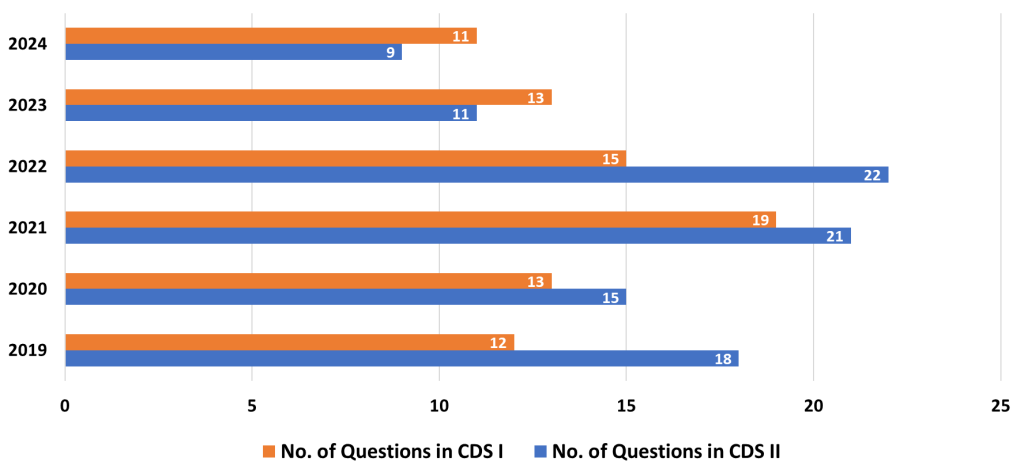
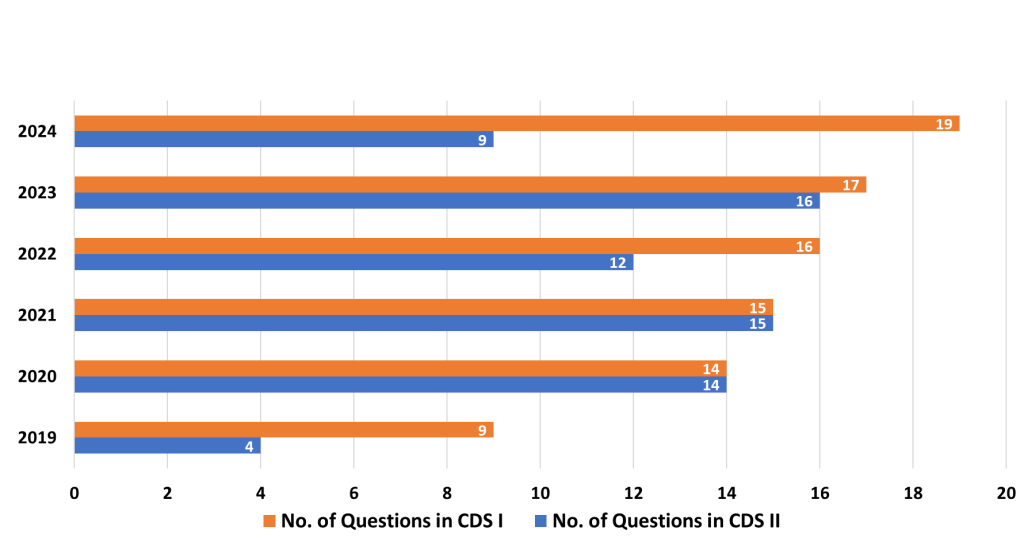
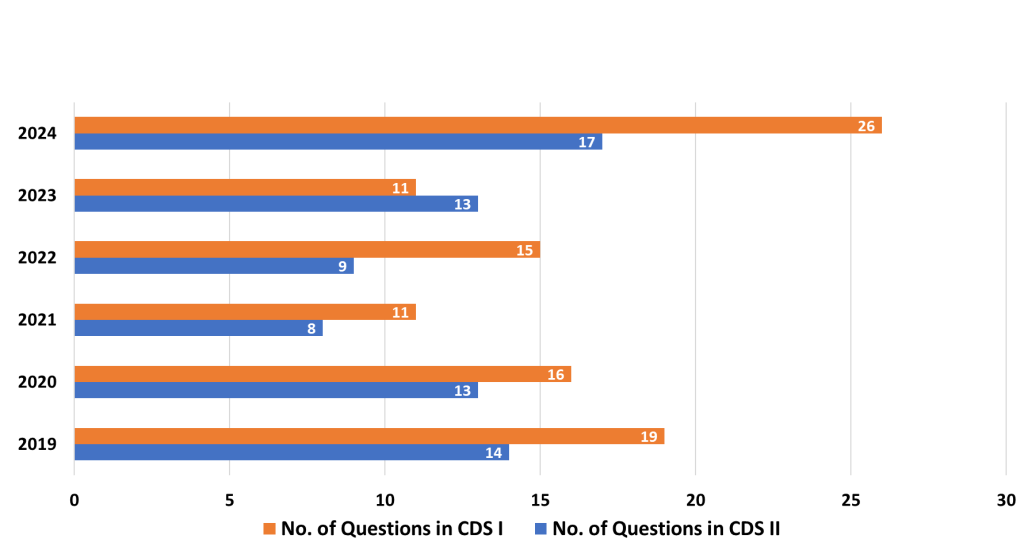
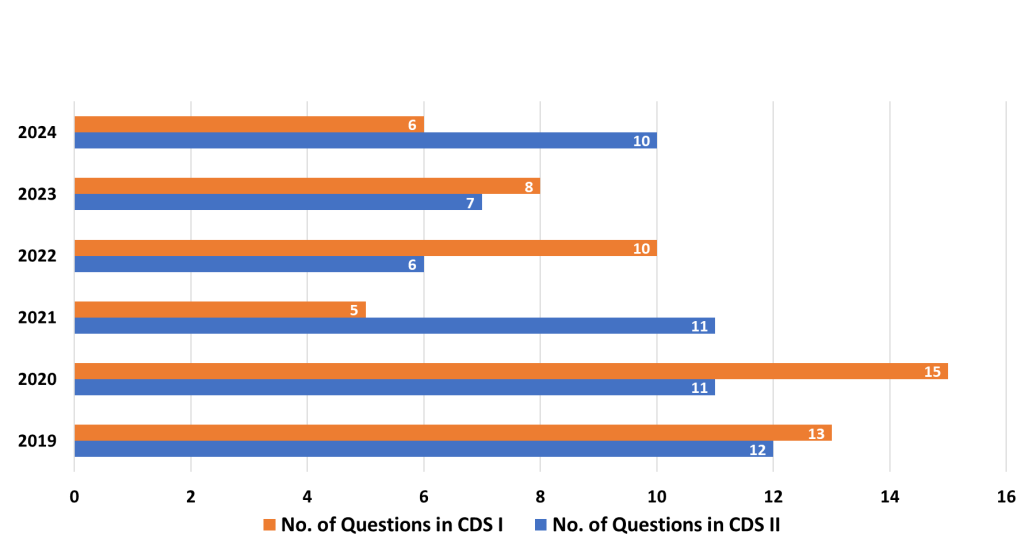
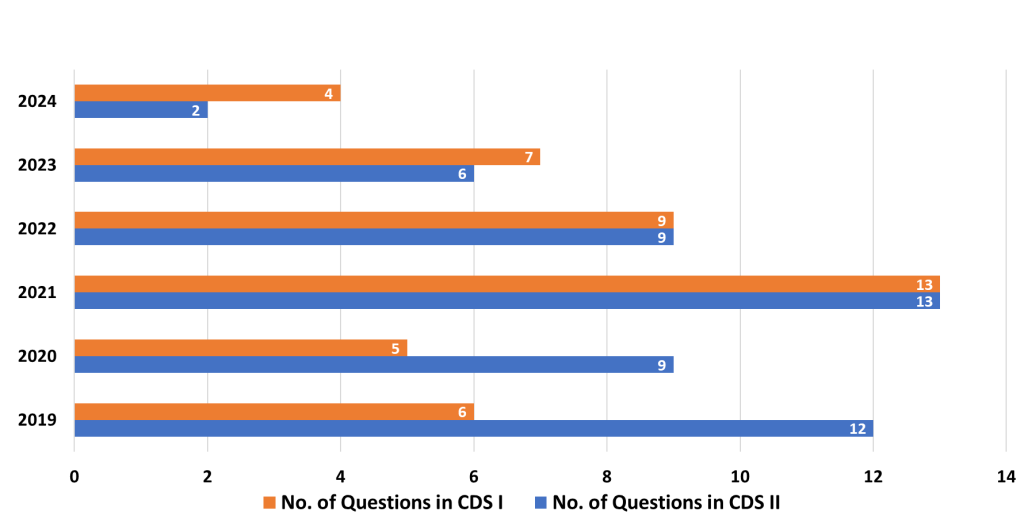
The Elementary Maths Paper of the Combined Defence Services (CDS) exam tests candidates on a range of topics that cover high school mathematics. These questions require a good understanding of basic concepts, quick problem-solving skills, and accuracy. Below is a detailed analysis of the important topics, medium-weightage topics, and the least-weightage topics, along with strategies to approach each of them effectively.
