China asserts sovereignty over the Indian state of Arunachal Pradesh. Why is China acting in this manner? What are its justifications? Let us See the reason behind this.
History of Arunachal Pradesh
Arunachal Pradesh is a state in India’s northeastern region. Arunachal Pradesh’s history may be traced back to prehistoric periods, with signs of human presence extending back to the Neolithic period. The state’s earliest known history dates back to the first millennium BCE, when the territory was populated by numerous tribes such as the Monpa, Adi, Apatani, Mishmi, Nyishi, and others.
These tribes were formed into small separate kingdoms that were frequently at odds with one another. Various kingdoms and empires influenced Arunachal Pradesh during the mediaeval period. The Ahom Kingdom had a significant impact on the history of Assam from the 13th to the 18th centuries after conquering the province in the 16th century. Arunachal Pradesh, which means “Land of the Rising Sun,” is mentioned in ancient Hindu texts such as the Kalika Purana, Mahabharata, and Ramayana.
The British took control of the region in the nineteenth century, and Arunachal Pradesh became a part of the British Raj. The British established a foothold in the region but did not attempt to dominate it directly. Instead, they negotiated contracts with the local rulers to create a buffer zone between British India and Tibet. The Indian government inherited the British policy of non-interference in the region after India attained independence in 1947. The Indian government formed the North East Frontier Agency (NEFA) in 1951, which was in charge of administering the region. In 1972, the NEFA was renamed Arunachal Pradesh and became a union territory.
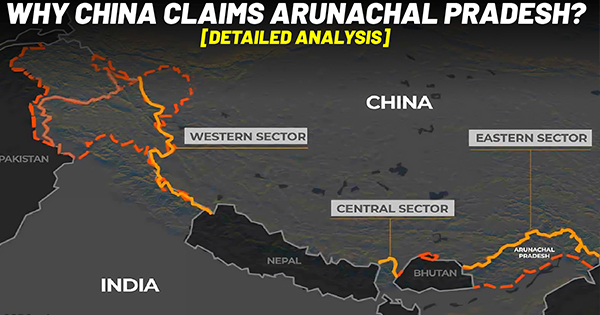
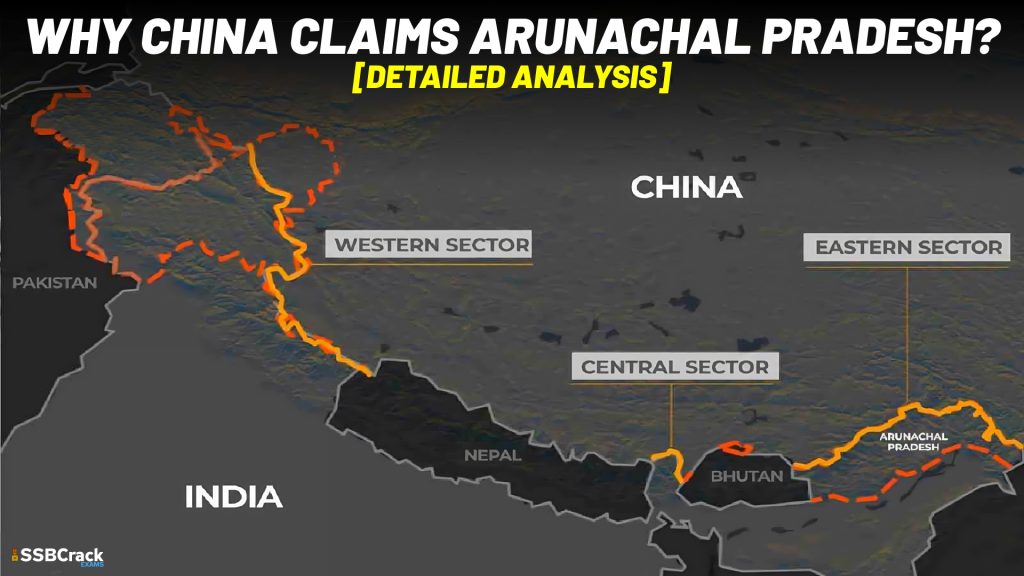
Arunachal Pradesh: Why China Claims it?
