Launch of 2nd Project 17A ship ‘Himgiri’
- ‘Himgiri’, the first of the three Project 17A ships being built at M/s Garden Reach Shipbuilders and Engineers Limited (GRSE), Kolkata was launched today, 14 Dec 20. She made her first contact with the waters of Hooghly River at 1335 Hrs at the launch ceremony, General Bipin Rawat, Chief of Defence Staff (CDS) was the Chief Guest. In keeping with Naval traditions Smt Madhulika Rawat, spouse of CDS launched the ship to the chanting of invocations from the Atharva Veda. The ship has taken its name and crest of the second Frigate of the Leander Class of ships, which incidentally was launched 50 years ago in 1970.
- Under the Project 17A program, a total of seven ships, four at Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Limited (MDL) and three ships at GRSE are being built with enhanced stealth features, advanced indigenous weapon and sensor fit along with several other improvements. The launch of ‘Himgiri’ has showcased GRSE’s commitment towards the building of three state-of-the-art warships of P17A for Indian Navy. Over the years, GRSE has emerged as a leading shipyard having built over 100 ships. The yard has scaled up its infrastructure and skill sets to meet new challenges in building of P17A ships. P17A ships are the first gas turbine propulsion and largest combat platforms ever built at GRSE.
- Since its inception, Project 17A has upheld India’s vision for Atmanirbhar Bharat. P17A ships have been indigenously designed by Directorate of Naval Design (Surface Ship Design Group) – DND(SSG), and are being built at indigenous yards namely MDL and GRSE. Naval shipbuilding provides a great opportunity to energise our economy post COVID-19. Project 17A ships are sourcing 80% of the material/ equipment required for the project from indigenous vendors and with employment generation for over 2000 Indian firms and MSMEs within the country. Modular construction of the ship through outsourcing, and integrated construction methodology are being used to enhance GRSE’s productivity for delivery of ship targeted in August 2023.
Indian Army Organises Webinar on Modernisation of Repair Echelons in Line with Latest Technology Trends
- Indian Army in partnership with the Society of Indian Defence Manufacturers (SIDM) held a one-day Webinar on 14 December 2020 on “Agile EME : Facilitating Boots on Ground through Aggressive Industrial Outreach”.
- The initiative will help the Indian Army to plan modernisation of its Repair Echelons in line with latest technology trends worldwide and also promote indigenisation to reduce dependency on imports and cut cost on repairs. But more important, the initiative will help reduce the time for which critical equipment of the field army remains unserviceable awaiting some critical spares/components to come from abroad (new or repaired)
- The three distinct sessions and panel discussions of webinar were dedicated to indigenisation, modernisation of Electronics and Mechanical Engineers (EME) Workshops and use of Condition Based Monitoring for repair of equipment.
- In the inaugural session, Lt Gen SK Upadhya, Master General of Sustenance, Indian Army conveyed that such digital interactions have become the new normal to do business. He further highlighted that Indian Industry is progressing fast towards becoming a major defence industrial base and the defence industry always offers new solutions to any arising problems of Armed forces.
- He said, “Given the situation we are facing at the Northern borders, we have very well been able to look after our equipment due to the constant support from defence industry”.
- He mentioned that the webinar is a step towards meeting indigenisation requirements of the EME and further stated that the Industry should assist Indian Army to meet these requirements in a timely and qualitative manner.
- Lt Gen Anil Kapoor, Director General Electronics and Mechanical Engineers (EME), in his theme address, said “the new mantra of agility is a compulsion and no longer a choice and in the EME, we definitely have to be agile”. He highlighted the importance of co-partnering through industrial outreach and derive common denominators and best practices to make sure that EME becomes contemporary and futuristic to handle the challenges ahead. He further said, “India and Indians are synonymous with innovation and challenges to address any obstacle; Indigenisation can be achieved with a similar spirit and fervour”.
- Mr Jayant Patil, President, SIDM, while giving out Industry perspective mentioned that India is facing security challenges from all domains. The country has to maintain its position as a leading regional power capable of not only defending its sovereignty but also acting as a net security provider in challenging regions.
- To maintain and achieve this objective, our military has to be equipped with the best-in-class equipment, which preferably, should be ‘Made-in-India’. He stated that the Indian Industry is capable of meeting the requirements of the defence sector which will allow India to increasingly become ‘Self-reliant’.
- The Webinar was attended by 140 Industry delegates and military officers.
Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi lit up ‘Swarnim Vijay Mashaal’ and began 50th anniversary celebrations of Indo-Pak War 1971
- In December 1971, the Indian Armed Forces secured a decisive and historic Victory over Pakistan Army, which led to creation of a Nation – Bangladesh and also resulted in the largest Military Surrender after the World War – II.
- From today, the Nation will be celebrating 50 Years of Indo-Pak War, also called ‘Swarnim Vijay Varsh’.
- Various commemorative events are planned across the Nation.
- Inaugural event was held at the National War Memorial (NWM) in New Delhi which was attended by Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi. On his arrival, the Prime Minister was received by Raksha Mantri Shri Rajnath Singh at the venue.
- The Prime Minister, Chief of Defence Staff & Tri-Service Chiefs laid wreath and paid homage to the fallen soldiers. Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi lit up the ‘Swarnim Vijay Mashaal’ from the eternal flame of NWM on the occasion. Four Victory Mashaals (flames) were lit from the Eternal Flame of NWM. These Mashaals will be carried to various parts of the country including to villages of Param Vir Chakra and Maha Vir Chakra Awardees of 1971 War. Soil from the villages of these Awardees and from areas where major battles were fought in 1971 were brought to the NWM.
- Various commemorative events will be conducted pan-India wherein war Veterans and Veer Naris will be felicitated and events like band displays, seminars, exhibitions, equipment displays, film festivals, conclave and adventure activities are planned.
- Raksha Rajya Mantri Shri Shripad Yesso Naik and other senior civil & military officials of the Ministry of Defence were also present on the occasion.
Russia successfully test launches heavy lift space rocket after long hiatus
- Six years after launching for the first time, a Russian Angara A5 heavy-lift rocket took off on its second test flight Monday and successfully delivered a dummy payload into orbit.
- Russian officials confirmed the Angara A5 rocket and its Breeze M upper stage performed as intended during the test flight, which carried a mass simulator into orbit on a marathon nine-hour mission mimicking a mission profile that might be required by future Russian military and commercial payloads.
- The Angara A5 is the most powerful new Russian launcher since the 1980s, and is designed to replace the Proton M rocket to carry the country’s heaviest payloads into orbit. But the program is years behind schedule, and despite a successful inaugural test flight in 2014, it took six years to launch a second Angara A5 rocket.
- “She’s flying, damn it!!!” tweeted Dmitry Rogozin, head of Roscosmos, the Russian space agency.
- Five kerosene-fueled RD-191 engines powered the heavy-lifter off its launch pad at Site 35 at the Plesetsk Cosmodrome, a military-run space base 500 miles (800 kilometers) north of Moscow in Russia’s Arkhangelsk region, at 0550 GMT (12:50 a.m. EST; 8:50 a.m. local time).
- Generating more than 2 million pounds of thrust, the engines steered the Angara A5 rocket to the east from Plesetsk.
- The Angara A5’s four strap-on boosters shut down and separated nearly three-and-a-half minutes into the flight. Then the rocket’s core stage, which fired its RD-191 engine at a lower throttle setting in the early phase of flight, powered up to full throttle to continue climbing into space.
- The core stage — also known as the second stage — switched off its engine and dropped away from the Angara’s third stage nearly five-and-a-half minutes after liftoff. A kerosene-fueled RD-0124 engine ignited on the third stage and fired for nearly seven minutes.
- The Angara’s payload fairing jettisoned early in the third stage burn, revealing the rocket’s dummy payload after climbing into space.
- The rocket’s Breeze M upper stage separated from the Angara third stage at T+plus 12 minutes, 28 seconds, according to statements issued by Roscosmos and the Russian Defense Ministry. The Breeze M stage burned its engine four times, first to reach a parking orbit around Earth, then to move into a circular orbit more than 22,000 miles (36,000 kilometers) above the equator.
- The Breeze M upper stage simulated a payload separation maneuver around 1500 GMT (10 a.m. EST), more than nine hours after taking off from Plesetsk, Roscosmos tweeted. The Breeze M was then expected to fire thrusters to maneuver into a “graveyard” orbit near the geostationary belt.
India, Bangladesh to secure ‘chicken’s neck’ with Haldibari – Chilahati rail service after 55 years
- In a decision that will have huge geopolitical implications, India and Bangladesh have decided to resume trans-border railway connectivity between Haldibari in West Bengal and Chilahati located across the border in Nilphamari district after almost 55 years. The move will not only boost India-Bangladesh ties but will also open up connectivity for New Delhi with the north-eastern part and other bordering countries while reducing emerging vulnerabilities, especially at a time when an aggressive China is making steady inroads in the region through its much-hyped Belt and Road Initiative. Until 1965, when the India-Pakistan war took place, trains used to ply on this route.
