In Monthly Defence Current Affairs for July 2025, we will see the latest national and international current affairs news. These important current affairs will be beneficial for your upcoming NDA, CDS, CDS OTA, AFCAT, TA, Agniveer Army, Agniveer Navy, Agniveer Air Force, Women Military Police, INET, MNS, ACC exams, SCO, PCSL, CAPF, and SSB interviews, and direct entries for Army, Navy, and Air Force like SSC Tech, TGC, JAG, NCC, TES, 10+2 Cadet. Download a PDF file about current events at the end of this article. Let us now see the Current Affairs.
Monthly Defence Current Affairs July 2025
QUAD Nations Launch First-Ever ‘At Sea Observer Mission’
- In a significant stride toward strengthening maritime security and interoperability in the Indo-Pacific, the Coast Guards of India, Japan, the United States, and Australia have launched the first-ever ‘QUAD at Sea Ship Observer Mission’ under the Wilmington Declaration.
- The cross-embarkation mission marks an unprecedented step in QUAD Coast Guard collaboration, enhancing joint readiness, operational coordination, and domain awareness in support of a Free, Open, Inclusive, and Rules-Based Indo-Pacific.
- The mission reflects the vision laid out at the QUAD Leaders’ Summit in September 2024 and signifies a deepening of operational ties between the ICG, Japan Coast Guard, US Coast Guard, and Australian Border Force.
- India’s participation reinforces its strategic maritime vision of SAGAR (Security and Growth for All in the Region) and complements national efforts under the Indo-Pacific Oceans Initiative (IPOI), with an emphasis on capacity-building, humanitarian outreach, and maritime rule of law.
- The QUAD at Sea initiative thus sets the foundation for a ‘QUAD Coast Guard Handshake,’ fostering stronger trust, coordination, and collective resilience amid evolving maritime challenges in the region.
India’s DRDO Advances Conventional Agni-V ICBM with 7.5-Ton Airburst
- India is undertaking a significant strategic initiative to develop a conventional, non-nuclear variant of its Agni-V intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM), marking a transformative shift in its missile doctrine and tactical capabilities.
- DRDO aims to equip the Agni-V platform with a massive 7.5-ton conventional warhead, a move that dramatically enhances India’s ability to deliver high-impact, precision strikes against a range of strategic targets.
- While the nuclear-capable Agni-V can target locations beyond 5,000 kilometres, the conventional version will have an estimated range of 2,000 to 2,500 kilometres.
INS Tamal Commissioned
- The Indian Navy commissioned INS Tamal (F 71) on 01 Jul 2025 at Yantar Shipyard, Kaliningrad, Russia, in the presence of VAdm Sanjay Jasjit Singh, the Flag Officer Commanding-in-Chief, Western Naval Command.
- INS Tamal is the eighth multi-role stealth frigate in the series of Project 1135.6 and the second of the additional follow-on Tushil class of ships. The first ship of Tushil class (INS Tushil) was commissioned on 09 Dec 24.
- All seven ships inducted thus far are part of the Western Fleet – ‘The Sword Arm’ of the Indian Navy under the Western Naval Command.
- Tamal being the 51st ship being produced under this collaborative effort in the past 65 years.
- The ship has 26% indigenous components, including the BrahMos long-range cruise missile and Humsa-NG Sonar system.
- INS Tamal is manned by a crew of about 250 sailors and 26 officers. The officers and sailors of this ship embody the ships motto – Sarvatra Sarvada Vijaya (Victory always everywhere)’.
Project 17A Indigenous Stealth Frigate Udaygiri Delivered
- Yard 12652 (Udaygiri), the second ship of Project 17A stealth frigate, being built at Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Limited (MDSL), was delivered to the Indian Navy on 01 July 2025.
- The Project is a follow-on of the Shivalik class (Project 17) frigates active in service. Udaygiri is the second among the seven P17A frigates under construction at MDL, Mumbai and GRSE, Kolkata.
- These multi-mission frigates are capable of operating in a ‘Blue Water’ environment dealing with both conventional and non-conventional threats in the area of India’s Maritime Interests.
- Udaygiri is a modern Avatar of its predecessor, erstwhile INS Udaygiri which was a Steam Ship, decommissioned on 24 August 2007 after rendering 31 years of glorious service to the nation.
- The weapon suite comprises supersonic Surface-to-Surface missile system, Medium-Range Surface to Air Missile system, 76 mm Gun, and a combination of 30 mm and 12.7 mm rapid-fire close-in Weapon Systems.
India and France Wrap up SHAKTI 2025
- The 13th French Foreign Legion Demi-Brigade (13th DBLE) hosted the eighth edition of the Indo-French Army exercise SHAKTI from 18 June to 1 July 2025 in France.
- The exercise involved more than 500 legionnaires and military personnel from various units of the French Army, the Foreign Legion, as well as the French Air and Space Force, and the French Navy.The Indian contingent of 90 personnel primarily comprised a battalion of the Jammu and Kashmir Rifles, besides personnel from other arms and services. About 50 armoured and tactical vehicles and fighter jets have been deployed in this exercise.