Most Important Topics
1. Algebra
- Analysis: Algebra plays a crucial role in the CDS exam, with a significant number of questions focused on simplifying expressions, solving equations, and understanding inequalities. Candidates may face problems involving polynomials, quadratic equations, or linear equations with one or more variables.
- Strategy: Focus on mastering the manipulation of algebraic expressions and equations. Practice solving equations under time pressure and work on simplifying expressions efficiently. Understanding the relationship between different variables is crucial to answering these questions quickly and accurately.
2. Trigonometry
- Analysis: Trigonometry involves the study of angles and relationships between sides of triangles. The CDS exam frequently tests your ability to apply trigonometric ratios, identities, and angles to solve both theoretical and practical problems. Questions often relate to heights, distances, and angle measurements.
- Strategy: Develop a strong conceptual understanding of trigonometric functions and their applications. Practice applying trigonometric concepts to real-world problems, especially height and distance questions. Regular practice with trigonometric identities and angle transformations is essential.
3. Number System
- Analysis: The Number System forms the foundation for many mathematical topics and appears regularly in the exam. This topic includes questions on factors, multiples, divisibility, prime numbers, and integers. The clarity of these basic concepts can help solve various complex problems.
- Strategy: Strengthen your understanding of prime numbers, divisibility rules, and properties of numbers. Being able to quickly identify patterns and relationships in numbers will be helpful. Practice problems involving least common multiples (LCM) and greatest common divisors (GCD) to build confidence.
4. Geometry
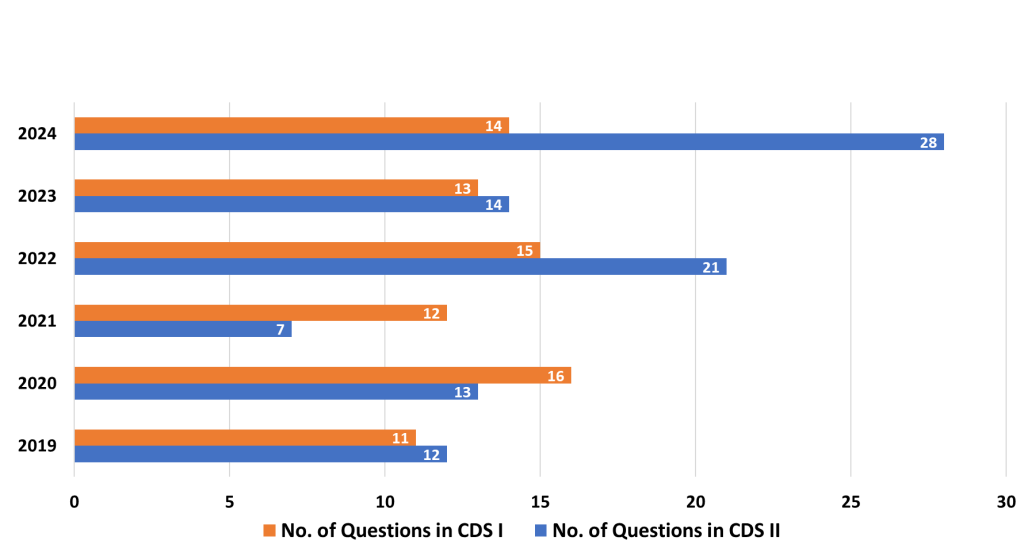
- Analysis: Geometry involves understanding the properties and relationships of points, lines, angles, shapes, and figures. The CDS exam tests knowledge of angles, triangles, circles, quadrilaterals, and coordinate geometry. Questions often require both theoretical knowledge and practical application.