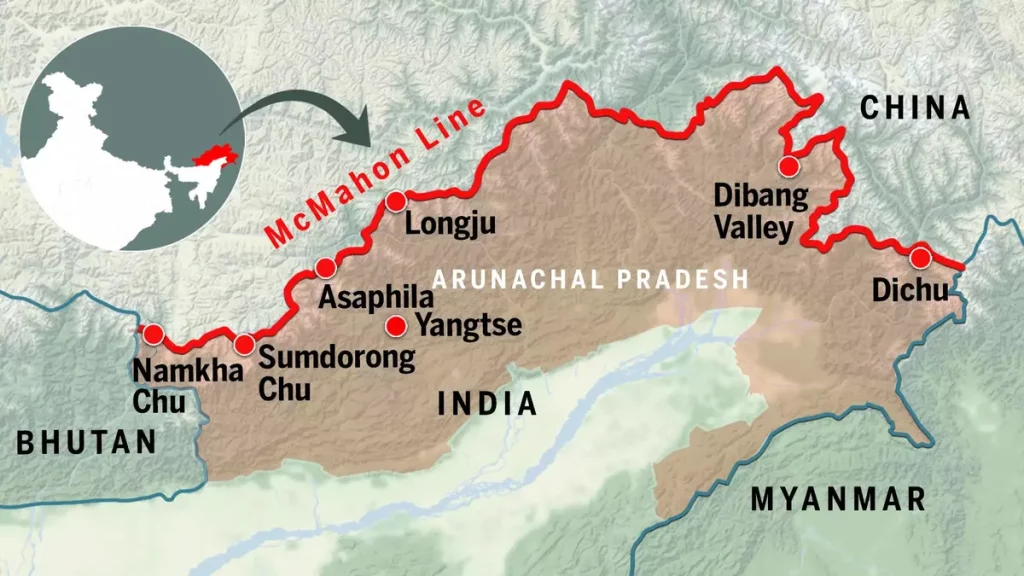
Arunachal Pradesh, or what China refers to as Zangnan, is referred to as “South Tibet” by China, which claims it is a part of its territory. The main reason China claims Arunachal Pradesh is because of its connections to Tibet historically and culturally. An adjacent area of Arunachal Pradesh called Tawang has long had a special place in Tibetan culture. It’s because Urgyeling, a town close to Tawang, is where Tsangyang Gyatso, the Sixth Dalai Lama, was born. Even the 14th Dalai Lama entered Tawang in 1959 to escape China’s occupation of Tibet. Therefore, by claiming Arunachal, China intended to affirm its rule over Tibet. In order to bolster its claim, China routinely distributes fictional maps that show Arunachal as a region of China.
In order to convince India to accept Aksai Chin as Chinese territory, China aims to use its claim to Arunachal Pradesh as a negotiating tool. Beijing valued the Aksai Chin more strategically than the NEFA even during the conflict of 1962. China retained Aksai Chin after the battle but withdrew from NEFA. Arunachal is all about trade with China. India will recognise the NEFA, or presently Arunachal, as Indian territory if Beijing can persuade New Delhi to recognise Aksai Chin as Chinese territory. China’s claims are unfounded, but India has constantly refuted them and maintained that Arunachal Pradesh is a legitimate portion of its sovereignty.
Several Development Projects
Despite being a frontline state of strategic significance, Arunachal Pradesh did not receive adequate attention. The state thus has a number of development obstacles, including weak infrastructure, poor levels of education, and high rates of poverty. Arunachal Pradesh has started a number of development projects to solve these issues.
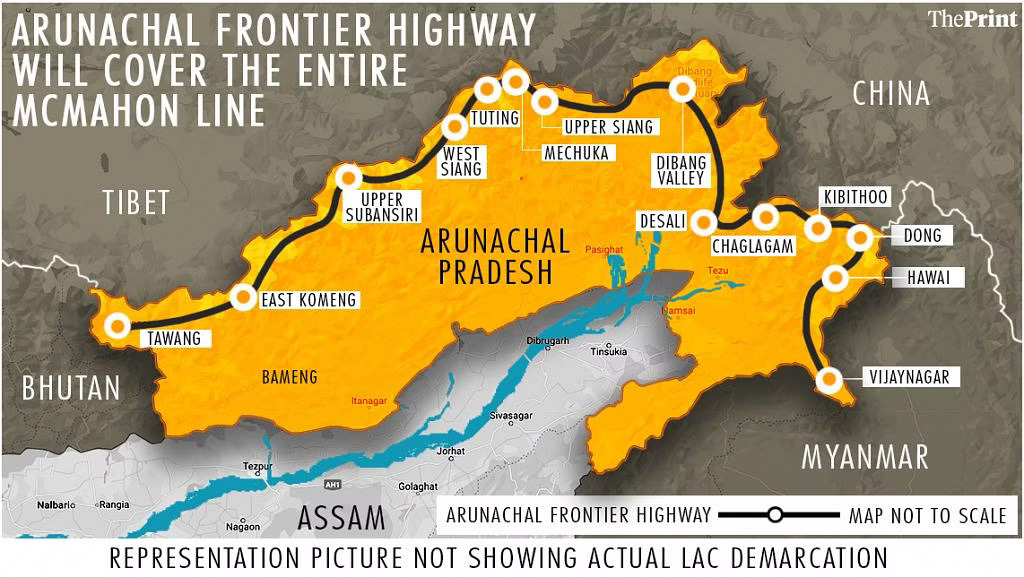
The Government of India approved a 44,000 crore rupee project for Arunachal Pradesh’s 2574 km Frontier route in 2022. This comprises:
- The 1465-kilometer-long two-lane Frontier Highway is worth Rs. 27,349 crore.
