In Current Affairs for 26 December 2025, we will see the latest national and international current affairs news. These important current affairs will be beneficial for your upcoming NDA, CDS, CDS OTA, AFCAT, TA, Agniveer Army, Agniveer Navy, Agniveer Air Force, Women Military Police, INET, MNS, ACC exams, SCO, PCSL, CAPF, and SSB interviews, and direct entries for Army, Navy, and Air Force like SSC Tech, TGC, JAG, NCC, TES, 10+2 Cadet. Download a PDF file about current events at the end of this article. Let us now see the Current Affairs.
Defence Current Affairs 26 December 2025
India and the global security environment witnessed several significant developments in recent days, ranging from advanced missile trials and internal military policies to strategic assessments by the United States and progress in India’s nuclear deterrence capability. These developments highlight India’s growing defence preparedness amid evolving geopolitical challenges.
Akash-NG Missile Successfully Completes User Trials
The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) has successfully concluded user evaluation trials of the next-generation Akash missile system, commonly known as Akash-NG. This achievement marks a crucial step towards the missile’s induction into the Indian Armed Forces.
During the trials, Akash-NG demonstrated exceptional accuracy against a wide range of aerial threats, including fast-moving targets flying at low altitudes as well as long-range threats operating at high altitudes. The missile successfully intercepted targets under multiple operational scenarios, including near-boundary and extended-range engagements, meeting all prescribed qualitative requirements.
Akash-NG is equipped with an indigenous radio-frequency seeker, a dual-pulse solid rocket motor, and fully indigenous radar and command-and-control systems. These features significantly enhance India’s air defence capability by providing greater precision, flexibility, and self-reliance in critical defence technologies.
Indian Army Restricts Social Media Usage
The Indian Army has introduced a revised policy governing the use of social media platforms by its personnel. Under the new guidelines, soldiers are permitted to access platforms such as Instagram strictly for viewing and monitoring purposes. Posting content, sharing opinions, or commenting is not allowed.
Messaging applications including WhatsApp, Telegram, Skype, and Signal may be used only for exchanging unclassified information of a general nature, and that too with verified contacts. The responsibility of ensuring correct identification of recipients lies entirely with the user. The policy aims to prevent inadvertent leakage of sensitive information while allowing personnel to stay informed about national and global events.
During the Chanakya Defence Dialogue, Army Chief General Upendra Dwivedi emphasised the importance of responsible smartphone usage, highlighting the need to differentiate between impulsive reactions and well-considered responses in the digital domain.
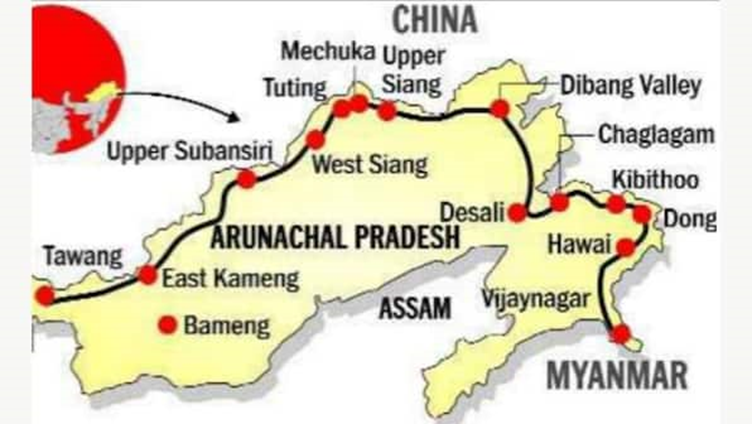
US Report Flags China’s Interest in Arunachal Pradesh
The latest annual report by the United States Department of Defence on China’s military capabilities has drawn attention to Beijing’s expanding territorial ambitions. The report identifies Arunachal Pradesh as a “core interest” for China, placing it on par with Taiwan and disputed regions in the South and East China Seas.
According to the assessment, China’s People’s Liberation Army has increased its activities along the Line of Actual Control, particularly in the eastern sector covering Sikkim and Arunachal Pradesh. Despite partial disengagements at friction points such as Depsang and Demchok, both Indian and Chinese forces remain forward-deployed along the LAC.
India has significantly strengthened its defences in Arunachal Pradesh, especially in the strategically critical Tawang sector. High troop density, artillery deployments, and integrated weapon systems ensure robust preparedness against potential threats.
The report also highlights China’s rapid military modernisation, including a sharp expansion of its nuclear arsenal, which is expected to cross 1,000 warheads by 2030. Additionally, China plans to expand its naval power by adding multiple aircraft carriers in the coming years. Of particular concern to India is China’s sustained military support to Pakistan, aimed at balancing India’s strategic focus in South Asia.
K-4 Missile Test Enhances India’s Nuclear Deterrence
India’s sea-based nuclear deterrence received a major boost following the reported test launch of the K-4 submarine-launched ballistic missile from INS Arighat, conducted off the coast of Visakhapatnam. Although the Ministry of Defence did not issue an official confirmation, such tests are traditionally kept confidential.
