The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) on Sunday launched its first new rocket the Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV-D1) carrying Earth Observation Satellite (EOS-02) and a student-made satellite-AzaadiSAT from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC) in Andhra Pradesh’s Sriharikota.
ISRO OFFICIAL STATEMENT: SSLV-D1 Rocket Placed Satellites Into The Wrong Orbit, No Longer Usable: ISRO.
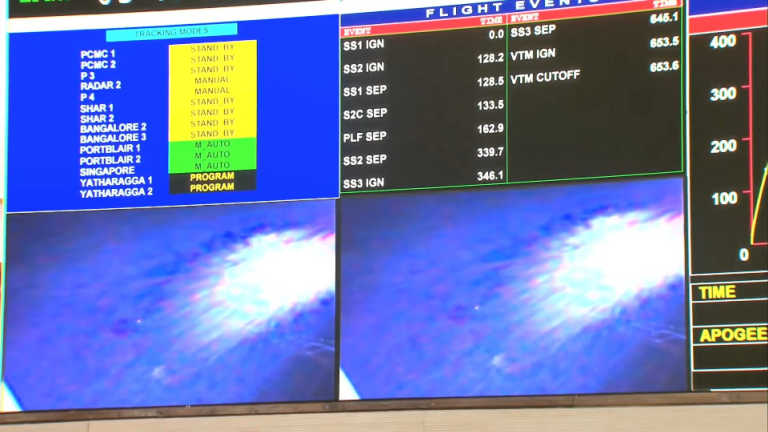
“SSLV-D1/EOS-02 Mission: Maiden flight of SSLV is completed. All stages performed as expected. Data loss is observed during the terminal stage. It is being analysed. Will be updated soon.”
Also Read: Top 7 Rockets Launchers By ISRO [Fully Explained]
To mark the country’s celebrations of “Azaadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav”, the SSLV, co-passenger satellite called “AzaadiSAT” comprising 75 payloads built by 750 students from 75 rural government schools across India was launched on Sunday.
Girls who designed Satelite also witnessed the SSLV-D1 launch.
Also Check: 500+ ISRO Related GK Questions For All Defence Exams And SSB Interviews
The general public also witnessed the launch from the viewing gallery of Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC) in Sriharikota.
Speaking to media, Shreya a student from St Francis Girls High School, Telangana said, “Three groups from our school have participated in this SSLV launch. I am very glad that we got this opportunity. We really worked hard on it and today we will witness the launch of the AzaadiSAT satellite.”
Founder and CEO, science and tech incubator Space Kidz India, Dr Srimathy Kesan said this launch is to mark the 75th year of independence and to bring the focus that girls should be encouraged.
The ground testing of the newly developed solid booster stage (SS1) for the new launch vehicle of ISRO i.e. Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV) was carried out on March 14 2022 at Satish Dhawan Space Centre Sriharikota at 1205 hrs.
All the propulsion parameters during the test are found satisfactory and closely matching with the predictions.

SS1 motor is a three-segmented solid propulsion stage incorporating many new technologies and innovative processes which include a bond-free joint between the segments, high power electromechanical actuator with digital control electronics, optimized ignitor and simultaneous propellant casting of all segments, which have been successfully validated in the ground test.
The successful test of the solid booster stage has given sufficient confidence to proceed with the first developmental flight of SSLV (SSLV-D1) which is scheduled for May 2022. The remaining stages of SSLV i.e. SS2 & SS3 stages have successfully undergone necessary ground tests and are ready for integration.
