In Current Affairs for 02 December 2025, we will see the latest national and international current affairs news. These important current affairs will be beneficial for your upcoming NDA, CDS, CDS OTA, AFCAT, TA, Agniveer Army, Agniveer Navy, Agniveer Air Force, Women Military Police, INET, MNS, ACC exams, SCO, PCSL, CAPF, and SSB interviews, and direct entries for Army, Navy, and Air Force like SSC Tech, TGC, JAG, NCC, TES, 10+2 Cadet. Download a PDF file about current events at the end of this article. Let us now see the Current Affairs.
Defence Current Affairs 02 January 2026
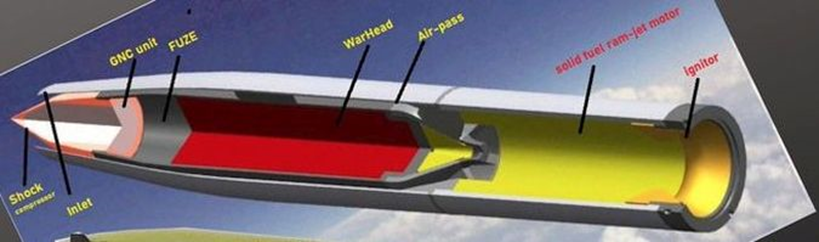
Indian Army Poised to Deploy Ramjet-Powered 155 mm Artillery Shells
The Indian Army is on the verge of achieving a historic breakthrough in artillery warfare by becoming the first military force in the world to operationalise ramjet-assisted 155 mm artillery shells. This cutting-edge development represents a major leap in India’s artillery modernisation and indigenous defence innovation.
Aligned with the national vision of Atmanirbhar Bharat, the project is being developed in collaboration with IIT Madras, leveraging advanced propulsion concepts traditionally used in missile systems. The ramjet-powered shell is expected to enhance the firing range of existing 155 mm artillery ammunition by 30–50 per cent, without compromising destructive capability or accuracy.
Improving reach, precision, and munition effectiveness has been a central objective of the Indian Army’s artillery upgrade programme. As modern battlefields demand longer standoff distances and higher accuracy, the ramjet-assisted shell emerges as a transformational solution that blends missile-grade technology with conventional artillery platforms.
The project is being executed under the aegis of the Army Technology Board (ATB) and has received formal approval, reflecting strong institutional support. Successful trials have already been conducted at the Pokhran Field Firing Ranges in Rajasthan, a key testing site for indigenous weapons.
The Indian Army currently operates a mix of artillery systems, including legacy 130 mm M-46 guns, 122 mm field guns, and 105 mm light artillery. However, the 155 mm calibre, compliant with NATO standards, forms the backbone of modernisation due to its superior range, precision, and interoperability. Artillery roles are broadly categorised by calibre, with light guns (up to 105 mm) supporting infantry at close ranges, while medium guns (106–155 mm) deliver long-range bombardment.
Kalyani Group’s Indigenous Naval Guns to Enter Testing Phase in 2026
India’s push for self-reliance in naval weaponry has gained momentum with Kalyani Strategic Systems Limited (KSSL), a wholly owned subsidiary of Bharat Forge, preparing to begin proof trials of its indigenously designed 76 mm and 30 mm naval guns in 2026.
These systems are fully Indian-origin naval cannons, specifically engineered for maritime environments, marking a departure from land-based artillery adaptations. The 30 mm naval gun is expected to be ready for testing by August 2026, signalling rapid progress.
Bharat Forge has steadily emerged as a global artillery manufacturer. Its recent Letter of Intent with US defence company AM General, signed at IDEX 2025 in Abu Dhabi, marked the first instance of an Indian firm exporting advanced artillery systems to the United States. This agreement reflects international confidence in Kalyani’s artillery expertise, particularly in the 105 mm and 155 mm segments, which have provided the technological foundation for naval variants.
The 30 mm naval cannon draws upon Bharat Forge’s experience with modular turrets for infantry combat vehicles, using the 30×173 mm calibre, a widely adopted NATO standard known for balancing firepower, accuracy, and adaptability in close-range combat.
DRDO Successfully Tests Pralay Tactical Ballistic Missile
India’s missile development programme achieved another major milestone with the successful salvo user trials of the Pralay tactical short-range ballistic missile, conducted by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
The trials took place on 31 December 2025 at the Integrated Test Range (ITR), Chandipur, Odisha. Two canisterised missiles were launched in rapid succession from the same launcher, validating the system’s reliability and operational readiness for salvo firing—an essential capability for modern battlefield scenarios.
