What is Accessible India Campaign?
- Sugamya Bharat Abhiyan is a nation-wide Campaign launched by Dept. of Empowerment of Persons with Disabilities of Ministry of Social Justice & Empowerment.
- Launched on International Day of Persons with Disabilities on 3rd December 2015.
- Aim:
- To provide universal accessibility to persons with disabilities and
- To provide equal opportunity to persons with disabilities to participate in all the aspects of life and live independently
- Three Components of AIC
- Built Environment Accessibility
- Transportation System Accessibility
- Information and Communication Eco-System Accessibility
- The scheme also comes under Persons with Disabilities Act, 1995 under section 44, 45, 46 for equal Opportunities and protection of rights which provides non-discrimination in Transport to Persons with Disabilities.
Blue Flag Beaches
- Union Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) announced the names of eight beaches of India recommended for the International eco-label, the Blue flag certification.
- It also launched India’s own eco-label BEAMS.
- The eight beaches are:
- Shivrajpur in Gujarat
- Ghoghla in Daman & Diu
- Kasarkod and Padubidri beach in Karnataka
- Kappad in Kerala
- Rushikonda in Andhra Pradesh
- Golden beach of Odisha and
- Radhanagar beach in Andaman and Nicobar.
- What is ‘Blue Flag’ certification?
- The ‘Blue Flag’ is a certification that can be obtained by a beach, marina, or sustainable boating tourism operator, and serves as an eco-label.
- The certification is known as an indication of high environmental and quality standards.
- Blue Flag beaches are considered the cleanest beaches of the world.
- It is run by an international, non-governmental, non-profit organisation Foundation for Environmental Education (FEE).
- It was first started in France in 1985 and has been implemented in Europe since 1987. Since 2001 it has been implemented in areas outside Europe when South Africa joined.
- BEAMS (Beach Environment & Aesthetics Management Services)
- India has also launched India’s own eco-label BEAMS under ICZM (Integrated Coastal Zone Management) project.
- Launched by the Society of Integrated Coastal Management (SICOM) and the Union Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC).
Vaibhav Summit
- PM to inaugurate Vaishwik Bharatiya Vaigyanik (VAIBHAV) Summit on 2nd October 2020.
- It is a global summit of Overseas and Resident Indian scientists and academicians.
- Aim: developing mechanisms for involving Indian Diaspora working in top universities and R&D organisations across the world, to further enhance the knowledge-base of Indian Research and Academic Institutions.
- Key areas of discussion: artificial intelligence, quantum technologies, machine learning, electronics, semiconductor technologies, photonics, data science, and aerospace technologies among others.
Epidemic Diseases Amendment Bill, 2020
- Rajya Sabha has passed the Epidemic Diseases (Amendment) Bill, 2020
- It amends the Epidemic Diseases Act, 1897.
- The Bill repeals the Epidemic Diseases (Amendment) Ordinance that was promulgated on April 22, 2020.
- The Act provides for the prevention of the spread of dangerous epidemic diseases.
- The Bill amends the Act to include protections for healthcare personnel combatting epidemic diseases
- It expands the powers of the central government to prevent the spread of such diseases.
- The legislation makes harm, injury, hurt or danger to the life of healthcare service personnel as a cognizable and non-bailable offence.
Indus Water Treaty
- The Indus Water Treaty (IWT) between India and Pakistan marks its 60th anniversary on 19th September 2020.
- IWT was signed in Karachi on 19 September 1960 by Jawaharlal Nehru and Ayub Khan.
- The World Bank, as the third party, played a pivotal role in crafting the IWT.
- Under the treaty, India has control over water flowing in the eastern rivers– Beas, Ravi and Sutlej.
- Pakistan has control over the western rivers– Indus, Chenab and Jhelum.
- India conceded 80.52% of the aggregate water flows in the Indus system to Pakistan and also gave Rs. 83 crore in pounds sterling to Pakistan to help build replacement canals from the western rivers.
- India conceded its upper riparian position on the western rivers for the complete rights on the eastern rivers.
- Water from the ‘eastern rivers’ were important for the proposed Rajasthan canal and the Bhakra Dam without which both Punjab and Rajasthan would be left dry, severely hampering India’s food production.
- Indus River System
- It is one of the largest river basins of the world.
- It is also known as the Sindhu, is the westernmost of the Himalayan rivers in India.
- Source of origin: Bokhar Chu in the Tibetan region near the Mansarovar Lake.