- Indo-French defence exercises such as Exercise GARUDA between the air forces, Exercise VARUNA between the navies, and Exercise SHAKTI between the armies are held regularly and have grown in scope and complexity over the years.
- In this context, the Indo-French Joint Military Exercise SHAKTI-VIII continues to strengthen operational interoperability and mutual cooperation between the Indian and French Armies.
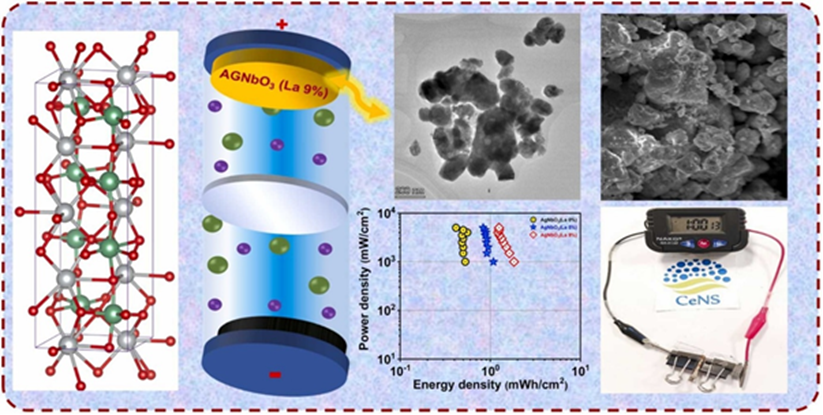
Indian Scientists Engineer Supercharged Green Energy Material
- In a remarkable scientific achievement, researchers from Bengaluru, in collaboration with Aligarh Muslim University, have developed a groundbreaking energy storage material that significantly boosts the performance of supercapacitors—devices vital for modern-day energy systems.
- At the heart of modern energy storage lies the supercapacitor—a device that can rapidly store and release large amounts of energy making them crucial for powering everything from mobile devices and electric vehicles to renewable energy systems.
- What are Supercapacitors?
- Supercapacitors are energy storage devices that can rapidly charge and discharge large amounts of energy. Unlike conventional batteries, they offer quicker energy transfer rates and longer lifespans.
- However, one of the limitations of supercapacitors has been their lower energy storage capacity compared to batteries. To overcome this challenge, scientists around the world have been in search of materials that can enhance energy density while maintaining speed and longevity.
- The Breakthrough Innovation
- A team led by Dr. Kavita Pandey at the Centre for Nano and Soft Matter Sciences, Bengaluru—an autonomous institution under the Department of Science and Technology (DST), Government of India—has made significant progress in this domain.
- The researchers concentrated on silver niobate (AgNbO₃), a lead-free and environmentally friendly compound known for its impressive electrical properties.
- To improve this material further, the team introduced lanthanum, a rare-earth element with excellent electronic characteristics, into the silver niobate nanoparticles. This process, known as lanthanum doping, had a dual effect:
- It reduced the particle size, which increased the surface area available for energy storage.
- It enhanced electrical conductivity, leading to faster charge-discharge cycles.
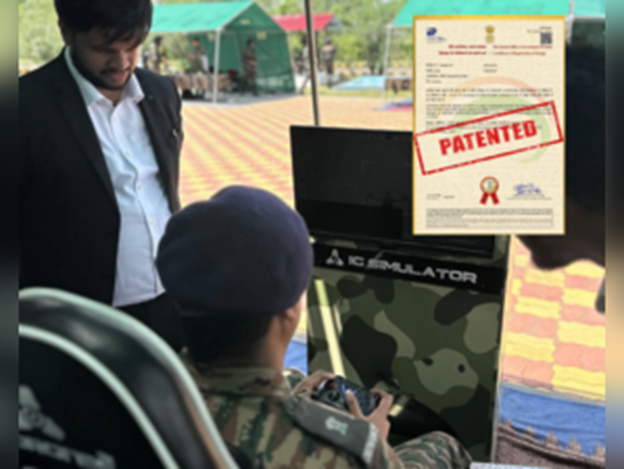
IG Drones Bags Patent
- IG Drones said that it has been granted the patent for India’s first indigenous defence drone simulator, a move hailed as a major step towards technological sovereignty and defence self-reliance under the government’s Aatmanirbhar Bharat initiative.
- The simulator, initially unveiled by Prime Minister Narendra Modi during Defence Expo 2022, has been developed entirely in India.
- It is designed to offer realistic, high-fidelity training to the Indian Army, Navy, Air Force, and paramilitary forces for combat drone operations in complex scenarios such as GPS-denied zones and coordinated multi-drone missions, the company said.
- The simulator is built using AI-based technologies, physics engines, and real-time terrain dynamics, and replaces reliance on imported systems and offers a secure, cost-effective alternative rooted in domestic innovation.
