The objective type question paper includes various topics of elementary mathematics. Candidates should have posses knowledge about these topics. There are lots of topics to cover which are as following:
- Arithmetic: Aspirants need to perform well in arithmetic which includes Number System, Fundamental Operations, Unitary Methods, and Elementary Number Theorems etc.
- Algebra: The applicants should able to solve basic operations, Remainder Theorem, Quadratic Equations, Linear equations and practical problems etc.
- Geometry: The candidates should able to answer geometric questions which contain Lines and angles, plane and plane figures and their related questions.
- Trigonometry: The applicants need to know the values of Sine x, cosine x and tangent x.
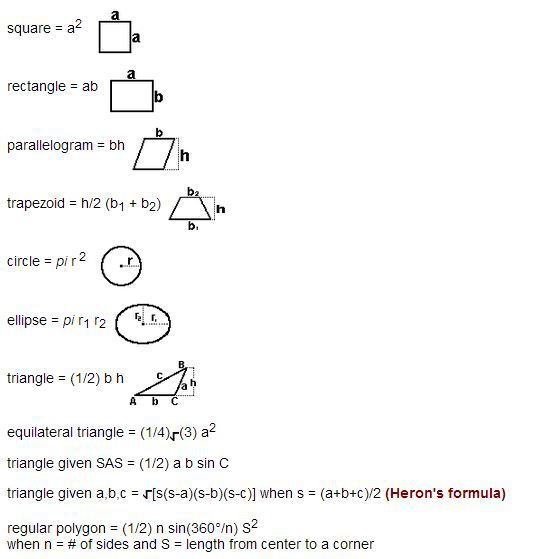
- Mensuration: The all candidates applying for the test should have knowledge of calculating areas of squares, rectangles, triangles, circles and parallelograms etc.
- Statistics: Everyone needs to know the collection and tabulation of data, histograms, pie and bar charts etc.
CDS Exam Coaching IMA NA
Elementary Mathematics CDS Exam Preparation Tips

Number System:
- Positive integers 1, 2, 3, 4, … are called natural numbers. Smallest natural number is 1 and there is no largest natural number. The set of natural numbers N is infinite.
- All natural numbers together with zero are whole numbers. 0 is the smallest whole number. The set of whole numbers W is infinite.
- Set of natural numbers is a subset of set of whole numbers, 0 being the exception
- Even numbers are divisible by 2 and the set of even numbers E includes 0. E={0, 2, 4, 6, …}.
- Odd numbers are not exactly divisible by 2. O = {1, 3, 5, 7….}
- Prime numbers are natural numbers having exact two distinct factors i.e. 1 and the number itself (2, 3, 5, 7, 11…). 2 is the smallest prime number.
- Natural numbers having more than 2 factors are called composite number. E.g. 4, 6, 8, 9, 10, …
- 1 is neither prime nor composite. All even numbers except 2 are composite.
- Co-prime or relatively prime numbers are two natural numbers that may not be prime numbers and that have only 1 as common factor. E.g. 8 and 9, 15 and 16, 26 and 33.
- Pairs of prime numbers which have only one composite number between them are called twin primes. E.g. 3,5; 5,7; 11,13
- The numbers which can be expressed in the form of p/q, where p and q are integers and q is not 0, are called rational number. The set of rational numbers is denoted by Q.
- A number which cannot be expressed as terminating nor a non-terminating repeating decimal is called an irrational number.
- A pure recurring decimal is a decimal in which all the digits after the decimal point are repeated. Mixed recurring decimal is a decimal in which at least one digit after the decimal point is not repeated.
- Short cut method for converting pure recurring decimal to a rational number. Write the repeated digit or digits only once in the numerator and take as many nines in the denominator as there are repeating digits in the given number. For example, 0.33333 = 3/9 = 1/3 or 0.387387387 = 387/999
- Short cut method for converting mixed recurring decimal to a rational number. Form a fraction in which the numerator is the difference between the number formed by all the digits after the decimal point taking the repeating digits only once and that formed by the digits which are not repeated and the denominator is the number formed by as many nines as there are repeated digits followed by as many zeros as there are non-repeated digits. e.g. 0.74353535 = 7435-74 / 9900 = 7361/9900 or 0.1272727 = 127 1/990 = 7/55
Best books for CDS exam preparation
- Important formulas for CDS Exam Mathematics: Make list on important formulas, theorems and tips when preparing for mathematics it will help you in last minute revision. Below given are few important formulas that you can add in your list:-
Geometry:
- Equal chords of circle subtends equal angle at center and vice versa. If AB =CD in figure then
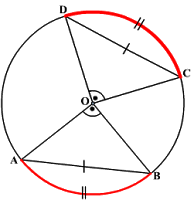
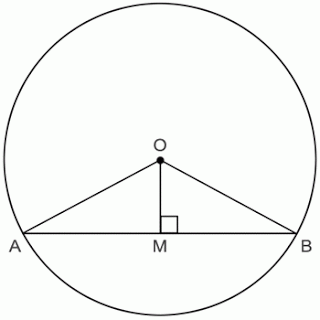
- Perpendicular from the center of the circle to a chord bisects the chord. If
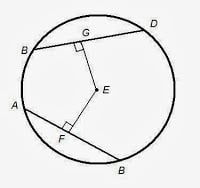
- Equal chords of the circle are equidistant from Center. If AB=BD then GE=EF
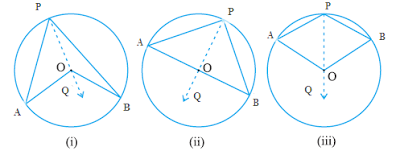
- The angle subtended by an arc at the center is double the angle subtended by it at any point on the remaining part of the circle. In each case
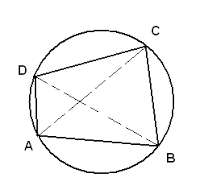
- The sum of the either pair of opposite angles of cyclic quadrilateral is 180.a quadrilateral is cyclic if all the four vertices of it lie on a circle. Here
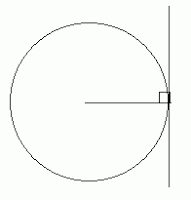
- The tangent at any point of a circle is perpendicular to the radius through the point of contact.
