53rd Goods and Services Tax (GST) Council met in Delhi under the Chairpersonship of Nirmala Sitharaman, Union Minister for Finance and Corporate Affairs. The council recommended taxes on items such as milk cans and solar cookers and announced some relief for students living in certain kinds of rented accommodation.
53rd GST Council Meeting
Why In News
- 53rd Goods and Services Tax (GST) Council met in Delhi under the Chairpersonship of Nirmala Sitharaman, Union Minister for Finance and Corporate Affairs. The council recommended taxes on items such as milk cans and solar cookers and announced some relief for students living in certain kinds of rented accommodation.
- The Chief Ministers of Goa and Meghalaya, Deputy Chief Ministers of Bihar, Haryana, Madhya Pradesh, and Odisha, and the Finance Ministers of States & UTs (with legislature) were also at the meeting. Here’s how the body functions and why it matters.
What Is The GST Council
- The GST regime came into force after the Constitutional (122nd Amendment) Bill was passed by both Houses of Parliament in 2016. More than 15 Indian states then ratified it in their state Assemblies, after which then-President Pranab Mukherjee gave his assent. It came into effect in 2017 and was billed as an attempt to simplify the existing tax structure in India, where both the Centre and states levied multiple taxes, and to make it uniform.
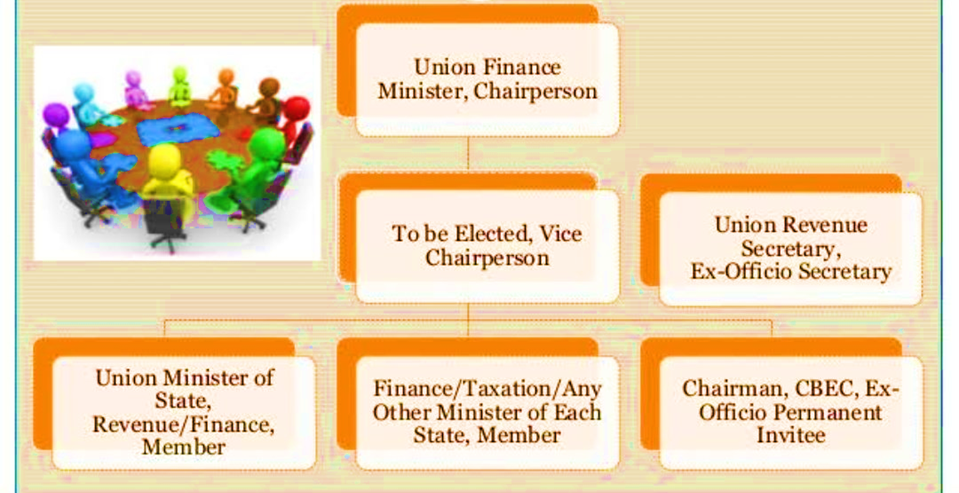
- The President set up the GST Council as a joint forum of the Centre and the states, under Article 279A (1) of the amended Constitution.
- It said that members of the Council include the Union Finance Minister (chairperson), and the Union Minister of State (Finance) from the Centre. Each state can nominate a minister in charge, of finance or taxation or any other minister, as a member.
Why Was The GST Council Set Up
- According to Article 279, the council is meant to “make recommendations to the Union and the states on important issues related to GST, like the goods and services that may be subjected or exempted from GST, model GST Laws”.
- It also decides on various rate slabs of GST, whether they need to be modified for certain product categories, and so on.
Changes in GST rates of Goods:
- Aircraft Parts and Tools: 5% IGST on imports of parts, components, testing equipment, tools and tool-kits of aircrafts.
- Milk Cans: 12% GST on all steel, iron, and aluminium milk cans.
- Carton Boxes: GST on cartons, boxes, and cases of paper reduced from 18% to 12%.
- Solar Cookers: 12% GST on all solar cookers whether single or dual energy source
- Poultry Machinery Parts: 12% GST on parts of poultry keeping machinery.
- Sprinklers: 12% GST on all types of sprinklers, including fire water sprinklers.
Exemptions
- Defence Imports: IGST exemption on specified defence items extended until 30th June, 2029.
- RAMA Programme Imports: IGST exemption on research equipment/buoys under RAMA programme.
- SEZ Imports: Compensation Cess exemption on imports by SEZ units/developers since 01.07.2017.
Service Exemptions:
- The council also proposed critical adjustments concerning services.
- Certain Indian Railways services and intra-railway supplies have been exempted, such as services like platform tickets, retiring rooms, cloak rooms, battery-operated car services, and intra-railway transactions.
- Accommodation Services: Accommodation services exemptions for relief to students and working professionals. Accommodation up to Rs 20,000/month per person for stays of 90+ days have been exempted.
- SPV Services: SPV services to Indian Railway and maintenance services provided by Indian Railways to SPVs have been exempted.
Other Recommendations:
- Interest and Penalties: Waive interest and penalties for Section 73 demand notices for FY 2017-18, 2018-19, 2019-20 if full tax is paid by 31.03.2025.
- Input Tax Credit (ITC): Time limit for ITC on invoices/debit notes under Section 16(4) for FY 2017-18 to 2020-21 deemed as 30.11.2021 for returns filed by this date.
- Monetary Limits For GST Appeals: Monetary limits for department appeals: Rs 20 lakh (GST Appellate Tribunal), Rs 1 crore (High Court), Rs 2 crore (Supreme Court).
- Aadhaar Authentication: The GST Council recommended nationwide implementation of biometric-based Aadhaar authentication for GST registration applicants in phases. This aims to enhance registration integrity, curb fraudulent input tax credit claims via fake invoices.