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi and his Bangladesh counterpart Shiekh Hasina are expected to inaugurate this route on December 16, which is observed at the Vijay Diwas marking Dhaka’s victory over Pakistani armed forces, the reports said. Rail service is expected to resume from March 26, Bangladesh’s Independence Day. Haldibari, in Cooch Behar is strategically located.
- It is just 75 kilometres away from the critical Siliguri Corridor marking the 22 kilometre “Chicken Neck” that connects the rest of India with the north eastern States and other countries including Nepal, Bangladesh and Bhutan. “The rail service will be very important for India as it will provide the much required access to New Delhi to the north-eastern part and other neighbouring countries,” a foreign policy expert, on condition of anonymity told indianarrative.com.
- “The area is of strategic importance to India as it the gateway to the North-East and the eastern part of India. The area especially around Nath-La Pass and even Doka La has seen several conflicts and now with an aggressive and increasingly belligerent China, India needs to protect this region. In case any other external force manages to break this corridor, India’s connectivity with the north east will be cut off,” the analyst said, adding that the new rail route will also boost trade between the two neighbours. Besides, there has also been demand from people from both sides to resume the rail service. Many Bangladeshis visit the region every year.
- While many of them come for trade and healthcare reasons, there is a large number of tourists as well. In the initial stage though, the Haldibari-Chilahati rail service could be restricted for cargo purpose. At present, India is connected with Bangladesh through four border links — Petrapole-Benapole, Singhabad-Rohanpur, Gede-Darshana and Radhikapur-Birol besides having one trans-border passenger train service, the Maitree Express.
- The Maitree Express connects Kolkata with Dhakaand Khulna. India is also looking at fast-tracking the Bangladesh-Bhutan-India Nepal (BBIN) initiative which will boost connectivity among the South Asian neighbours through rail and road. “The BBIN project is important for the region and we will expedite it. Bhutan will play an important role and through this the country will get access to ports.
- The project is beneficial to all member countries which are closely linked to each other for trade and other economic co-operation. We are keen to give it shape since it will increase regional connectivity and increase trade and not because of other any external factors or countries,” Gopal Krishna Agarwal, BJP’s spokesperson on economic affairs said.
HAL’s Avionics Division Assembles first Israeli AESA Radar for Jaguar jets locally
- HAL’s Avionics Div, Hyderabad has acquired clearance for the primary AESA Radar (CBU part) to be fitted on the Jaguar DARIN III UPG plane. That is the primary AESA radar being fitted on any platform in India.
- HAL Hyderabad is the manufacturing company for a complete of 54 AESA radars underneath ToT from IAI, Elta Methods, Israel In a short ceremony held on 20 November 2020, the Clearance Certificates was handed over by HV Kumar, RDAQA (Hyd) to Mr Rajeev Kumar, GM (AD).
- “ELTA ELM-2052 is a Hearth Management Radar FCR designed for air-to-air superiority/strike missions, based mostly on totally solid-state Energetic Electronically Scanning Array AESA tech enabling the radar to attain lengthy detection ranges and multi-target monitoring capabilities”: IAI web site
- In February 2020, HAL entered right into a contract with IAI for 54 of those underneath ToT. As a part of the TOT, HAL will manufacture Gallium arsenide (GaAs) based mostly transistors and receivers that are a part of the radar Antenna . ELTA ELM-2052 can also be being chosen for the 83 Tejas Mk1A fighter jets.
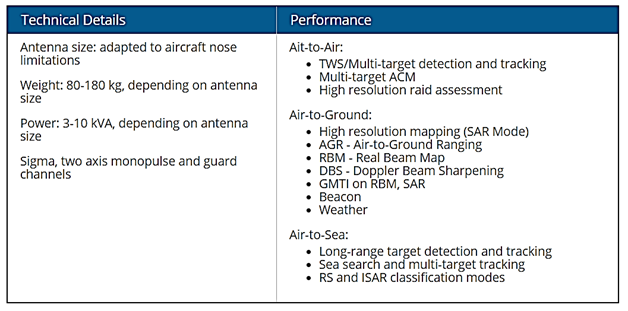
India working on next ‘Astra’ missile with 160 km range as Mk1 is integrated in IAF & Navy
- India is working on an extended range of the indigenous beyond-visual-range (BVR) air-to-air missile ‘Astra’ (Sanskrit/Hindi for a launched weapon), which will enable it to strike enemy targets 160 km away, without getting out of its own airspace.