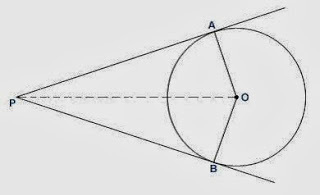
- The lengths of the tangents drawn from external point on circle are equal. Here PA=PB
Speed Distance and Time
- Speed = Distance/Time, Time = Distance/Speed, Distance = Speed * Time
- Km/hr to m/sec conversion: x Km/hr = [x * (5/18)] m/sec
- m/sec to Km/hr conversion: x m/sec = [x*(18/5)] Km/hr
- Suppose a man covers a certain distance at x Km/hr and equal at y Km/hr then, the average speed during the whole journey is [2xy/(x+y)] Km/hr
CDSE Train Problems Tips
- Time taken by a train of length l metres to pass a pole or standing man or a signal post is equal to the time taken by the train to cover l metres.
- Time taken by a train of length l metres to pass a stationery object of length b metres is the time taken by the train to cover (l + b) metres.
- Suppose two trains or two objects bodies are moving in the same direction at u m/s and v m/s, where u > v, then their relative speed is = (u – v) m/s.
- Suppose two trains or two objects bodies are moving in opposite directions at u m/s and v m/s, then their relative speed is = (u + v) m/s.
- If two trains of length a metres and b metres are moving in opposite directions at u m/s and v m/s, then, the time taken by the trains to cross each other = (a+b)/(u + v) sec.
- If two trains of length a metres and b metres are moving in the same direction at u m/s and v m/s, then, the time taken by the faster train to cross the slower train = (a + b)/(u – v) sec.
CDSE Boat and Stream Formula
- Downstream/Upstream: In water, the direction along the stream is called downstream. And, the direction against the stream is called upstream.
- If the speed of a boat in still water is u km/hr and the speed of the stream is v km/hr, then: Speed downstream = (u + v) km/hr. Speed upstream = (u – v) km/hr.
- If the speed downstream is a km/hr and the speed upstream is b km/hr, then: Speed in still water = ½ (a + b) km/hr; Rate of stream = ½ (a – b) km/hr.
Math Formula For Area
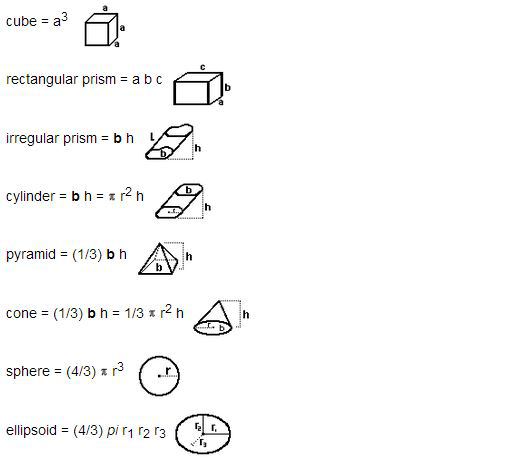
Math Formula For Volume
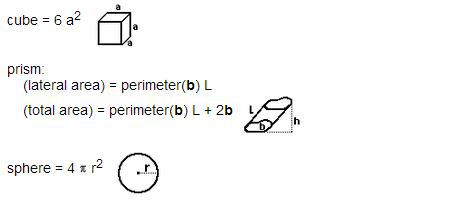
Math Formula For Surface Area
Algebra
- (a + b)(a – b) = (a2 – b2)
- (a + b)2 = (a2 + b2 + 2ab)
- (a – b)2 = (a2 + b2 – 2ab)
- (a + b + c)2 = a2 + b2 + c2 + 2(ab + bc + ca)
- (a3 + b3) = (a + b)(a2 – ab + b2)
- (a3 – b3) = (a – b)(a2 + ab + b2)
- (a3 + b3 + c3 – 3abc) = (a + b + c)(a2 + b2 + c2 – ab – bc – ac)