In Current Affairs for 11 February 2026, we will see the latest national and international current affairs news. These important current affairs will be beneficial for your upcoming NDA, CDS, CDS OTA, AFCAT, TA, Agniveer Army, Agniveer Navy, Agniveer Air Force, Women Military Police, INET, MNS, ACC exams, SCO, PCSL, CAPF, and SSB interviews, and direct entries for Army, Navy, and Air Force like SSC Tech, TGC, JAG, NCC, TES, 10+2 Cadet. Download a PDF file about current events at the end of this article. Let us now see the Current Affairs.
Defence Current Affairs 11 February 2026
India is witnessing significant developments across defence diplomacy, internal security, space advancement, and military reforms. From deepening engagement with Middle Eastern partners to accelerating indigenous defence production and space ambitions, the country is moving towards greater strategic self-reliance and global influence.
India–Middle East Defence Engagement Gains Momentum
India’s defence outreach in West Asia received renewed attention at the World Defence Show 2026 in Riyadh. Minister of State for Defence Sanjay Seth held high-level talks with Saudi Arabia’s Assistant Minister of Defence for Executive Affairs, Khaled bin Hussein Al-Biyari. The interaction reflects the expanding strategic understanding between New Delhi and Riyadh, especially in the defence sector.
The World Defence Show serves as a global platform for military collaboration, innovation, and technology partnerships. India’s presence highlights its intent to strengthen defence cooperation, encourage joint ventures, and promote indigenous capabilities in the Gulf region.
This engagement follows India’s participation in the 8th Abu Dhabi Dialogue, where discussions focused on labour mobility, migrant welfare, and skill partnerships. The Dialogue, launched in 2008, includes major Asian labour-origin countries and destination nations, aiming to improve cooperation in contractual employment frameworks.
Expanding India–Saudi Arabia Strategic Partnership
India and Saudi Arabia share a relationship that has evolved far beyond energy trade. Diplomatic ties began in 1947, but major progress occurred after the Delhi Declaration (2006) and the Riyadh Declaration (2010), which elevated relations to a Strategic Partnership. In 2019, the establishment of a Strategic Partnership Council further institutionalised cooperation.
Economic and Energy Cooperation
Saudi Arabia remains one of India’s leading trade partners in West Asia. Bilateral trade consistently remains robust, driven largely by energy imports. India sources crude oil, LPG, and petrochemicals from the Kingdom, while exporting food products, chemicals, machinery, textiles, and engineering goods.
Both countries are also exploring collaboration in renewable energy, green hydrogen, and strategic petroleum reserves. Indian companies are participating in projects aligned with Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030 reform agenda.
People-to-People and Security Ties
With nearly 2.5 million Indians residing in Saudi Arabia, the diaspora plays a vital role in strengthening cultural and economic linkages. Defence cooperation includes joint exercises, intelligence sharing, maritime security collaboration, and counter-terrorism coordination.
Government Targets Elimination of Maoist Insurgency
On the internal security front, the government has reiterated its commitment to ending Left-Wing Extremism by March 31, 2026. During a high-level review meeting in Raipur, Union Home Minister Amit Shah stated that a combination of strong security operations, infrastructure expansion, and disruption of extremist funding networks has significantly weakened Maoist groups.
Recent data indicates intensified action in Chhattisgarh, particularly in the Bastar region, where numerous Maoist operatives have been neutralised, arrested, or have surrendered. Senior insurgent leaders have also been eliminated. However, security experts caution that extremist elements still maintain influence in parts of Jharkhand, Odisha, and Maharashtra.
The government maintains that coordinated efforts between central and state agencies are steadily restoring stability in affected areas.
ISRO Speeds Up Space Station and Satellite Missions
India’s space programme is entering an ambitious phase, with ISRO accelerating plans for the country’s first space station. Alongside this effort, work is underway on nearly 80 satellites designed to enhance scientific research, disaster response, navigation accuracy, and national security.
These satellites will also support the Gaganyaan human spaceflight mission by ensuring reliable communication between spacecraft and ground stations. Program officials have emphasised that strengthening satellite infrastructure is essential for technological self-reliance.