All About SSLV-D1/EOS-02 Mission
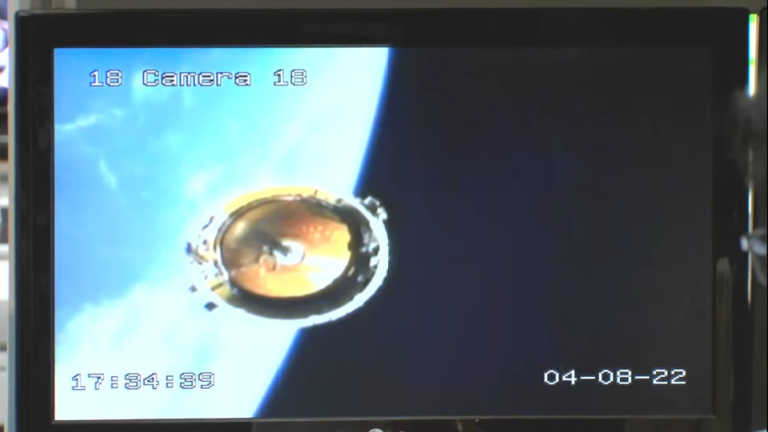
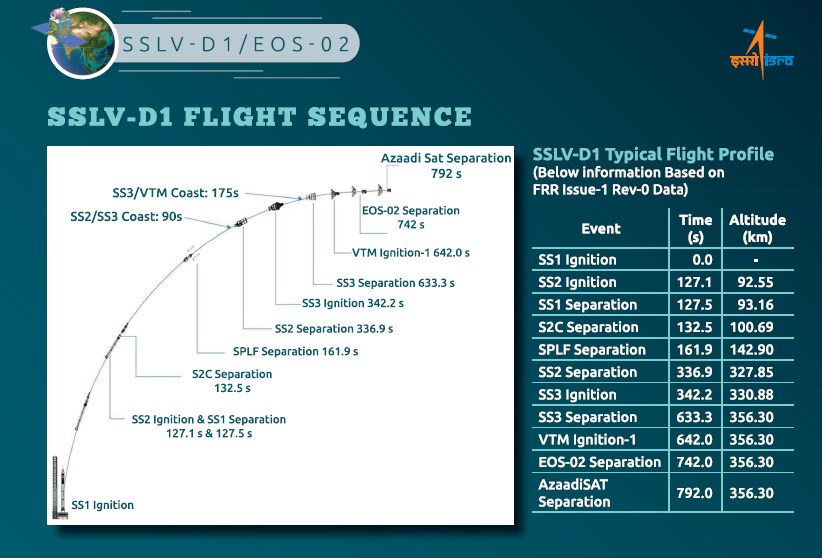
ISRO developed a small satellite launch vehicle (SSLV) to cater the launch of up to 500 kg satellites to Low Earth Orbits on ‘launch-on-demand’ basis. The first developmental flight SSLV-D1/EOS-02 Mission is scheduled for August 7, 2022 at 09:18 am (IST) from the First Launch Pad of Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota. SSLV-D1 mission would launch EOS-02, a 135 kg Satellite, into low earth orbit of about 350 km to the equator, at an inclination of about 37 degrees. The mission also carries AzaadiSAT satellite.
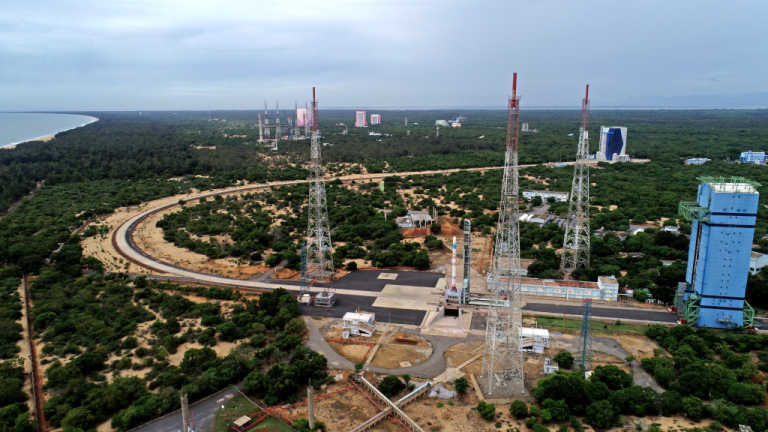
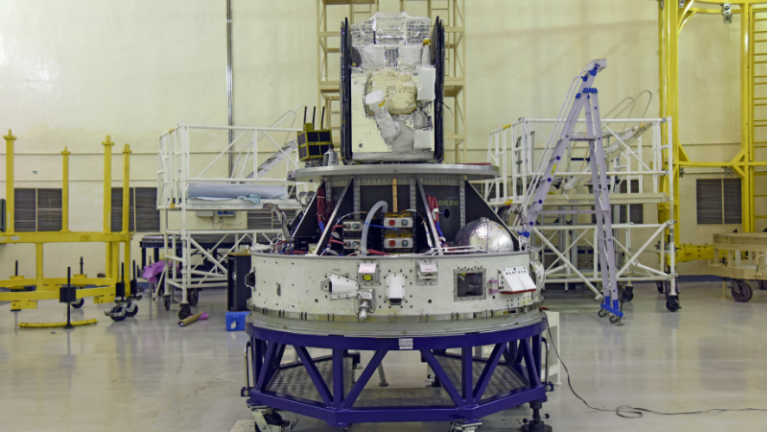



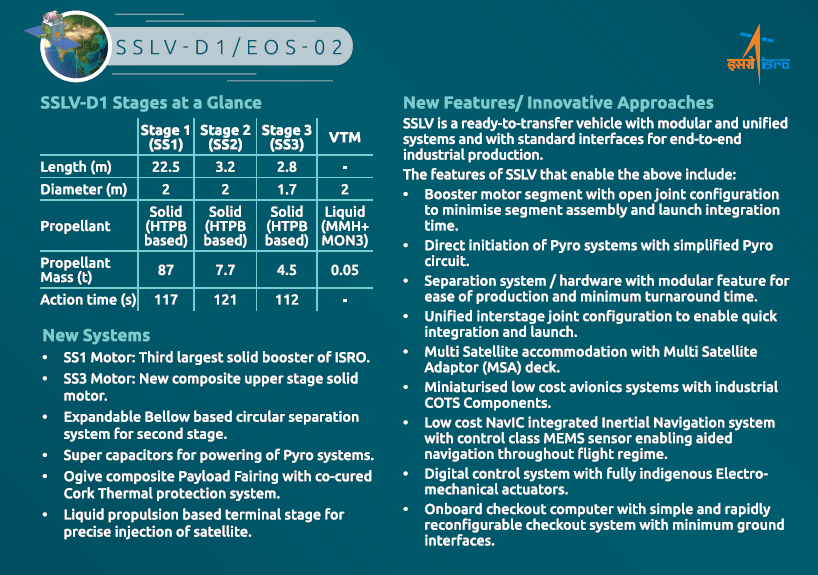