Pralay is a solid-fuel, quasi-ballistic missile weighing approximately five tonnes, capable of delivering a one-tonne payload up to 350 km, extendable to 500 km with reduced payload. The missile is equipped with advanced guidance, navigation, and control systems, enabling mid-course manoeuvring, high accuracy, and hit-to-kill performance.
During the trials, Pralay accurately followed its planned trajectories and successfully met both minimum and maximum range objectives. Senior DRDO scientists, officials from the Indian Army and Indian Air Force, and industry partners were present to witness the tests. Terminal phase data was confirmed using ship-based telemetry systems.
Defence Minister Rajnath Singh lauded DRDO, the armed forces, defence PSUs, and industry partners for demonstrating the missile’s salvo-launch capability, which significantly enhances India’s tactical strike potential.
Indigenous FPV Drones Launched by Dehradun-Based BSS Materiel
In a significant boost to India’s unmanned warfare capabilities, BSS Materiel Limited, headquartered in Dehradun, Uttarakhand, has introduced a new line of indigenous First-Person View (FPV) drones designed for tactical military operations.
These drones are manufactured with zero Chinese components, fully complying with Indian defence procurement restrictions aimed at securing supply chains. They also meet US National Defense Authorization Act (NDAA) standards, enhancing their export potential and interoperability with allied forces.
BSS Materiel operates under the Make in India and Start-Up India initiatives and specialises in UAVs, counter-UAV systems, and weaponised drone platforms. The company combines collaboration with foreign OEMs and domestic engineering expertise, prioritising locally sourced subsystems for greater operational resilience.
The FPV drones are optimised for intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) as well as tactical strike roles. Key specifications include a range of 8 km, top speed of 120 km/h, maximum weight of 3.6 kg, and a payload capacity of up to 2 kg. Their agility and manoeuvrability make them suitable for short-range combat missions, particularly in contested and high-risk environments.
India and Pakistan Continue Annual Exchange of Nuclear Installations List
Despite persistent bilateral tensions, India and Pakistan exchanged lists of their nuclear installations on 1 January 2026, marking the 35th consecutive annual exchange under a long-standing confidence-building agreement.
The Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) confirmed that the exchange was conducted simultaneously through diplomatic channels in New Delhi and Islamabad. The practice is rooted in the Agreement on the Prohibition of Attack against Nuclear Installations and Facilities, signed on 31 December 1988 and enforced from 27 January 1991.
Under the agreement, both countries commit to annually notifying each other of nuclear facilities that are prohibited from attack, thereby reducing the risk of accidental escalation. The pact emerged against the backdrop of regional tensions during the 1980s, particularly following India’s Operation Brasstacks (1986) and fears of pre-emptive strikes on nuclear sites.
Over the decades, this mechanism has endured multiple crises, including the Kargil conflict (1999), military standoffs in 2001–02, terror attacks in Pathankot and Uri, the Balakot airstrikes (2019), and hostilities in May 2025. The uninterrupted continuation of the exchange highlights its importance as a stabilising confidence-building measure.
While the exchanged lists remain classified, past references suggest India includes facilities such as BARC Trombay, Tarapur, Kakrapar, and Kalpakkam, while Pakistan lists sites like Chashma, Karachi Nuclear Power Plant, and Kahuta Research Laboratories. Neither side publicly discloses changes, maintaining strategic ambiguity.
Review Questions
- The ramjet-powered 155 mm artillery shell being developed for the Indian
Army aims to primarily enhance which capability?
A. Rate of fire
B. Shell payload capacity
C. Firing range without loss of lethality
D. Barrel life of artillery guns
ANSWER: C - The development of the ramjet-assisted 155 mm artillery shell is being carried
out in collaboration with which institution?
A. IIT Kanpur
B. DRDO
C. IIT Madras
D. BHEL
ANSWER: C - Which organisation is responsible for the successful user trials of the Pralay
tactical ballistic missile?
A. Indian Army
B. Indian Air Force
C. Bharat Dynamics Limited
D. DRDO
ANSWER: D - Kalyani Strategic Systems Limited is set to test which indigenous naval gun
calibres in 2026?
A. 105 mm and 155 mm
B. 76 mm and 30 mm
C. 130 mm and 122 mm
D. 40 mm and 57 mm
ANSWER: B - Under which agreement do India and Pakistan annually exchange lists of their
nuclear installations?