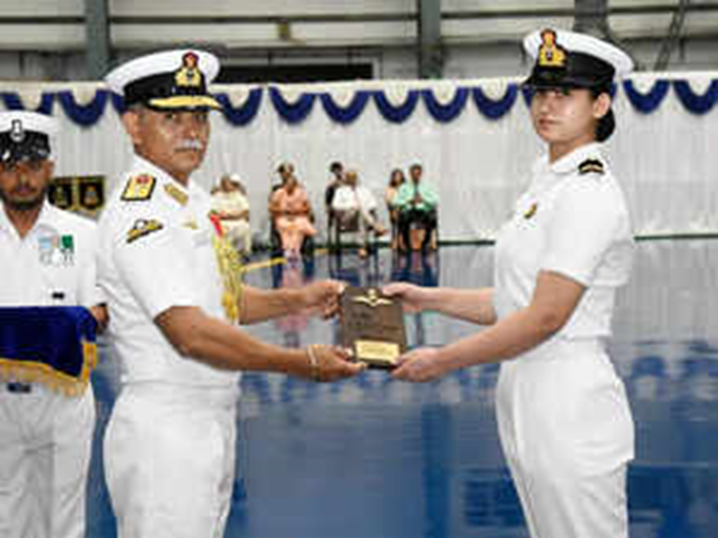
Sub Lt Poonia Becomes First Woman To Be Inducted Into Fighter Stream
- Sub Lt Aastha Poonia has become the first woman to be inducted into the fighter stream of naval aviation, paving the way for a new era of women fighter pilots in the force.
- She will now undergo training for qualifying as a fighter pilot. The Indian Navy celebrated the graduation of the Second Basic Hawk Conversion Course at INS Dega, Visakhapatnam. The Indian Navy has already inducted women officers as pilots and naval air operations officers in Maritime Reconnaissance (MR) aircraft and helicopters, the statement said.
- Streaming of Sub Lt Poonia into the fighter stream highlights the Navy’s commitment towards “gender inclusivity in naval aviation”, fostering a culture of equality and opportunity, it added.
India Completes Development of K-5
- DRDO has successfully completed the development of the K-5 submarine-launched ballistic missile (SLBM), marking a significant advancement in the country’s nuclear deterrence capabilities.
- The missile’s completion was revealed during the foundation stone laying ceremony of the Kerala Space park (KSPACE) in Thiruvananthapuram on June 25, 2025, where a former BrahMos Aerospace scientist confirmed that the K-5 has an operational range of 5,000 to 6,000 kilometres.
- The K-5 represents the pinnacle of India’s secretive “K” series of submarine-launched ballistic missiles, named in honour of former President A.P.J. Abdul Kalam.
- This development builds upon the successes of its predecessors, including the K-15 (750 km range) and K-4 (3,500 km range), which have already been successfully tested and inducted into service.
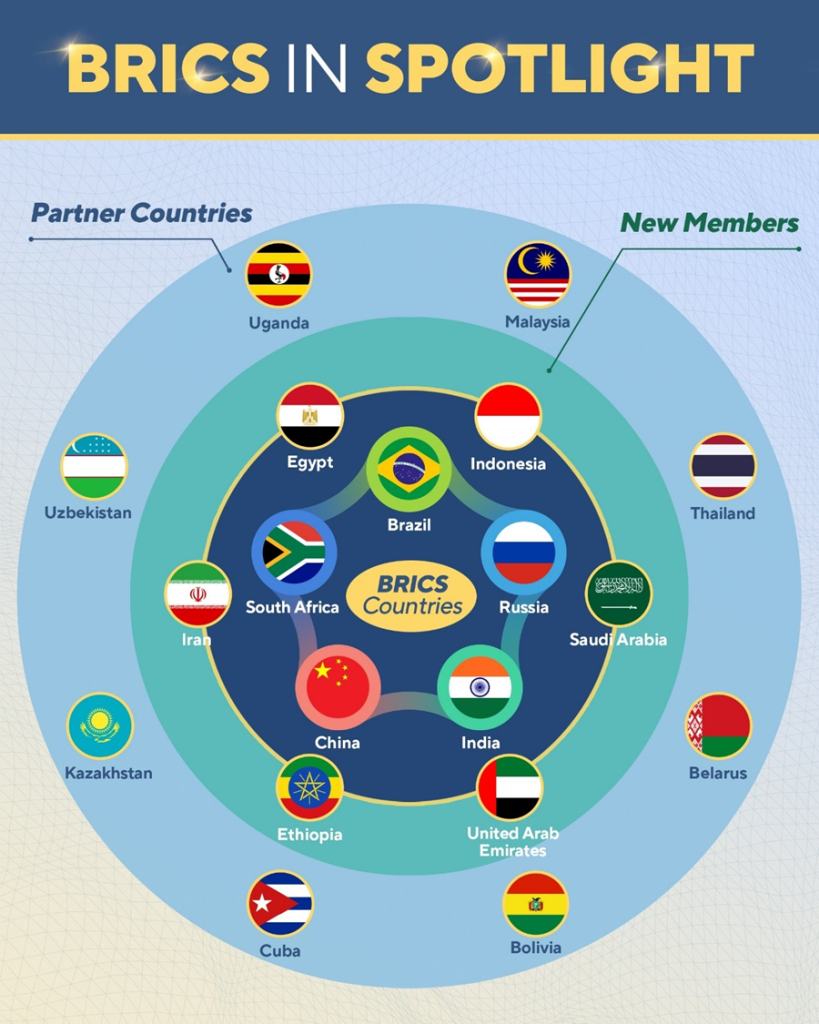
17th BRICS Summit
- Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi participated in the 17th BRICS Summit, held in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, on 6–7 July 2025, marking a significant step in India’s diplomatic engagements with the BRICS nations – Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa. The summit witnessed wide-ranging and productive discussions on critical issues such as reform of global governance, peace and security, multilateral cooperation, development priorities, and Artificial Intelligence (AI).