The K-4 missile, with a range of around 3,500 kilometres, represents a significant upgrade over the earlier K-15 missile, which had a much shorter range. INS Arighat, India’s second nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarine, was commissioned in August 2024 and operates under the Strategic Forces Command.
Submarine-launched ballistic missiles are designed to withstand immense underwater pressure, making them heavier and structurally stronger than land-based missiles. The successful testing of the K-4 strengthens India’s second-strike capability, ensuring credible deterrence against potential adversaries.
Conclusion
These developments collectively underscore India’s commitment to strengthening its defence capabilities while maintaining strategic stability. From advancements in indigenous missile technology and responsible digital conduct within the armed forces to heightened vigilance along contested borders and enhanced nuclear deterrence, India continues to adapt proactively to a complex and evolving security landscape.
Review Questions
MCQ 1
Which organisation successfully conducted the user evaluation trials of the Akash-NG missile system?
A. Indian Air Force
B. Ministry of Defence
C. Defence Research and Development Organisation
D. Strategic Forces Command
✅ Correct Answer: C. Defence Research and Development Organisation
MCQ 2
Akash-NG missile system is equipped with which type of seeker?
A. Infrared seeker
B. Laser-guided seeker
C. Indigenous RF seeker
D. Electro-optical seeker
✅ Correct Answer: C. Indigenous RF seeker
MCQ 3
Which feature of Akash-NG provides enhanced propulsion and performance?
A. Liquid-fuel engine
B. Ramjet engine
C. Dual-pulse solid rocket motor
D. Turbojet engine
✅ Correct Answer: C. Dual-pulse solid rocket motor
MCQ 4
According to the Indian Army’s new social media policy, personnel are allowed to use platforms like Instagram primarily for:
A. Posting official updates
B. Commenting on national issues
C. Viewing and monitoring only
D. Interacting with civilians
✅ Correct Answer: C. Viewing and monitoring only
MCQ 5
Which messaging platforms are permitted for exchanging unclassified information with known persons?
A. Facebook and Twitter
B. Skype, WhatsApp, Telegram and Signal
C. Instagram and Snapchat
D. YouTube and LinkedIn
✅ Correct Answer: B. Skype, WhatsApp, Telegram and Signal
MCQ 6
The US Department of Defence report equated China’s interest in Arunachal Pradesh with which other issue?
A. Hong Kong
B. Tibet
C. Taiwan
D. Xinjiang
✅ Correct Answer: C. Taiwan
MCQ 7
Which sector of Arunachal Pradesh is described as strategically vital and heavily fortified by India?
A. Bomdila sector
B. Walong sector
C. Tawang sector
D. Along sector
✅ Correct Answer: C. Tawang sector
MCQ 8
By 2030, China’s nuclear warhead stockpile is projected to exceed approximately:
A. 500 warheads
B. 800 warheads
C. 1,000 warheads
D. 1,500 warheads
✅ Correct Answer: C. 1,000 warheads
MCQ 9
The K-4 submarine-launched ballistic missile was reportedly tested from which submarine?
A. INS Arihant
B. INS Chakra
C. INS Arighat
D. INS Kalvari
✅ Correct Answer: C. INS Arighat
MCQ 10
Which missile has been made operationally obsolete for true deterrence after the successful K-4 launch?
A. Agni-III
B. Pralay
C. K-15 (BO-5)
D. BrahMos
✅ Correct Answer: C. K-15 (BO-5)
ALSO READ:
- Latest Daily Current Affairs and Defence Updates
- Latest Daily Current Affairs November 2025[DOWNLOAD PDF]
- Latest Daily Current Affairs October 2025[DOWNLOAD PDF]
- Latest Daily Current Affairs August 2025[DOWNLOAD PDF]
- Latest Daily Current Affairs July 2025[DOWNLOAD PDF]
- Monthly Defence Current Affairs June 2025 [DOWNLOAD PDF]
- Monthly Defence Current Affairs May 2025 [DOWNLOAD PDF]
- Monthly Defence Current Affairs April 2025 [DOWNLOAD PDF]
- Monthly Defence Current Affairs March 2025 [DOWNLOAD PDF]
- Monthly Defence Current Affairs February 2025 [DOWNLOAD PDF]
- Monthly Defence Current Affairs January 2025 [DOWNLOAD PDF]
- Defence Current Affairs Year End Review 2024
- Monthly Defence Current Affairs November 2024 [DOWNLOAD PDF]
- Monthly Defence Current Affairs October 2024 [DOWNLOAD PDF]
- Monthly Defence Current Affairs September 2024 [DOWNLOAD PDF]
- Monthly Defence Current Affairs August 2024 [DOWNLOAD PDF]
- Monthly Defence Current Affairs July 2024 [DOWNLOAD PDF]
- Monthly Defence Current Affairs June 2024 [DOWNLOAD PDF]