Financial Action Task Force (FATF)
What Is FATF?
- It Is The Global Money Laundering And Terrorist Financing Watchdog. The Inter-governmental Body Sets International Standards That Aim To Prevent These Illegal Activities And The Harm They Cause To Society.
- As A Policy-making Body, The FATF Works To Generate The Necessary Political Will To Bring About National Legislative And Regulatory Reforms In These Areas. With More Than 200 Countries And Jurisdictions Committed To Implementing Them.
- It developed the FATF Standards, to ensure a coordinated global response to prevent organized crime, corruption, and terrorism. They help authorities go after the money of criminals dealing with illegal drugs, human trafficking, and other crimes. Also works to stop funding for weapons of mass destruction.
Establishment Of FATF:
- 1989: The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) Was Established In July 1989 By A Group Of Seven (G-7) Summit In Paris, Initially To Examine And Develop Measures To Combat Money Laundering.
- 2001: In October 2001, The FATF Expanded Its Mandate To Incorporate Efforts To Combat Terrorist Financing, In Addition To Money Laundering.
- 2012: In April 2012, it added efforts to counter the financing of proliferation of weapons of mass destruction.
FATF Members:
- The FATF currently has 39 members including 2 regional organizations – the European Commission and Gulf Cooperation Council.
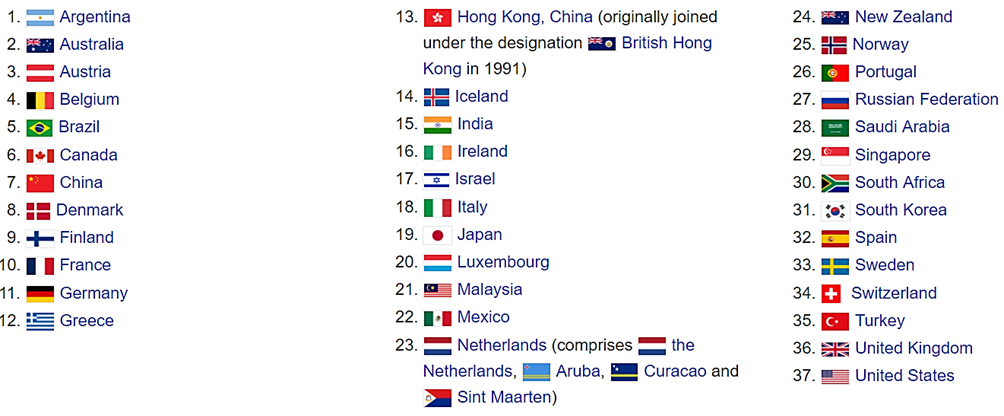
FATF Observers:
- FATF Observers: Indonesia
- Observer Organizations:

FATF President:
- The FATF President Is A Senior Official Appointed By The FATF Plenary From Among Its Members. In April 2019, The Revised Mandate Extended The Terms Of The FATF Presidency To A 2-year Period. The FATF Plenary Is The Decision-making Body Of The FATF. It Meets 3 Times Per Year.
- The term begins on 1 July and ends on 30 June two years after assuming office. The President convenes and chairs the meetings of the FATF Plenary and the Steering Group, and he/she oversees the FATF Secretariat. The President is the principal spokesperson for the FATF and represents the FATF externally.
- Current President:
- Dr. Marcus Pleyer of Germany assumed the position of President of the FATF on 1 July 2020. He succeeded Xiangmin Liu of the People’s Republic of China.
FATF Secretariat:
- The Secretariat Is Located At The OECD Headquarters In Paris. Career Opportunities At The FATF Secretariat Are Advertised And Filled In Accordance With The OECD Procedures. Funding For The FATF Secretariat And Other Services Is Provided By The FATF Annual Budget To Which Members Contribute.
Lists Under FATF:
- Grey List: Countries that are considered a safe haven for supporting terror funding and money laundering are put in the FATF grey list. This inclusion serves as a warning to the country that it may enter the blacklist.
- Consequences of being in the FATF grey list:
- Economic sanctions from IMF, World Bank, ADB
- The problem in getting loans from IMF, World Bank, ADB, and other countries
- Trade sanctions: Reduction in international trade
- International boycott
- Blacklist: Countries known as Non-Cooperative Countries or Territories (NCCTs) are put on the blacklist. These countries support terror funding and money laundering activities. The FATF revises the blacklist regularly, adding or deleting.