- Inaugural Session: Reforming Global Governance and Peace & Security
- In his address during the inaugural session on “Reform of Global Governance and Peace and Security,” Prime Minister Modi strongly reaffirmed India’s commitment to enhancing the voice of the Global South. He highlighted the need for greater support for developing nations, particularly in accessing climate finance and advanced technology for sustainable development.
- He emphasized that 20th-century global institutions are not equipped to face 21st-century challenges, making urgent reforms necessary. Institutions like the UN Security Council, IMF, World Bank, and WTO must be restructured to reflect the contemporary global order. He appreciated the summit’s strong language on the urgency of UNSC reforms in the ‘Rio de Janeiro Declaration’.
- On the topic of peace and security, the Prime Minister condemned terrorism, calling it a grave threat to humanity. Referring to the Pahalgam terror attack in April 2025, he asserted that it was not just an assault on India but an attack on all of humanity. He urged for zero tolerance against terrorism and demanded strict action against those funding, promoting, or sheltering terrorists. He also thanked the BRICS leaders for strongly condemning the Pahalgam attack and called for unified efforts to combat the menace globally.
- The Prime Minister also expressed concern over the ongoing conflicts from West Asia to Europe, reiterating India’s consistent stance advocating for dialogue and diplomacy as the only viable means to resolve disputes.
- Session on Strengthening Multilateralism, Economy, and AI
- In the session titled “Strengthening Multilateralism, Economic-Financial Affairs and Artificial Intelligence,” which included BRICS partner and invited countries, Prime Minister Modi emphasized the significance of diversity and multipolarity as key strengths of the BRICS platform. He remarked that in today’s unstable global environment, the relevance of BRICS is greater than ever, as it can contribute meaningfully to shaping a balanced and multipolar world.
- He proposed four key suggestions to enhance BRICS cooperation:
- BRICS New Development Bank should follow a demand-driven approach and prioritize long-term sustainability in funding projects.
- Establishment of a Science and Research Repository to benefit the Global South.
- Strengthening and securing the supply chains of critical minerals to build resilience.
- Promoting responsible use of Artificial Intelligence – ensuring AI governance while encouraging innovation in the sector.
- Conclusion and the Rio de Janeiro Declaration
- The summit concluded with the adoption of the ‘Rio de Janeiro Declaration’, encapsulating the collective vision of the BRICS nations to reform global institutions, combat terrorism, strengthen multilateralism, and promote inclusive and sustainable development, particularly through emerging technologies like AI.
- Prime Minister Modi thanked the President of Brazil for his warm hospitality and the successful organization of the summit, reaffirming India’s active role and continued commitment to the BRICS agenda.
Key Highlights:
- PM Modi called for urgent UNSC reforms and stronger Global South representation.
- Condemned terrorism and demanded zero tolerance globally.
- Suggested a science repository, resilient mineral supply chains, and responsible AI innovation.
- Participated in two major sessions and endorsed the Rio de Janeiro Declaration.
- This summit marked yet another strong assertion of India’s global leadership in diplomacy, peace, innovation, and development partnerships.
India Secures Strategic Lithium Deals in Argentina
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s ground breaking bilateral visit to Argentina on July 5-6, 2025, marked a watershed moment in India’s quest for critical mineral security, particularly lithium, as both nations deepened their strategic partnership across multiple sectors.
- This historic visit—the first by an Indian PM to Argentina in 57 years—has resulted in significant agreements that position India as a key player in Argentina’s lithium-rich landscape within the globally significant “Lithium Triangle.”
- The strategic importance of this partnership cannot be overstated, as Argentina holds approximately 22 million metric tons of lithium reserves, making it the world’s second-largest holder of lithium resources after Bolivia, accounting for around 20-21% of global lithium reserves.
- Two major Indian public sector companies—Coal India Limited and Khanij Bidesh India Limited (KABIL)—have signed five concession agreements and are working on finalizing investments to produce, refine, and export lithium minerals.