A. Shimla Agreement
B. Lahore Declaration
C. Agreement on the Prohibition of Attack against Nuclear Installations and
Facilities
D. Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT)
ANSWER: C - Full Form of ‘SAMAR’ is
A. System for Advance Manufacturing Assessment and Rating
B. System for Array Manufacturing Assessment and Rating
C. System for Advance Manufacturing Assessment and Rate
D. None
ANSWER: A - Where is the world’s highest battlefield, Siachen Glacier, located?
A. Near the Indo-Pak Line of Control
B. On the Indian Peninsula
C. In the Southern Naval Command (SNC) region
D. In the Indian Search and Rescue Region (ISRR)
ANSWER: A - Manufacturing Facility For Production Of Airbus C295 Aircraft To Come Up
In___.
A. New Delhi
B. Chennai
C. Vadodara
D. Noida
ANSWER: C - On 1 Apr 1954, the President’s Colours Were Presented To The IAF By Which
President Of India?
A. Rajendra Prasad
B. V.V. Giri
C. Radhakrishanan
D. Pratibha Singh Patil
ANSWER: A - Ex GARUDA SHAKTI, IND-INDO CORPAT, IND-INDO BILAT Conducted b/w India
&
A. Qatar
B. Sri Lanka
C. Indonesia
D. Maldives
ANSWER: C - SIMBEX Series Of Exercises Began In 1994 And Were Initially Known As
A. Exercise Lion King
B. Exercise Asia King
C. Exercise Jungle King
D. None of the above
ANSWER: A - Northrop Grumman Is The Defence Manufacturing Company of Which
Nation?
A. USA
B. UK
C. Israel
D. Russia
ANSWER: A - The Unending Game Book Written By
A. Vikram Sood
B. Shivshankar Menon
C. Ravi Shastri
D. Salman Rushdie
ANSWER: A - What Is The Capital Of Andorra?
A. Maseru
B. Andorra la Vella
C. Yamoussoukro
D. Addis Ababa
ANSWER: B - “The School for Good Mothers ” Book Written By
A. Jessamine Chan
B. Beatrice Hitchman
C. Hew Strachan
D. Nikki May
ANSWER: A - Lal Bahadur Shastri National Academy of Administration Is In
A. H.P
B. U.P
C. U.K
D. M.H
ANSWER: C - “Discipline and united action are the real sources of strength for the nation.”
Said By
A. Gandhi Ji
B. Lal Bahadur Shastri
C. Pt. Nehru
D. Gopal Krishna Gokhale
ANSWER: B - Commodore Rank Of Indian Navy Is Equivalent To Which Rank of IAF?
A. Air Commodore
B. Air Marshal
C. Wing Commander
D. Major
ANSWER: A - Ex GARUDA Conducted b/w India &
A. Qatar
B. Sri Lanka
C. France
D. Maldives
ANSWER: C - Ex Desert Eagle Conducted b/w India &
A. Qatar
B. Sri Lanka
C. UAE
D. Maldives
ANSWER: C
ALSO READ:
- Latest Daily Current Affairs and Defence Updates
- Latest Daily Current Affairs November 2025[DOWNLOAD PDF]
- Latest Daily Current Affairs October 2025[DOWNLOAD PDF]
- Latest Daily Current Affairs August 2025[DOWNLOAD PDF]
- Latest Daily Current Affairs July 2025[DOWNLOAD PDF]
- Monthly Defence Current Affairs June 2025 [DOWNLOAD PDF]
- Monthly Defence Current Affairs May 2025 [DOWNLOAD PDF]
- Monthly Defence Current Affairs April 2025 [DOWNLOAD PDF]
- Monthly Defence Current Affairs March 2025 [DOWNLOAD PDF]
- Monthly Defence Current Affairs February 2025 [DOWNLOAD PDF]
- Monthly Defence Current Affairs January 2025 [DOWNLOAD PDF]
- Defence Current Affairs Year End Review 2024
- Monthly Defence Current Affairs November 2024 [DOWNLOAD PDF]
- Monthly Defence Current Affairs October 2024 [DOWNLOAD PDF]
- Monthly Defence Current Affairs September 2024 [DOWNLOAD PDF]
- Monthly Defence Current Affairs August 2024 [DOWNLOAD PDF]
- Monthly Defence Current Affairs July 2024 [DOWNLOAD PDF]
- Monthly Defence Current Affairs June 2024 [DOWNLOAD PDF]