- Strategy: Develop a deep understanding of basic geometric concepts like angles, congruence, similarity, and properties of polygons. Visualization skills are important to solving geometry questions quickly. Focus on problems involving construction and measurement, as well as coordinate geometry applications.
5. Mensuration (2D)
- Analysis: Mensuration in 2D focuses on calculating areas and perimeters of different geometric shapes like triangles, rectangles, circles, and polygons. The ability to visualize and quickly compute dimensions is tested.
- Strategy: Practice solving a variety of problems related to the area and perimeter of 2D shapes. Focus on understanding the properties of regular and irregular polygons. Accuracy is important, as small errors in calculation can lead to incorrect answers.
Medium Weightage Topics
6. Mensuration (3D)
- Analysis: 3D mensuration problems require calculating volumes, surface areas, and lateral surface areas of solid figures like cylinders, cones, spheres, and cubes. These questions are often more complex than 2D mensuration problems due to the additional dimensions.
- Strategy: Practice visualizing 3D objects and understanding their properties. Focus on memorizing important concepts related to surface area and volume and apply them to real-world problems. Be prepared to solve questions that combine multiple shapes or require converting units of measurement.
7. Statistics
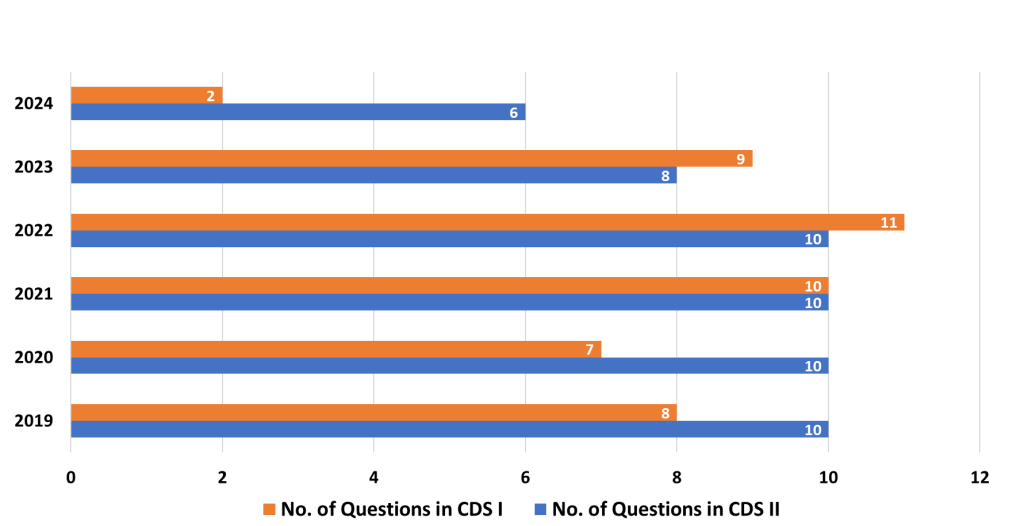
- Analysis: Statistical problems involve understanding and analyzing data, with questions commonly focused on measures of central tendency (mean, median, mode) and data interpretation. These questions test your ability to analyze numerical data and draw conclusions.
- Strategy: Practice calculating averages, and focus on reading and interpreting graphs, charts, and tables. Work on solving word problems related to statistics that require understanding trends or relationships between data sets.