Key initiatives include advanced Earth Observation systems, improvements to India’s regional navigation network, and the Indian Data Relay Satellite System to enable real-time communication with spacecraft in low Earth orbit.
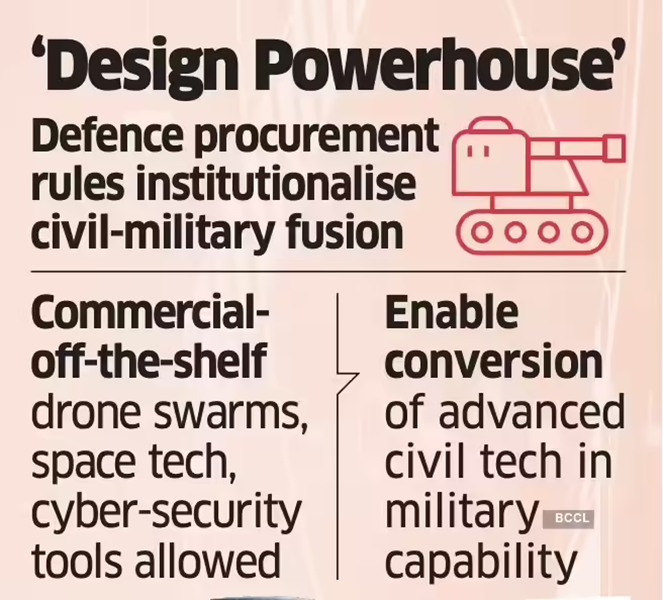
Defence Procurement Reform: From ‘Made in India’ to ‘Owned by India’
In a major policy shift, the government is revising defence procurement norms under the draft Defence Acquisition Procedure (DAP). The proposed changes aim to reduce dependence on simple technology transfers and instead promote indigenous research, intellectual property ownership, and innovation.
The traditional L1 (lowest bidder) system is being modified to incorporate technical merit and indigenous design as evaluation criteria. The reform seeks to strengthen domestic manufacturers and startups by prioritising companies that retain control over source codes and design data, ensuring long-term upgrade flexibility.
This move represents a transition toward deeper technological sovereignty in defence manufacturing.
Dedicated Support Structure for Ex-Agniveers
The Ministry of Home Affairs has established a specialised wing and cell to manage rehabilitation and career progression for former Agniveers after completion of their service tenure. The initiative aims to streamline coordination and create structured pathways for employment and reintegration.
The government clarified in Parliament that this responsibility has been formally assigned to the Home Ministry. The new mechanism will focus on policy development, monitoring, and ensuring smooth post-service transitions for personnel under the Agnipath scheme.
Conclusion
India is simultaneously strengthening its global defence partnerships, enhancing domestic security, accelerating space exploration, and reforming military procurement systems. These interconnected developments reflect a broader national objective: achieving strategic autonomy while expanding international cooperation.
Whether in West Asia diplomacy, counter-insurgency operations, space innovation, or defence reforms, India’s approach signals a determined push toward resilience, modernization, and self-reliance.