- The development comes even as work is on to integrate the current 110 km version of the Astra Mk 1 on board the Indian Air Force’s MiG-29 and Light Combat Aircraft ‘Tejas’ Mk 1, and the Indian Navy’s MiG-29K aircraft. The Astra Mark 1 is already integrated with the IAF’s Su-30 MKI fighters, and the production process — by state-owned Bharat Dynamics Limited — has begun.
- Once the overall integration plans are completed, the Astra will be the standard long-range air-to-air missile across India’s entire fighter fleet, except the French-origin Rafale and Mirage.
- In July this year, the defence ministry formally sanctioned the purchase of 248 Astra missiles, including 48 for the Navy, after a successful September 2019 trial in which it hit a target 90 km away.
- Sources said Astra has export potential too, and will be considered for sale to friendly countries.
Mk 2 by May 2022
- As of now, with a range of over 110 km and a maximum speed of Mach 4.5 (over 5,500 kmph), the Astra Mk 1 is seen as a game-changer, which can bring back India’s air-to-air combat superiority over Pakistan.
- While India now also has European developer MBDA’s Meteor missiles with the Rafale’s induction, they are much more costly (Rs 25 crore each) compared to the Astra (Rs 7-8 crore).
- For the second version of the Astra missile, called Mark 2, the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) is working on dual-pulse rocket motor to extend the range up to 160 km by May 2022, sources in the defence and security establishment.
- Work is also going on to replace the Russian radio frequency (RF) seekers’ on the missile with indigenous ones, a source said.
- “Three air launch and captive flight tests have been completed with indigenous RF seekers. The indigenous seeker will be proven by June 2021. Subsequently, Astra Mk-1 & Mk-2 missile will be using the indigenous seeker in production,” the source said.
- At present, all subsystems, except the RF seeker and the inertial measurement unit (IMU), are indigenous. The seekers are being indigenised by Bharat Electronics Limited, Bengaluru, and will be inducted by June 2021, sources said, adding that efforts are on for the development of the indigenous IMUs too.
Project Astra was initiated in 2001
- In 2001, the DRDO had initiated discussions with various stakeholders on the design and development of an indigenous air-to-air missile system, which could take on adversary targets beyond the visual range, thus providing a strategic advantage.
- Subsequently, Hyderabad’s Defence Research and Development Laboratory (DRDL) was identified as the nodal lab, and a task force was formed to undertake preliminary studies.
- Sources said although financial sanctions were not available then, activities were initiated with the internal funds of the DRDO.
- “The major challenges were the development of RF Seeker, miniaturised and robust missile hardware, and integration on IAF frontline aircraft without the support of the foreign Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM),” a source said, adding that DRDO’s management wanted DRDL to demonstrate the basic capability even before the project sanction.
- Simultaneously, the IAF was requested to generate the programme standard and quality requirement (PSQR).
Testing phase
- The initial effort was to prove the Astra’s performance in ballistic launch from the ground launcher. A source explained that this was done to demonstrate its safe release from the ground, before testing it on manned aircraft.
- In May 2003, three ballistic missile tests were conducted from the Integrated Test Range, Balasore, using the ground launcher.
- The propulsion system was proven and the safe release from ground was demonstrated. Subsequently, the PSQR was released, and the project named Astra was sanctioned on 1 April 2004 for a duration of 101 months.
- During this period, Astra was to be developed and integrated on the Su-30 MKI with the feasibility for integration on MiG-29, Mirage 2000 and LCA platforms as well.
- “One of the specifications in the PSQR was the requirement of a smokeless propellant system. However, the propulsion system used in the 2003 ground flight trials was with a certain level of smoke. This called for a re-development of a new smokeless propellant for Astra,” a source said.
- The team then started working on the system, even as in parallel, a team was formed within DRDO laboratories for the development of the avionics system, meeting Astra’s space constraints.
- In 2007, the control and guidance flight trials were initiated. In the first trial, it was found that the missile was experiencing wing-induced oscillations, which had serious implications for the performance.
- “One of the most critical technologies required for Astra was the RF seeker technology which was not available in the country then. Therefore, a decision was taken to develop the seeker to meet Astra specifications through AGAT, Russia, an established seeker manufacturer,” the last source cited above said.
- In 2011, the final missile configuration was frozen and hardware developed to conduct the guided trials, which were conducted successfully in December 2012.
- Meanwhile, SDI Bangalore was identified to modify the software of Su-30 MKI aircraft — mission computer, radar computer and display computer — to integrate the Astra missile.