TASL ALS-250, Indigenous Loitering Munition
- TATA Advanced Systems Limited’s (TASL) ALS-250 represents a significant leap in India’s indigenous defence capabilities, particularly in the domain of long-range precision strike weaponry.
- The ALS-250 is a fully indigenous loitering munition, engineered to deliver high-precision strikes at ranges up to 250 kilometers.
- Its deployment can significantly alter the operational calculus by threatening a range of high-value military and strategic assets, thereby enhancing India’s deterrence posture and offering a credible option for punitive or pre-emptive actions in the event of hostilities.
Indian Navy Signs Contract with BEL
- The Indian Navy has signed a contract with a major defence PSU for the implementation of the National Maritime Domain Awareness (NMDA) Project towards strengthening maritime and coastal security, the defence ministry said.
- The contract was signed in the presence of Deputy Chief of the Naval Staff, Vice Admiral Tarun Sobti, and Chairman and Managing Director, Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL), Bengaluru, Manoj Jain.
- The project will bring in an integrated approach to data collation, analysis and information sharing among the various maritime stakeholders.
- The project entails the upgrade of the existing National Command, Control, Communication and Intelligence (NC3I) Network to the NMDA Network along with the incorporation of AI-enabled software, the ministry said.
- The existing Information Management and Analysis Centre (IMAC) at Gurugram, which is the nodal centre of NC3I Network, will also be upgraded into a multi-agency NMDA Centre hosting representatives from various national agencies
Indian Ocean Region With Six Stealth Frigates
- The Indian Navy will sharpen its edge in the Indian Ocean region with the induction of six locally made warships in around a year, a step towards strengthening its hold on the vast maritime expanse where China is steadily boosting its influence, officials aware of the matter said.
- The Project 17A stealth frigates that the navy will commission into service by August-September 2026 are Udaygiri, Taragiri, Mahendragiri, Himgiri, Dunagiri and Vindhyagiri — platforms that will showcase the country’s warship building prowess.
- Have an indigenous content of 75% and come with modern weapons, sensors and systems to dominate the sea battlespace
- The navy inducted the first P-17A warship INS Nilgiri in January and is expected to commission Udaygiri in August. The ₹45,000-crore P-17A is a follow-on of the Shivalik-class (P-17) stealth frigates and represents a significant upgrade over the previous warships.
- Taragiri and Mahendragiri are being built at MDL and Himgiri, Dunagiri and Vindhyagiri are in different stages of construction at GRSE Limited.
- Taragiri and Mahendragiri will be delivered to the navy after the completion of necessary trials in October 2025 and February 2026,
- The navy usually commissions a warship one or two months after its delivery. MDL delivered Udaygiri to the navy on July 1. The weapons on the P-17A warships include BrahMos supersonic cruise missiles and the medium-range surface-to-air missile system.
- Himgiri, Dunagiri and Vindhyagiri are expected to be delivered to the navy in July-end, early next year and August 2026, people aware of the matter said.
- The P-17A stealth frigates have a displacement of 6,670 tonnes, are 149 metres long, can reach a top speed of 28 knots and carry 225 personnel.
Delivery of First Indigenous DSV
- ‘Nistar’, the first indigenously designed and constructed Diving Support Vessel, was delivered by Hindustan Shipyard Limited to the Indian Navy on 08 Jul 2025 at Visakhapatnam.
- The ship is highly specialised and can undertake Deep Sea Diving and Rescue Operations – a capability with select Navies across the globe.
- The ship’s name, ‘Nistar’, originates from Sanskrit and means liberation, rescue or salvation.
- The ship, measuring 118 m with a tonnage of nearly 10,000 tons, is installed with state-of-the-art Diving Equipment and has the capability to undertake Deep Sea Saturation Diving up to 300 m depth.
- The ship also has a Side Diving Stage for undertaking Diving Operations up to 75 m depth.
- The delivery of Nistar, with nearly 75% indigenous content, is yet another milestone in the Indian Navy’s quest for indigenous construction.
LORA Could Be India’s Next Big Strike Weapon
- The Indian Air Force wants more reach. Despite owning the formidable BrahMos, it’s now looking at Israel Aerospace Industries’ Air-Launched Long-Range Artillery (Air LORA) missile.
- This comes hot on the heels of May’s Operation Sindoor, where the Rampage missile got its first taste of combat and proved how vital stand-off range really is.
- Air LORA isn’t a minor tweak. It’s a quasi-ballistic, supersonic missile that flies about 400–430 kilometres and lands within ten metres of its target.
- LORA isn’t your typical cruise missile. It blends ballistic missile traits with air-launch flexibility. Instead of hugging the ground like BrahMos, it soars on a high, depressed trajectory. That makes it trickier to shoot down.
- Back in 2023, IAI and Bharat Electronics Limited signed a Memorandum of Understanding to co-produce advanced missile systems. If LORA gets the green light, expect licensed production under Make in India.