SSLV is configured with three solid stages 87 t, 7.7 t and 4.5 t. The satellite insertion into the intended orbit is achieved through a liquid propulsion-based velocity trimming module. SSLV is capable of launching Mini, Micro, or Nanosatellites (10 to 500 kg mass) to a 500 km planar orbit. SSLV provides low-cost access to Space on demand basis. It offers low turn-around time, flexibility in accommodating multiple satellites, launch-on-demand feasibility, minimal launch infrastructure requirements, etc. SSLV-D1 is a 34 m tall, 2 m diameter vehicle having a lift-off mass of 120 t.
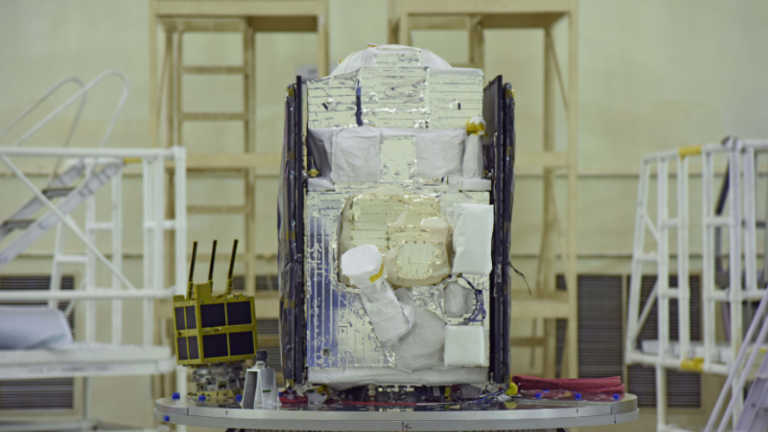
EOS-02 is an earth observation satellite designed and realised by ISRO. This microsat series satellite offers advanced optical remote sensing operating in infra-red band with high spatial resolution. The bus configuration is derived from IMS-1 bus.