Review Questions
1. Where was the World Defence Show 2026 held?
A) Abu Dhabi
B) Doha
C) Riyadh
D) Muscat
Answer: C) Riyadh
2. Who represented India at the World Defence Show 2026?
A) Rajnath Singh
B) Sanjay Seth
C) Ajit Doval
D) S. Jaishankar
Answer: B) Sanjay Seth
3. Sanjay Seth met which Saudi official during the event?
A) Mohammed bin Salman
B) Khaled bin Hussein Al-Biyari
C) Faisal bin Farhan
D) Turki Al-Faisal
Answer: B) Khaled bin Hussein Al-Biyari
4. The Abu Dhabi Dialogue was established in which year?
A) 2005
B) 2008
C) 2012
D) 2015
Answer: B) 2008
5. The Abu Dhabi Dialogue primarily focuses on:
A) Defence procurement
B) Oil trade
C) Labour mobility and migrant welfare
D) Space cooperation
Answer: C) Labour mobility and migrant welfare
6. Diplomatic relations between India and Saudi Arabia were established in:
A) 1945
B) 1947
C) 1950
D) 1962
Answer: B) 1947
7. The Riyadh Declaration (2010) elevated India–Saudi ties to:
A) Economic Partnership
B) Defence Pact
C) Strategic Partnership
D) Trade Alliance
Answer: C) Strategic Partnership
8. Approximately how many Indians live in Saudi Arabia?
A) 1 million
B) 1.5 million
C) 2.5 million
D) 4 million
Answer: C) 2.5 million
9. The government has set what deadline to eliminate Maoist insurgency?
A) 31 December 2025
B) 26 January 2026
C) 15 August 2026
D) 31 March 2026
Answer: D) 31 March 2026
10. Which state has witnessed major anti-Naxal operations recently?
A) Bihar
B) Chhattisgarh
C) West Bengal
D) Telangana
Answer: B) Chhattisgarh
11. Bastar region is located in which state?
A) Odisha
B) Maharashtra
C) Chhattisgarh
D) Jharkhand
Answer: C) Chhattisgarh
12. India’s human spaceflight mission is called:
A) Chandrayaan
B) Mangalyaan
C) Gaganyaan
D) Aryabhata
Answer: C) Gaganyaan
13. ISRO is working on approximately how many satellites currently?
A) 25
B) 40
C) 60
D) 80
Answer: D) 80
14. The Indian Data Relay Satellite System (IDRSS) is meant to:
A) Track weather changes
B) Provide continuous communication with satellites
C) Launch rockets
D) Monitor borders
Answer: B) Provide continuous communication with satellites
15. The Navigation with Indian Constellation (NVS) programme aims to improve:
A) Defence missiles
B) Space tourism
C) Satellite navigation services
D) Nuclear research
Answer: C) Satellite navigation services
16. The draft Defence Acquisition Procedure (DAP) emphasizes:
A) Foreign imports
B) Lowest price only
C) Indigenous design and IPR ownership
D) Reduced defence spending
Answer: C) Indigenous design and IPR ownership
17. The traditional L1 formula in defence procurement refers to:
A) Long-term contract
B) Lowest bidder
C) Level-1 security
D) Logistics model
Answer: B) Lowest bidder
18. The ex-Agniveer wing has been set up under which ministry?
A) Ministry of Defence
B) Ministry of Labour
C) Ministry of Home Affairs
D) Ministry of Skill Development
Answer: C) Ministry of Home Affairs
19. Saudi Arabia’s long-term reform and diversification plan is known as:
A) Vision 2025
B) Gulf Reform Plan
C) Vision 2030
D) National Growth Strategy
Answer: C) Vision 2030
20. India–Saudi defence cooperation includes collaboration in:
A) Agriculture research
B) Maritime security and counter-terrorism
C) Film production
D) Banking reforms
Answer: B) Maritime security and counter-terrorism
ALSO READ:
- Latest Daily Current Affairs and Defence Updates
- Latest Daily Current Affairs January 2026[DOWNLOAD PDF]
- Latest Daily Current Affairs November 2025[DOWNLOAD PDF]
- Latest Daily Current Affairs October 2025[DOWNLOAD PDF]
- Latest Daily Current Affairs August 2025[DOWNLOAD PDF]
- Latest Daily Current Affairs July 2025[DOWNLOAD PDF]
- Monthly Defence Current Affairs June 2025 [DOWNLOAD PDF]
- Monthly Defence Current Affairs May 2025 [DOWNLOAD PDF]
- Monthly Defence Current Affairs April 2025 [DOWNLOAD PDF]
- Monthly Defence Current Affairs March 2025 [DOWNLOAD PDF]
- Monthly Defence Current Affairs February 2025 [DOWNLOAD PDF]
- Monthly Defence Current Affairs January 2025 [DOWNLOAD PDF]
- Defence Current Affairs Year End Review 2024
- Monthly Defence Current Affairs November 2024 [DOWNLOAD PDF]
- Monthly Defence Current Affairs October 2024 [DOWNLOAD PDF]
- Monthly Defence Current Affairs September 2024 [DOWNLOAD PDF]
- Monthly Defence Current Affairs August 2024 [DOWNLOAD PDF]
- Monthly Defence Current Affairs July 2024 [DOWNLOAD PDF]
- Monthly Defence Current Affairs June 2024 [DOWNLOAD PDF]