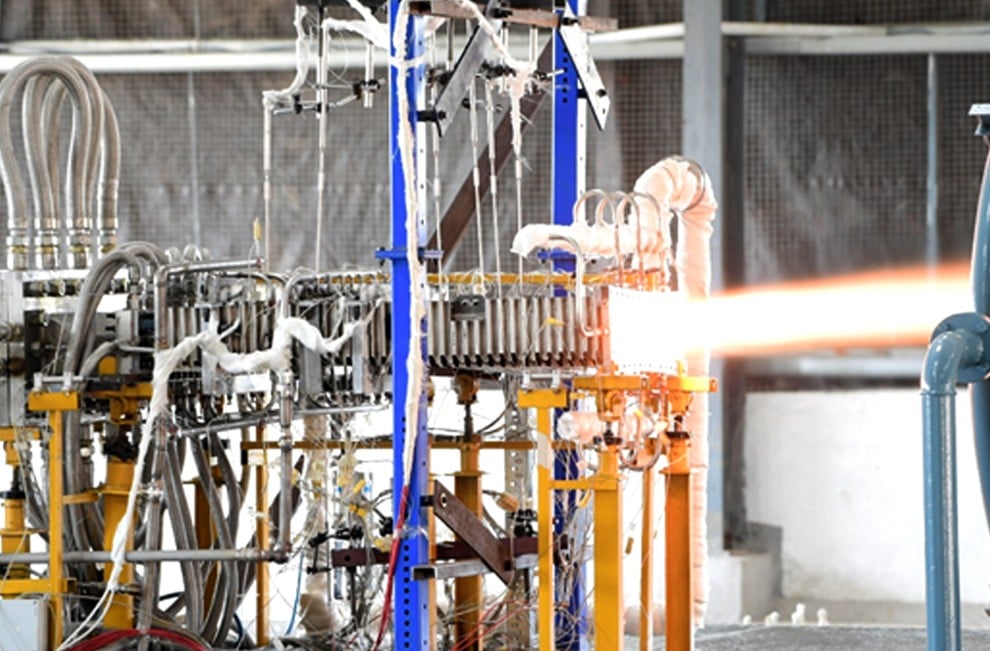
India has successfully completed an extensive ground test of its Actively Cooled Scramjet Full-Scale Combustor, a crucial component for future hypersonic cruise missile systems. The initiative was executed by the Defence Research & Development Laboratory (DRDL) located in Hyderabad, serving as a key part of the country’s Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
The test was conducted at the Scramjet Connect Pipe Test (SCPT) Facility, lasting over 12 minutes, during which the performance and design integrity of the full-scale combustor were thoroughly validated. Both the combustor and the SCPT facility were developed by DRDL, with significant contributions from various industry partners.
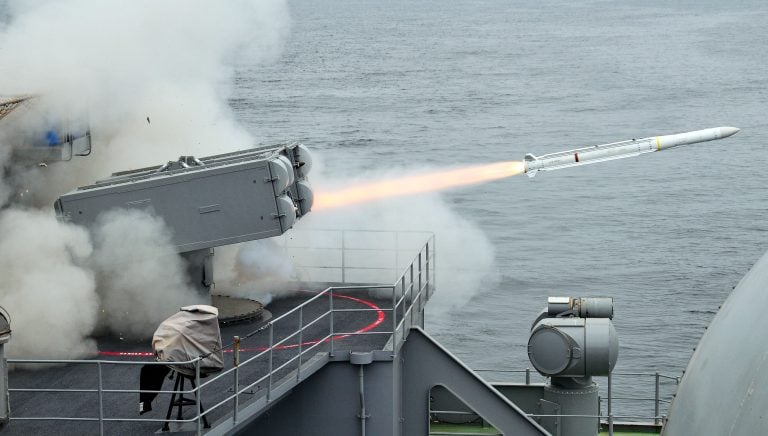
The Indian defense ministry emphasized that the recent test signifies a substantial advancement in the nation’s hypersonic missile development program. This initiative aims to create missiles capable of enduring flight at speeds exceeding Mach 5 (approximately 6,100 kilometers or 3,800 miles per hour), utilizing an air-breathing scramjet engine. This engine type supports supersonic combustion, thereby facilitating long-duration flight while enhancing overall performance.
India views hypersonic technology as an essential means to establish a rapid, low-flying, and highly maneuverable strike capability, which is inherently more challenging to detect and track compared to traditional ballistic missiles. To further this objective, India has been engaged in a series of flight and ground tests over the past few years.
These recent trials are an extension of prior undertakings, including an approved launch last June of a new hypersonic missile with a remarkable capacity to reach speeds of Mach 8 (around 9,875 kilometers or 6,140 miles per hour). This missile, known as the Extended Trajectory Long Duration Hypersonic Cruise Missile, boasts a range of about 1,500 kilometers (932 miles) and operates on an air-breathing scramjet engine that utilizes atmospheric oxygen to maintain its high-speed flight.
The inaugural flight test of an Indian hypersonic missile occurred in late 2024, originating from Abdul Kalam Island, situated off the east coast of India in the Bay of Bengal. As India progresses in its hypersonic capabilities, defense experts are closely monitoring developments that could significantly alter the strategic landscape of the region.