- Confluence or Mouth: Drains into the Arabian Sea near the port city of Karachi, Pakistan.
Amendment to Foreign Contribution Act
- The Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Amendment Bill, 2020, was introduced in the Lok Sabha.
- It proposes to make Aadhaar a mandatory identification document for all the office-bearers, directors and other key functionaries
- It provides that no foreign contribution shall be accepted by any public servant.
- It has proposed to limit the foreign funds received under the act from 50% to 20%.
- These funds are predominantly used for administration purposes.
- FCRA 2010
- Foreign funding of voluntary organizations in India is regulated under FCRA act
- Implemented by the Ministry of Home Affairs.
- The Act aims to curb such contributions which might be detrimental to the national interest.
- Any organisation, association or NGO in India cannot receive foreign funds if they do not have a license under the FCRA.
21 September: International Day of Peace
- International Day of Peace is observed around the world on 21st September every year.
- The World Peace Day was first established by the United Nations in 1981.
- It was dedicated to peace education by the United Nations in 2013.
- Theme: Shaping Peace Together
- The United Nations (UN) General Assembly has declared this as a day devoted to strengthening the ideals of peace, through observing 24 hours of non-violence and cease-fire.
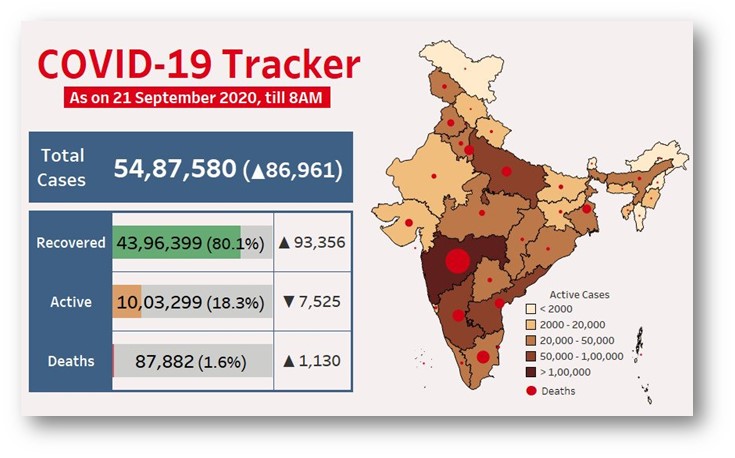
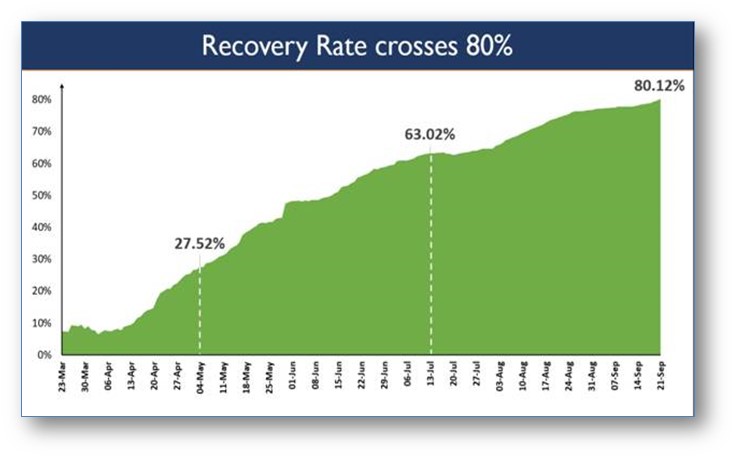
Current COVID19 Situation in India
QUIZ TIME
How many beaches of India recommended for the International eco-label, the Blue flag certification?
- 4
- 2
- 8
- 7
Answer – C
The Indus Water Treaty (IWT) between India and Pakistan was signed on:
- 19 September 1960
- 19 September 1950
- 19 September 1970
- 19 September 1990
Answer – A
Where does Indus river originates from?
- Rohtang pass
- South eastern part of Kashmir
- Bokhar Chu
- None of the above
Answer – C
When International Day of Peace is celebrated?
- 19 September
- 20 September
- 21 September
- 22 September
Answer – C
Foreign Contribution Act is implemented by:
- Ministry of External Affairs
- Ministry of Finance
- NITI Ayog
- Ministry of Home Affairs
Answer – D
Question of the Day
What is Biotech-KISAN Programme?
Answer in next session…