Tracing The Landmarks In FATF Journey Till Now:
- Amsterdam, 23-25 June 2010: India became a full member of the FATF, and the mutual evaluations of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, India and Brazil were approved.
- Paris, 15-17 February 2012: FATF approved the new FATF Recommendations, to counter the financing of proliferation of weapons of mass destruction.
- Paris 17-19 October 2012: The Plenary also revised 2 Best Practices Papers and the Reference Guide and Information Note on the use of the FATF Recommendations to support the fight against Corruption.
- London, 24 April 2013: FATF met with Non-Profit Organisations (NPOs) the aim of the meeting was to stress the importance of ensuring that FATF Recommendation 8 on NPOs is not being implemented in a manner that disrupts or discourages legitimate charitable activity.
- Paris, 22 June 2014: FATF in coordination with relevant bodies from the United Nations, organized an Experts Meeting on Targeted Financial Sanctions. Aim to bring together targeted financial sanction experts at the global level, to increase collaboration & coordination between relevant bodies.
- Paris, 16 October 2016: Anti-money laundering/counter-terrorist financing experts and anti-corruption experts came together to discuss transparency and beneficial ownership during a joint FATF and G20 Anti-Corruption Working Group (ACWG) joint Experts Meeting on Corruption on 16 October 2016.
- Paris, 20-22 February 2019: During the second Plenary under the US Presidency of Mr. Marshall Billingslea delegates discussed a range of important issues to protect the integrity of the financial system and contribute to global safety and security.
- Paris, 23 October 2020: During the first Plenary meeting under the German Presidency of Marcus Pleyer, delegates worked through an agenda of key issues, including maintaining FATF work during the COVID-19 Crisis.
- Paris, 21 October 2021: During the three days of this hybrid FATF Plenary, delegates from the Global Network and observer organizations finalized work in several important areas, including updated guidance for a risk-based approach to virtual assets and virtual asset service providers.
India And FATF:
- India became an Observer at FATF in 2006. Since then, it had been working towards full-fledged membership. On June 25, 2010, India was taken in as the 34th country member of FATF.
- The EAG (Eurasian Group) is a regional body comprising 9 countries: India, Russia, China, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, and Belarus.
Pakistan and FATF:
- Pakistan, Which Continues To Remain On The “Grey List” Of FATF, Had Earlier Been Given The Deadline Till June To Ensure Compliance With The 27-point Action Plan Against Terror Funding Networks. It Has Been Under The FATF’s Scanner Since June 2018.
- FATF and its partner the Asia Pacific Group (APG) are reviewing Pakistan’s processes, systems, and weaknesses based on a standard matrix for anti-money laundering (AML) and combating the financing of terrorism (CFT) regime.
REVIEW QUESTIONS
- Full Form Of FATF
- Financial Action Transfer Force
- Financial Action Task Force
- Finance And Telecommunication Foundation
- Finance And Transport Foundation
ANSWER: B
- FATF Was Established In
- 1979
- 1989
- 1999
- 2009
ANSWER: B
- FATF Was Established With Initiative Of
- G6
- G7
- G8
- G20
ANSWER: B
- FATF Was Mandated To Look After Terror Financing In
- 1989
- 1999
- 2001
- 2011
ANSWER: C
- Current Membership Of FATF
- 35
- 39
- 41
- 43
ANSWER: B
- India Became A Member Of FATF In
- 2006
- 2010
- 2011
- 2018
ANSWER: B
- Pakistan Was Grey list In FATF In
- 2010
- 2012
- 2016
- 2018
ANSWER: D
- FATF Secretariat Is Located In
- London
- Paris
- New York
- Brussels
ANSWER: B
- Current President Of FATF
- Dr. Marcus Pleyer
- Xiangmin Liu
- Juan Manuel
- Roger Wilkins
ANSWER: A
- Apart From Iran ___ Is In The Current FATF Blacklist
- South Sudan
- Panama
- North Korea
- Jordan
ANSWER: C
To crack the SSB Interview, You can join our SSB interview live classes batch and we recommend you to Enroll SSB INTERVIEW ONLINE COURSE. Trusted by thousands of defence aspirants.
Also Read:
- What Is Quadrilateral Security Dialogue (QUAD)?
- Difference Between NATO Vs Russia [Expained]
- What Is United Nations Security Council (UNSC) [Explained]
- Everything You Need To Know About SAARC: South Asian Association For Regional Cooperation
- All About Russia Ukraine War: SSB Interview Topic [Fully Explained]







