DSRV Complex Inaugurated at Visakhapatnam under ENC
- Deep Submergence Rescue Vehicle (DSRV) Complex is inaugurated at Visakhapatnam by Vice Admiral Atul Kumar Jain FOC-in-C of Eastern Naval Command.
- The Complex accommodates newly inducted DSRV in a Rescue-Ready state.
Russia to unveil new version of Pantsir AAGM (Anti-Aircraft Gun Missile) during massive military parade in Moscow
- President Vladimir Putin ordered the military to hold the previously postponed Victory Day parade on June 24 as Russia appeared to stabilize its coronavirus outbreak. Russia plans to unveil its new advanced version of the “infamous” Pantsir anti-aircraft gun-missile (AAGM) system during the upcoming massive military parade in Moscow’s Red Square.
- For the first time will be demonstrating the upgraded Pantsir short-range air defense (SHORAD) system, called the Pantsir-S1M.
- The Pantsir-S1M air defense system is based on the Kamaz-53958 Typhoon chassis and equipped with a new radar and advanced infrared electro-optical target tracking system. It is designed to provide protection against fixed- and rotary-wing combat aircraft, unmanned aerial vehicles, and high-precision weapons, including anti-ship and cruise missiles.
- Also stated that the upgraded version of the air defense missile and artillery system Pantsir-S1M has acquired the ability to effectively hit all types of drones. The upgrade work was carried out on the basis of experience gained during the Syrian and Libyan conflicts. The new missile’s range has been increased to 30 kilometres.
- The new variant can launch a new high-speed two-stage missile with extended range and improved target interception characteristics, as well as the baseline 57E6 two-stage missile. Both missiles use a two-stage setup with a detachable boost stage and a passive second stage that lacks a sustainer. Instead it relies on kinetic energy imparted by the booster to reach its target.
- The Russian Armed Forces are looking more advanced and cost-effectivity air defense system to replace “troubled” Pantsir (SA-22 according to the NATO designation) anti-aircraft defense system.
U.S. Air Force F-22 Raptors intercepts Russian Tu-95 bombers
- The U.S. Air Force F-22 Raptor stealth fighters intercepted Russian Tu-95 bombers entering the Alaskan Air Defense Identification Zone early this morning, according to North American Aerospace Defense Command.
- The first formation consisted of two Tu-95 bombers, accompanied by two Su-35 fighter jets and an A-50 airborne early warning and control aircraft, which came within 20 nautical miles of Alaskan shores.
Ukraine plans to buy three divisions of Neptune coastal missile system
- The Armed Forces of Ukraine has plan to buy three divisions of RK-360MC Neptune coastal defense system with R-360 cruise missiles.
- The R-360 missile weighs 870 kg; the weight of its warhead is 150 kg; its launch range is up to 280 km and speed is about 900 km/h. It is able to get at a height of from 3 m to 10 m above the surface. The complex can simultaneously launch up to 24 missiles, i.e. a full salvo of 6 launchers, with an interval of launches in a salvo being from 3 to 5 seconds.
- If successful, Neptune would be a key technical and symbolic milestone in Ukraine’s missile development program. At the same time, the Neptune project is an apt illustration of the complex challenges and uncertainties awaiting Kyiv on the path to military modernization.
U.S. Navy and Army orders additional Centaur unmanned ground vehicles
- FLIR Systems, Inc., a world-leading industrial technology company focused on intelligent sensing solutions, announced that the U.S. Army and Navy have ordered in total more than 160 of the company’s Centaur unmanned ground vehicles (UGV), plus related spares and accessories.
- On Tuesday, the company press release said that the two contracts, totalling $23.5 million, are being sourced through the Army’s Man Transportable Robotic System Increment II (MTRS Inc II) program.
- Centaur is a medium-sized UGV that provides a standoff capability to detect, confirm, identify, and dispose of hazards. Weighing roughly 160 pounds, the open-architecture robot features an advanced EO/IR camera suite, a manipulator arm that reaches over six feet, and the ability to climb stairs. Modular payloads can be used for CBRNE detection and other missions.
- Since March, FLIR has announced orders totalling more than $65 million for nearly 500 Centaur UGVs from the United States Air Force, Marine Corps, and now Navy. Explosive Ordnance Disposal (EOD) teams will use the FLIR Centaur to assist in disarming improvised explosive devices, unexploded ordnance, and similar hazardous tasks. Operators can quickly attach different sensors and payloads to the robot to support other functions, including chemical, biological, radiological, and nuclear (CBRN) missions.
LAC row – China reaches accord with India
- China said on Wednesday it had “reached agreement” with India on the ongoing tensions along the Line of Actual Control (LAC), a day after India announced troops from both sides had begun a “partial disengagement” from some of the stand-off points.
- The Chinese Foreign Ministry said both sides had agreed to handle the situation “properly” and “in line with the agreement” to ease the situation, but did not provide specific details on some of the stand-off points, such as Pangong Lake, where Chinese troops are still present on India’s side of the LAC.
- The Chinese Foreign Ministry did not provide specifics on the sites of conflict. It only referred to the western section, which was the focus of Saturday’s talks, although a stand-off is also continuing at Naku La in Sikkim in the eastern section.