- A launcher was designed and developed to integrate Astra missiles on aircraft. The design of the launcher was such that it should let the missile be integrated on any aircraft with minimum changes, sources said.
- In May 2014, Astra was air-launched for the first time with all systems performing meeting mission requirements.
- “In order to prove in various scenarios and envelope of the aircraft, 35 air launches and 150 captive flight sorties were conducted to meet the requirements of the IAF. With the successful launches in September 2019, the Astra weapon was finally accepted by the users,” another source said.
Export potential of Astra
- Sources said the present Astra missile has export potential and can be offered to friendly countries.
- “No production version is required to be developed separately. The present version is a platform-independent design, but a few modifications may be required as per platform interfacing and data exchange between missile and aircraft,” a source said when asked if any changes need to be made for export.
- But the source added that integration of the Astra missile on an aircraft needs some changes in the fighter too, and hence, the LCA ‘Tejas’ will be a good platform to export, so that all technical expertise will be within the country.
Taiwan sees role as arms supplier for West as it launches new warship
- Taiwan may become a supplier of weapons to Western democracies, President Tsai Ing-wen said on Tuesday, praising the island’s ramped up weapons-design ability as she launched an advanced, missile-laden warship and commissioned a new minelayer.
- Tsai has made boosting the defence of the Chinese-claimed island a priority in the face of a growing military challenge from Beijing, which has never renounced the use of force to bring democratic Taiwan under its control.
- While Taiwan’s air force has benefited from big-ticket items like new and upgraded F-16s, the navy is Tsai’s next focus, with submarines in production and the Tuesday launch of the first of a fleet of highly manoeuvrable stealth corvettes.
- The new Tuo Chiang-class corvettes, a prototype of which is already in operation, has been dubbed by Taiwan’s navy the “aircraft carrier killer” due to its complement of anti-ship missiles. It can also carry Sky Sword anti-aircraft missiles.
- Speaking in the eastern port city of Suao for the launch of the Ta Chiang, the first mass production ship of the Tuo Chiang-class, Tsai said the vessel and the new minelayer would deter attacks and showcased Taiwan’s research and development ability.
- “We have the determination and capability to complete the task of building our own ships, letting the world see our defence research and development energy,” Tsai said.
- “In the future, we may also become a supply source of related equipment and components in Western democracies, driving the upgrading of the defence industry,” she said.
- The United States is Taiwan’s main foreign source of weapons. Most countries shy away from arming the island, wary of angering Beijing and loosing valuable commercial contracts with the world’s second-largest economy.
- Tsai, re-elected in a landslide in January on a vow to stand up to China, has championed the concept of “asymmetric warfare”, focusing on high-tech, mobile weapons designed to make any Chinese attack as difficult as possible.
- She has bolstered the domestic arms industry to try to make Taiwan as self-sufficient as possible.
QUICK REVIEW
- Project 17A ships are known as which class frigates?
- Kalvari
- Nilgiri
- Andaman
- Karwar
ANSWER: B
- How many Project 17A ships have been launched until now (by December 2020)?
- One
- Two
- Three
- Four
ANSWER: B
- Under the Project 17A program, a total of 7 ships, __ at Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Limited (MDL) and __ ships at Garden Reach Shipbuilders & Engineers are being built.
- 6, 1
- 3, 4
- 4, 3
- 1, 6
ANSWER: C
- Which city division of HAL has acquired clearance for manufacturing of AESA Radar to be fitted on the Jaguar DARIN III UPG plane?
- Kanpur
- Bangalore
- Lucknow
- Hyderabad
ANSWER: D
- HAL has acquired clearance for which AESA Radar to be fitted on the Jaguar DARIN III UPG plane?
- ELTA ELM-2052
- ELTA ELM-2053
- ELTA ELM-2054
- ELTA ELM-2055
ANSWER: A
- On 14 December 2020, Russia successfully test launched which heavy lift space rocket?
- Proton M
- Proton K
- Angara A5
- SHLV
ANSWER: C
- Indian Army organized a Webinar with SIDM on 14 December 2020. The theme of that webinar was:
- Agile EME: Facilitating Boots on Ground through Aggressive Industrial Outreach
- Agile EME: Facilitating UAV Technology through Aggressive Industrial Outreach
- Agile EME: Facilitating Radars through Aggressive Industrial Outreach
- Agile EME: Facilitating Boots in Air through Aggressive Industrial Outreach
ANSWER: A


