- Range: 400–430 km
- Speed: Supersonic, about Mach 5
- Accuracy: Less than 10-metre CEP
- Warhead: Blast fragmentation or deep-penetration, up to 570 kg
- Weight: 1,600 kg; Length: 5.2 metres
Successful Flight-Test of Astra
- DRDO & IAF successfully conducted the flight-test of indigenous Beyond Visual Range Air-to-Air missile (BVRAAM) ‘Astra’ equipped with indigenous Radio Frequency (RF) Seeker from Su-30 Mk-I platform off the coast of Odisha on July 11, 2025.
- During the tests, two launches were carried out against high-speed unmanned aerial targets at different ranges, target aspects and launch platform conditions. In both the cases, the missiles destroyed the targets with pin-point accuracy.
- Astra BVRAAM has a range exceeding 100 kms and is equipped with state-of-the art guidance and navigation system.
- In addition to various laboratories of DRDO, more than 50 public and private industries including HAL have contributed towards successful realisation of the weapon system.
Operation Baam
- Operation Baam (Dawn), launched by the Balochistan Liberation Front (BLF), represents the most extensive and coordinated militant offensive in Balochistan’s recent history, crippling large parts of the province through over 70 simultaneous attacks across multiple districts.
- The operation, named after the Balochi word for “dawn,” marks a strategic shift for the BLF from traditional hit-and-run tactics to open, frontal assaults on military posts, police checkpoints, and critical infrastructure.
- The attacks disrupted internet connectivity, halted train services, and blocked major highways, including key sections of the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC)—a central feature of China’s Belt and Road Initiative.
- Telecom towers were destroyed, and major roads such as the Quetta-Sibi Road and Kalat-Manguchar stretch were blocked, causing widespread paralysis of movement and commerce.
‘Maratha Military Landscapes of India’ on the UNESCO World Heritage List
- The Prime Minister, Shri Narendra Modi has expressed immense pride and joy over the inclusion of the Maratha Military Landscapes of India in the prestigious UNESCO World Heritage List.
- He noted that the inscribed heritage comprises 12 majestic forts- 11 located in Maharashtra and 1 in Tamil Nadu.
- The inscription recognises a strategic defence network developed between the 17th and 19th centuries across present-day Maharashtra and Tamil Nadu.
- The proposal was sent to the consideration of World Heritage Committee in January 2024 and after a rigorous eighteen-month long process involving several technical meetings with the advisory bodies and visit of International Council on Monuments and Sites mission to review the sites, this historic decision was taken by the members of the World Heritage Committee last evening at UNESCO Headquarters, Paris.
Exercise Talisman Sabre 2025
- The largest-ever war-fighting drills in Australia, Exercise Talisman Sabre, are underway and expected to attract the attention of Chinese spy ships.
- Talisman Sabre began in 2005 as a biennial joint exercise between the United States and Australia.
- This year, more than 35,000 military personnel from 19 nations, including Canada, Fiji, France, Germany, India, Indonesia, Japan, the Netherlands, New Zealand, Norway, Papua New Guinea, the Philippines, South Korea, Singapore, Thailand, Tonga, and the United Kingdom, will take part over three weeks.
- The exercise will also take place in Papua New Guinea, Australia’s nearest neighbor. It is the first time Talisman Sabre activities have been held outside Australia.
Kanpur’s MKU Wins Major Helmet Supply Contract
- Kanpur-based MKU Limited has achieved a major milestone by securing a multi-year contract to supply over 200,000 advanced ballistic helmets to an undisclosed Southeast Asian country, marking one of the largest such deals in the region’s defence sector.
- MKU’s helmets, certified to the NIJ Level IIIA standard, were chosen for their lightweight construction, comfort, and proven reliability in field conditions.
- The contract includes specialised helmet configurations for paratrooper and airborne units, tailored to meet the specific operational needs of the client’s military forces. These features highlight MKU’s ability to customise solutions for demanding military applications.
Romania to Become First European Country to Acquire Iron Dome
- In a landmark move, Romania has confirmed plans to acquire Israel’s Iron Dome system, becoming the first European country to integrate the combat-tested, short-range missile defense platform into its arsenal.
- Valued at over €2 billion (2.34 billion USD), the deal will deliver a comprehensive Very Short and Short Range Air Defense system, intended to plug a critical gap in Romania’s layered air defense network.
- Romania’s Iron Dome acquisition will include multiple batteries, each consisting of Tamir interceptor missiles, EL/M-2084 radar units, and advanced battle management systems.
- While Romania already fields US-made Patriot systems for medium- and long-range threats, it has lacked an effective counter to short-range projectiles, drones, and cruise missiles.
DRDO & AIIMS Bibinagar Unveil First Make-in-India Carbon Fibre Foot Prosthesis
- First Make-in-India cost-effective advanced Carbon Fibre Foot Prosthesis, indigenously designed and developed by DRDO’s Defence Research & Development Laboratory (DRDL) and AIIMS Bibinagar was unveiled at AIIMS Bibinagar, Telangana.