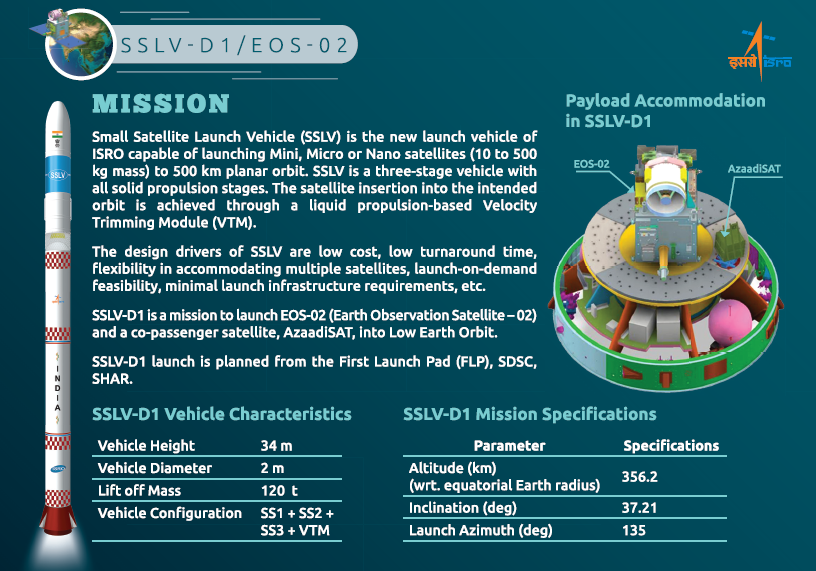


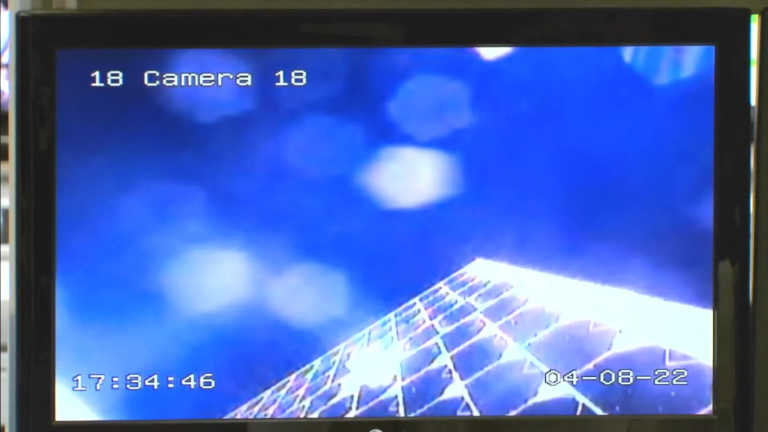
AzaadiSAT is a 8U Cubesat weighing around 8 kg. It carries 75 different payloads each weighing around 50 grams and conducting femto-experiments. Girl students from rural regions across the country were provided guidance to build these payloads. The payloads are integrated by the student team of “Space Kidz India”. The payloads include a UHF-VHF Transponder working in ham radio frequency to enable voice and data transmission for amateur radio operators, a solid state PIN diode-based Radiation counter to measure the ionising radiation in its orbit, a long-range transponder and a selfie camera. The ground system developed by ‘Space Kidz India’ will be utilised for receiving the data from this satellite.
To crack the SSB Interview, You can join our SSB interview live classes batch and we recommend you to Enroll SSB INTERVIEW ONLINE COURSE. Trusted by thousands of defence aspirants.
Also Read:
- 500+ ISRO Related GK Questions For All Defence Exams And SSB Interviews
- Top 7 Rockets Launchers By ISRO [Fully Explained]
- ISRO’s Chandrayaan-3 To Be Launched Into Space During The Third Quarter Of Next Year
- ISRO Successfully Conducts Third Vikas Engine Long Duration Hot Test For Gaganyaan Program
- 14 Inspiring Achievements Of ISRO
- Full List Of Indian Satellites, Launch Vehicles, Spacecrafts, And Dates [UPDATED]
- Full List Of 328 Foreign Satellites Launched By India [UPDATED]








