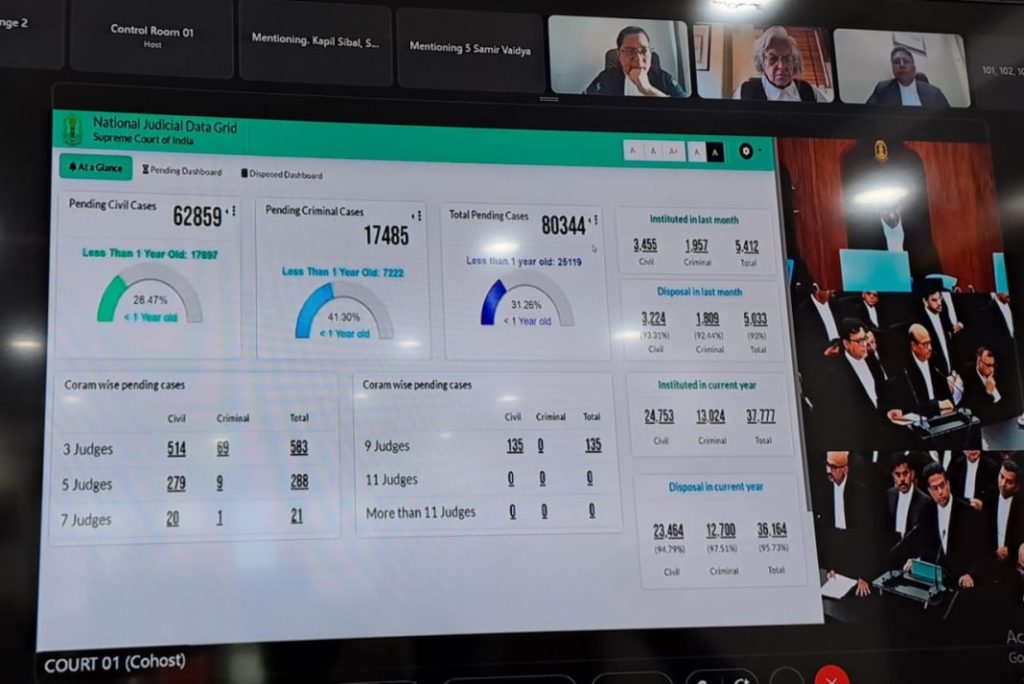
The Chief Justice of India (CJI) has declared a significant integration, announcing that the Supreme Court of India will now be part of the National Judicial Data Grid platform. This platform is recognized for offering a comprehensive tracking system for case backlogs. According to CJI, this move is set to usher in a new era of transparency and accountability in the judiciary.
Describing this monumental integration, CJI DY Chandrachud stated, “Today marks a landmark moment. This exceptional platform, a collaborative effort by the NIC and the in-house team of the Supreme Court, now ensures that with just a simple click, individuals can access real-time data on case backlogs, segregated by years, and gain insights into the overall pendency of both registered and unregistered cases. Furthermore, it allows a breakdown view of cases decided based on quorums.”
Why in News?
- The National Judicial Data Grid (NJDG) has recently become a focal point due to its transformative role in modernizing the management of judicial proceedings within India.
Understanding the National Judicial Data Grid (NJDG):
- About the NJDG:
- The NJDG serves as an expansive online platform database, housing orders, judgments, and specifics of cases from 18,735 District & Subordinate Courts as well as High Courts.
- The platform was initiated under the eCourts Project.
- It continually updates data nearly in real-time, sourced from the connected District and Taluka courts.
- NJDG encapsulates judicial proceedings and decisions from all computerized district and subordinate courts across India.
- Additionally, all High Courts have integrated with the NJDG, ensuring that the general public involved in litigations can access it seamlessly.
- Key Features:
- Integration with National Data Sharing and Accessibility Policy (NDSAP): NJDG adheres to the NDSAP by offering an Open Application Programming Interface (API) to both Central & State Governments.
- The API furnishes streamlined access to NJDG data through specifically assigned departmental IDs and access keys.
- Initially designed for institutional litigants, there are forthcoming plans to broaden the access to non-institutional litigants.
Why is the NJDG Critical?
- Case Management: NJDG serves as a pivotal tool in tracking, managing, and subsequently reducing case backlogs.
- Policy Development: It offers timely insights, enabling policy decisions aimed at curtailing delays in case resolutions, thereby aiding in trimming down case pendency.
- Performance Monitoring: The platform enhances the monitoring of court performance and pinpoints systemic issues, establishing itself as an indispensable resource management utility.
- Specialized Tracking: Addressing a common area of dispute, the Land Records data from 26 States have been synchronized with NJDG for efficient tracking of land-related cases.
International Acclaim for NJDG:
- The World Bank (WB) highlighted the NJDG in its Ease of Doing Business report for 2018. The NJDG was particularly applauded for generating case management reports that are instrumental in enforcing contracts.
- Such international commendations underscore the pivotal role of NJDG in elevating the business landscape in India.
National Judicial Data Grid SSB Interview Questions
- What is the primary purpose of the National Judicial Data Grid (NJDG)?
- a) To store music and videos.
- b) To provide a platform for online gaming.
- c) To maintain a database of orders, judgments, and case details of courts.
- d) To create online teaching modules for judiciary training.
Answer: c) To maintain a database of orders, judgments, and case details of courts.
- Which technology is used by the eCourts services platform to allow litigants to access case status information?
- a) Blockchain
- b) Quantum computing
- c) Elastic search technology
- d) Holographic technology
Answer: c) Elastic search technology
- As of the date mentioned in the data, how many orders/judgments can litigants access through the eCourts services platform?
- a) Over 18.75 crore orders
- b) Over 22.56 crore orders
- c) Over 23.58 crore orders
- d) Over 20.00 crore orders
Answer: b) Over 22.56 crore orders
- Which tool helps in the reduction of case pendency, monitoring of court performance, and identifying systemic bottlenecks?
- a) eCourts platform
- b) NJDG
- c) National Data Sharing and Accessibility Policy
- d) World Bank portal
Answer: b) NJDG
- For which year did the World Bank praise the National Judicial Data Grid in the Ease of Doing Business report?
- a) 2015
- b) 2018
- c) 2020
- d) 2022
Answer: b) 2018
- Under the National Data Sharing and Accessibility Policy (NDSAP), what has been provided to the Central & State Government to allow them to access the NJDG data?
- a) Open Internet Access
- b) Open Application Programming Interface (API)
- c) Direct Database Login
- d) Special Password
Answer: b) Open Application Programming Interface (API)
- The Land Records data of how many States have been linked with NJDG to track cases related to land disputes?
- a) 15 States
- b) 22 States
- c) 26 States
- d) 30 States
Answer: c) 26 States
- Which of the following services are provided by NJDG?
- a) Access to the age of the case and its relevant State and District.
- b) Updating weather forecasts.
- c) Providing online shopping facilities for court merchandise.
- d) Music and video streaming.
Answer: a) Access to the age of the case and its relevant State and District.
- Who can currently access the NJDG data using the Open API as announced by the NDSAP?
- a) Only institutional litigants.
- b) Both institutional and non-institutional litigants.
- c) Only non-institutional litigants.
- d) General public without any restrictions.
Answer: a) Only institutional litigants.
- Which institution recognized the National Judicial Data Grid for making it easier to enforce contracts?
- a) United Nations
- b) International Monetary Fund
- c) World Trade Organization
- d) World Bank
Answer: d) World Bank