- AIIMS Bibinagar – DRDL, DRDO Indigenously Developed Optimised Carbon Foot Prosthesis a major breakthrough under the Aatmanirbhar Bharat initiative, was launched by Distinguished Scientist & Director, DRDL Dr GA Srinivasa Murthy and Executive Director, AIIMS Bibinagar Dr Ahanthem Santa Singh.
- ADIDOC is biomechanically tested to loads up to 125 kgs with sufficient factor of safety. It has three variants to cater to patients of different weights.
- It is expected to reduce the cost significantly to as low as less than Rs 20,000 in production in comparison to the current imported similar products that cost around Rs two lakh.
Ultra Long-Range Strike Aircraft (ULRA)
- A plan to field the world’s first 12,000 km-class indigenous strategic bomber would vault the Indian Air Force from a regional force into a power with truly intercontinental reach.
- The proposed Ultra Long-Range Strike Aircraft (ULRA) is envisioned as a stealthy, swing-wing platform able to deliver nuclear or conventional payloads anywhere on the globe without aerial refuelling.
- If the Defence Ministry’s 2032-2035 prototype target is met, India would join the United States, Russia and China as the only nations operating strategic bombers.
- New Delhi therefore seeks a “sky-based” leg to complement its land- and sea-based nuclear forces, giving leaders a survivable platform able to launch retaliatory strikes even if forward bases or missile silos are compromised.
India Successfully Test-fires Prithvi-II and Agni-1
- India on Thursday conducted back-to-back test-firings of two short-range ballistic missiles—Prithvi-II and Agni-1—from its missile testing facility in Chandipur, Odisha. The Ministry of Defence confirmed the successful launch of both systems, stating they met all mission objectives.
- The Ministry posted on social media platform X that both launches were conducted under the Strategic Forces Command, the military arm responsible for managing India’s nuclear arsenal.
- Prithvi-II missile has a range of around 350 kms and it is capable of carrying a payload of up to 500 kgs. It can carry both conventional as well as nuclear warheads.
- The Agni-I missile has a range of 700-900 kms and it can carry a payload of 1,000 kgs. Both Prithvi-II and Agni-I missiles have been an integral part of India’s nuclear deterrence.
- India also test-fired the indigenously developed Akash Prime missile in Ladakh. This missile is designed to operate at altitudes above 4,500 meters.
- Akash Prime is an upgraded version of the Akash weapon system for the Indian Army. The test-firing in Ladakh is important because of its proximity to the Line of Actual Control (LAC).
SIMBEX Exercise 2025
- The Indian Navy will participate in the 32nd edition of exercise SIMBEX as part of its engagement with the Singapore Navy. It is one of the longest uninterrupted maritime exercises for India, High Commissioner to Singapore Shilpak Ambule has said.
- The Singapore India Maritime Bilateral Exercise (SIMBEX) is conducted annually by the Indian Navy and the Republic of Singapore Navy (RSN). It will be held in Singapore later this month.
- It was previously known as Exercise Lion King.
- The Indian naval ships’ visit is happening as India and Singapore celebrate the 60th anniversary of bilateral relations.
BEML Gets Order Worth Rs 157.33 cr
- BEML Ltd, a public sector undertaking, on Friday said it has been awarded a Rs 157.33 crore order by the Ministry of Defence for the supply of 79 units of its flagship Power Angling & Tilting (PAT) Bulldozers.
- Building on its proven track record of delivering robust machinery for challenging environments, BEML continues to play a vital role in supporting critical infrastructure and snow-clearing operations along India’s frontiers, the company said.
- This new order follows the company’s successful execution of an earlier contract for 66 Bulldozers, all of which were delivered well within the stipulated timeline, reflecting BEML’s commitment to quality and timely delivery.
- With an established in-house R&D setup and state-of-the-art production facilities in Bengaluru, Mysuru and KGF, BEML continues to strengthen India’s self-reliance in defence manufacturing, the company said.
Lakshadweep Govt Plans To Takeover Bitra Island For Defence Needs
- The government of Lakshadweep is set to take over Bitra island, an atoll in the Union Terrirtory, to make use of it for defence purposes. However, the move has been met with resistance with local MP Hamdullah Sayeed vowing to raise the issue in Parliament.
- A government notification, issued on July 11, outlined the proposal for Lakshadweep’s Department of Revenue to take over the entire land area of Bitra island and transfer it to relevant Central defense and strategic agencies.
- With 271 residents, as per the Census 2011, Bitra is the least populated among the 10 inhabited islands in the Lakshadweep UT.
- With this move, Bitra would become the third island in the archipelago with a defence establishment – two Indian naval bases in the archipelago are INS Dweeprakshak in Kavaratti, the capital of the UT, and INS Jatayu in Minicoy, the southernmost island.
