travel insurance
B. Increased pages in passport
C. Tamper-proof and secure documentation
D. Automatic visa approval
ANSWER: C - What is the objective of the Revised SHAKTI Policy
A. Promote solar energy
B. Replace oil imports
C. Streamline coal allocation and enhance energy security
D. Increase hydroelectric capacity
ANSWER: C - What Was The Theme Of The 58th Annual ADB Board Of Governors Meeting
In 2025
A. Inclusive Finance for All
B. Future Forward: Asian Prosperity
C. Sharing Experience, Building Tomorrow
D. Sustainable Growth and Equity
ANSWER: C - Which Among The Following Is An Extant Shaka Of The Rigveda Samhita
A. Saunaka
B. Ashvalayan
C. Shakala
D. Sankhayana
ANSWER: C