8. Speed, Distance, and Time
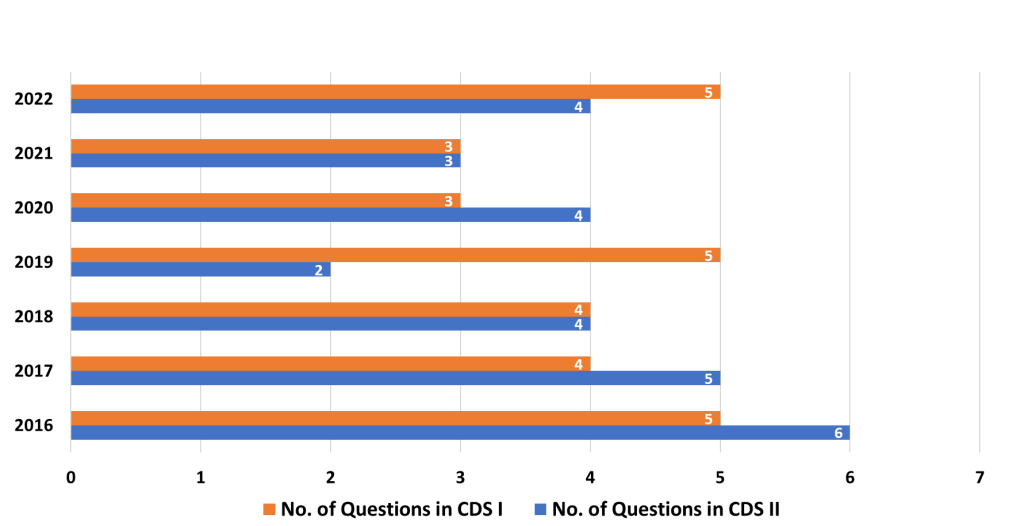
- Analysis: This topic requires applying logical reasoning and basic math to solve problems related to motion, speed, distance, and time. Common variations include relative speed, average speed, and problems with trains or boats.
- Strategy: Break down complex problems into simple components and practice solving questions step-by-step. Focus on understanding the relationship between time, distance, and speed under different scenarios. This will help solve problems efficiently.
Least Weightage Topics
9. Set Theory
- Analysis: Set Theory deals with the collection of objects or numbers and the relationships between them. CDS exam questions on this topic are generally straightforward, requiring basic operations like union, intersection, and complement.
10. Logarithms
- Analysis: Logarithmic functions are typically not heavily tested, but understanding their properties is essential for certain algebraic problems. Questions usually involve simplifying logarithmic expressions or solving for unknowns.
11. Average
- Analysis: Average, or arithmetic mean, is a simple but important concept that appears less frequently in the CDS exam. Questions usually revolve around calculating averages for given sets of numbers or quantities.
12. Percentage
- Analysis: Percentage problems, while not a major focus of the exam, appear occasionally, often in combination with profit, loss, or simple interest calculations. These questions test your ability to convert numbers into percentages and vice versa.
General Preparation Strategies for CDS Maths Paper
- Understand the Exam Pattern: Knowing the type of questions asked and the relative weightage of different topics will help you prioritize your preparation. Focus more on topics like Algebra, Trigonometry, and Geometry, while also preparing adequately for medium and lower weightage topics.
- Build Strong Foundations: The CDS Elementary Maths paper tests fundamental concepts. Make sure you have a solid understanding of basic mathematical principles, which will help you tackle more complex problems.
- Practice Time Management: The CDS exam is time-bound, so managing your time during preparation and in the exam is crucial. Focus on improving your problem-solving speed without compromising accuracy. Practice with mock tests and timed exercises to enhance your time management skills.
- Use Shortcuts and Tricks: Once you are comfortable with the basic concepts, learn shortcuts and tricks to solve problems faster. This is particularly useful for topics like mensuration, algebra, and geometry where lengthy calculations can slow you down.
- Revise Regularly: Consistent revision is essential to retain the concepts and formulas you’ve learned. Dedicate time to revise both high and medium-weightage topics regularly. This will ensure you can recall key concepts quickly during the exam.
- Analyze Past Papers: Reviewing previous years’ question papers helps you understand the type of questions that are likely to appear in the exam. It also gives you insight into which topics are frequently tested and which ones are less common.
- Focus on Accuracy: While speed is important, accuracy should not be compromised. Practice problems carefully and aim to avoid careless mistakes. Solving questions with precision will help you score higher.
Conclusion
By following these strategies and focusing on key topics, candidates can improve their performance in the Elementary Maths Paper of the CDS exam. Regular practice, combined with strong conceptual understanding, is the key to success in this exam.