Army plans to expand roles for elite special and airborne forces known for surgical strikes
- The Army is reviewing the selection process of its personnel volunteering for the elite special forces and airborne battalions, which are known for conducting cross-border surgical strikes and other covert operations, to expand their role in multiple operational theatres.
- Top defence sources said it is being proposed that there should be a centralised training-based selection process of volunteers at the Special Forces Training School (SFTS) at Nahan in Himachal Pradesh. The school may also shift to Bakloh in the same state.
- Currently, this rigorous training-based selection process, called probation, is conducted by different units of the Parachute Regiment.
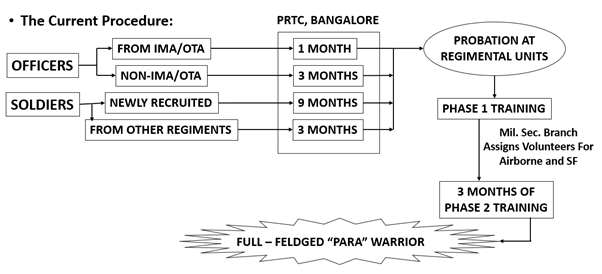
What is the current procedure?
- Officers who volunteer first go to the Parachute Regimental Training Centre (PRTC) in Bengaluru and are subsequently sent to the Parachute Regiment units for the probation period. However, other ranks directly go to the units for the probation.
- No one organisation conducts the probation, instead it is handled by the special forces unit taking in the volunteers.
- Each SF unit prides itself in certain traditions and ethos, the probation is to ensure that the soldier is mentally adapted to these and willing to accept them.
- Officers who volunteer directly from the Army training academies — such as the Indian Military Academy in Dehradun and the Officers Training Academy in Chennai — or after a few years of service undergo an initial month-long training at the PRTC in Bengaluru.
- The Military Secretary’s Branch assigns volunteers to airborne or special forces units during the phase 1 probation based on a battalion’s officer strength.
- On clearing phase 1, officers move to the phase 2 of probation for three months.
- In case of jawans, new recruits go to the PRTC and undergo the entire process. Those who volunteer from other regiments directly go to the units they are detailed for and undergo the three-month probation there.
- The Parachute Regiment units are allotted by infantry directorate based on deficiencies.
- Most Army personnel volunteer for the special forces within the first two years of their career.
What is the new proposal?
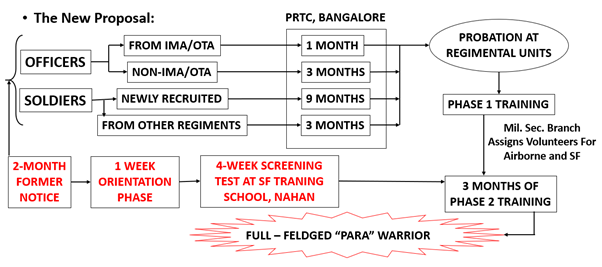
- The Army has proposed that volunteers for the special forces and the Parachute Regiment be given a two-month notice before the selection process begins, after which a week-long preparatory phase of orientation will take place.
- Once the orientation is done, the first phase of training will include a four-week selection and screening process at Special Forces Training School.
- After screening, they will be allotted to Parachute or special forces battalions through a board of officers.
- Once allotted a battalion, volunteers will undergo phase 2 of probation — three months of training in basic skills. This will be different for special forces and airborne volunteers.
- Subsequently, the selected group will go through a third level of training, which will include four weeks of the para basic course at the Parachute Training School in Agra.
- The proposal says four courses can be held throughout the year — in March, June, September, and December — with a maximum of 500 volunteers per course, including officers.
Why now?
- According to sources, the current selection to the Parachute Regiment is conducted by the units in line with their operational requirements based on fixed theatres.
- So if a person is selected for operating in the deserts, he usually continues to operate in that theatre. But with changing operational requirements, each special force unit may be needed to perform its role in more than one theatre.
- There is a requirement to multitask and also work in conjunction with other special forces units, and thus the need to expand the spectrum of training.
- Each soldier, after his probation, should expect and be prepared for operations in any terrain and operational environment.
- The new system will standardise the selection and training procedures.
- A need to revisit the selection process also arose to address the shortfall of volunteers with the expansion of Parachute Regiment and special forces.
REVIEW QUESTIONS
- FOC-in-C of Eastern Naval Command:
- Vice Admiral Ajit Kumar
- Vice Admiral Anil Kumar Chawla
- Vice Admiral Atul Kumar Jain
- Vice Admiral R B Pandit
ANSWER: C
- Russia plans to unveil its new advanced version of which AAGM system during the upcoming massive military parade in Moscow’s Red Square?
- Pantsir
- Tunguska
- Kashtan
- Krug
ANSWER: A
- Centaur unmanned ground vehicles are manufactured by?
- Rafael Defence
- Boeing Aerospace
- FLIR Systems
- Lockheed Martin
ANSWER: C
- Indian Army plans to expand roles for which forces?
- Air Defence Forces
- Engineer Troops
- Signal Regiments
- Special and Airborne forces
ANSWER: D