- A two-lane inter-connectivity corridor of 1048 km worth 15,720 cr.
- Two-lane Brahmakund (Parshuramkund) to Chowkham is 61 km, worth 915 cr.
This will protect the border between India, China, and Myanmar and manage migration from border regions while enhancing the state’s tourism infrastructure. In Arunachal Pradesh, the 600 MW Kameng Hydro Power Station was officially opened by the government in 2022. Arunachal will become a power-surplus state as a result, greatly enhancing the National Grid. Furthermore, the GOI approved 27 road projects to improve connectivity throughout the state. The Dibang Multipurpose Project in Arunachal, which will be the largest hydropower project ever, was approved by the GOI in 2023. In a year with a 90 per cent reliability, the plant will create 11,223 MU of energy using 2,880 MW (12240 MW) of power.
Along with a number of other electricity and infrastructural initiatives, India also hosted a crucial G20 summit in Arunachal Pradesh. China, which claimed it as its territory, was shocked by this action. Arunachal Pradesh gained international recognition as an Indian territory when the G20 summit took place. From the perspective of Indian interests, this decision turned out to be a stroke of genius. This helped to promote Arunachal Pradesh’s attractiveness to the world, which would further draw tourists and foreign investors. It also affirmed India’s claim to Arunachal Pradesh in the eyes of the international community.
Importance of Arunachal Pradesh For India
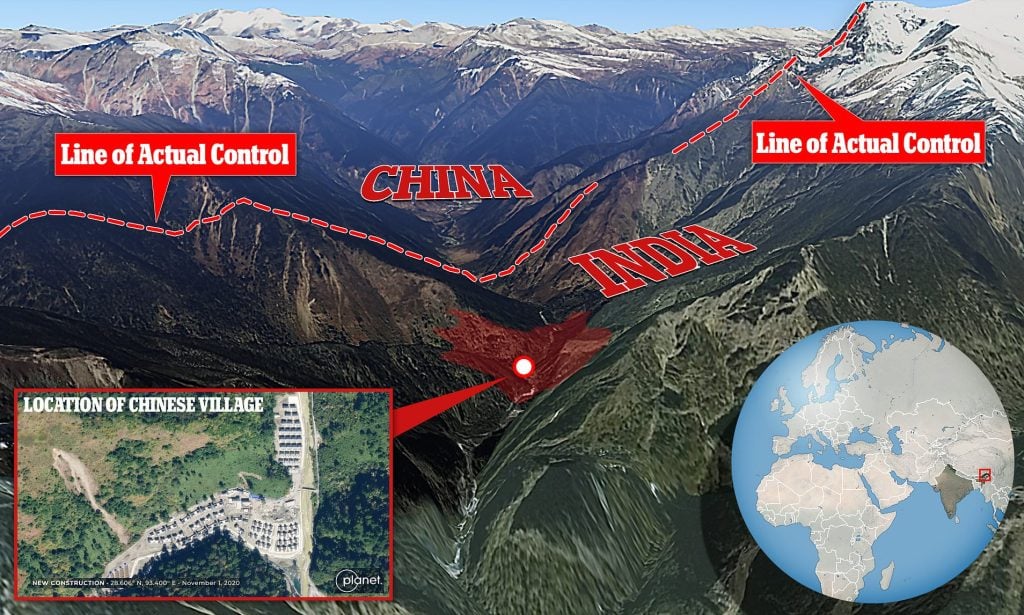
India’s northeastern border state is called Arunachal Pradesh. In the northeastern corner of the nation, it is strategically situated and borders Myanmar, China, and Bhutan. China claims ownership of the entire region of Arunachal Pradesh, which is a contested territory between India and China. As a result, the state becomes a crucial component of India’s military strategy and a national security problem for that country. Arunachal Pradesh has a sizable military presence because of its advantageous position. In the state, the Indian Army has a number of bases and airfields that act as a frontal defence against any potential threat from China or other nearby nations.
At the intersection of Southeast Asia, China, and India, lies the strategically important state of Arunachal Pradesh. This makes it a key part of India’s “Act East” policy, which strives to improve relations with Southeast Asian nations on the political and economic fronts. The state can function as a centre for trade and business between the two regions and acts as a gateway to India’s northeast. Arunachal has a wealth of natural resources, including forests, minerals, and potential for hydropower, in addition to its advantageous location. The natural resources of the area are crucial for India’s economic expansion and development.
In conclusion, because of its border security, natural resources, connectivity, and cultural significance, Arunachal Pradesh is a strategically significant state for India. India is dedicated to protecting its borders, fostering regional economic development, and preserving the region’s cultural legacy since the state’s security and development are essential for the country’s national interests.
To crack the SSB Interview and join the Indian Armed Forces as an Officer, You can join our SSB interview live classes batch and we recommend you to Enroll SSB INTERVIEW ONLINE COURSE. Trusted by thousands of defence aspirants.