Launch of Yard 3034 (AJAY)
- Yard 3034 (Ajay), the eighth and last ship of Anti-Submarine Warfare Shallow Water Craft (ASW SWC), indigenously designed and built by Garden Reach Shipbuilders and Engineers (GRSE) has been launched on 21 Jul 2025 at GRSE, Kolkata
- The first Ship of the class Arnala was commissioned on 18 Jun 2025 and delivery of the second ship is planned in Aug 2025. The warship will augment Indian Navy’s underwater domain awareness, Anti-Submarine Warfare and mine laying capabilities.
- The ship is equipped with role defining sensors such as a Hull Mounted Sonar and Low Frequency Variable Depth Sonar (LFVDS), and firepower provided by state-of-the-art Torpedoes, Anti-Submarine Rockets, NSG-30 Gun and 12.7 mm SRCG. The ship is powered by diesel engines and propelled by Waterjets.
- With an indigenous content of over 80%, the ship exemplifies the Government of India’s initiative of Aatmanirbhar Bharat and Make in India and will provide significant capabilities to secure our national maritime interests in the Indian Ocean Region.
India Set To Develop NETRA MK-II AWACS System
- India has taken a decisive step toward enhancing its air defence and battlefield situational awareness with the government’s clearance of the ₹20,000 crore NETRA MK-II project—an ambitious next-generation Airborne Warning and Control System (AWACS) initiative led by the DRDO.
- This significant undertaking will see six Airbus A321 aircraft, previously acquired from Air India, undergo extensive modifications in collaboration with Airbus and Indian private sector firms to serve as cutting-edge aerial surveillance platforms equipped with fully indigenous Active Electronically Scanned Array (AESA) radars.
- The NETRA MK-II’s technological centrepiece is its indigenous AESA radar, to be installed in a prominent dorsal fin-like structure atop each aircraft. This configuration delivers true 360-degree coverage, enabling long-range detection, tracking, and identification of enemy aircraft, missiles, UAVs, and select ground assets—well beyond India’s borders.
Indian Army Gets ‘Tank In The Air’
- The Indian Army has announced that it has received the first batch of three AH-64E Apache attack helicopters from the United States, marking a significant enhancement to its combat capabilities. The helicopters were formally inducted on July 22, 2025, following their arrival at Hindon Air Force Station near Delhi.
- The delivery had been delayed by over 15 months due to global supply chain disruptions and shifting geopolitical conditions.
- These helicopters were originally scheduled to arrive between May and June 2024 under a $600 million deal signed in 2020 to acquire six Apaches for the Army.
- The Apache squadron based in Jodhpur, Rajasthan, was established more than 15 months ago, but deployment was postponed awaiting these deliveries.
- It carries a 30mm chain gun, Hellfire missiles, rocket pods, and Longbow radar, enabling precision strikes in day, night, and adverse weather conditions.
Indigenous Pollution Control Vessel ‘Samudra Prachet’
- ‘Samudra Prachet’, the last of the two indigenous Pollution Control Vessels (PCVs) constructed by Goa Shipyard Ltd (GSL) was launched for Indian Coast Guard (ICG) in Goa on July 23, 2025.
- With 72% indigenous content, the project has significantly contributed to national capability-building, employment generation, and skills enhancement, through active engagement of the local industry and MSMEs.
- These ships have been fitted with state-of-art Response Equipment and these vessels will help ICG in quick and effective response to any oil spill in the Exclusive Economic Zone.
- With a length of 114.5 metres, a breadth of 16.5 metres, and a displacement of 4,170 tonnes, the ship will be manned by 14 officers and 115 sailors.
- The First Pollution Control Vessel was launched on August 29, 2024 and is expected to be delivered soon.
Turkey Now Has A Hypersonic Missile
- Turkey has unveiled its first hypersonic missile, the Tayfun Block-4, at the International Defence Industry Fair (IDEF) 2025 in Istanbul, marking a significant milestone in its defence capabilities.
- Developed indigenously by the Turkish defence firm Roketsan, the Tayfun Block 4 is a hypersonic ballistic missile weighing approximately 2,300 kilograms (about 7 tons according to some reports) and measuring around 6.5 to 10 meters in length.
- It boasts a range of about 800 kilometres, with plans to extend this to over 1,000 kilometres in future variants, enabling it to strike strategic targets deep inside enemy territory with high accuracy (within 5 to 10 meters) and high speed (estimated at Mach 5 or above) .
- This hypersonic weapon places Turkey in the ranks of a select group of nations—alongside the United States, Russia, and China—that have developed and deployed hypersonic missile technology, underlining the country’s growing military technological independence and regional strategic power .
Why Thailand and Cambodia are Fighting
- Tensions between Thailand and Cambodia have once again turned violent, with fighter jets, landmines, and diplomatic expulsions marking the worst escalation in years. At the centre of the dispute is the 11th-century Preah Vihear Hindu temple, located near their shared border.
- The Preah Vihear temple, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, sits atop the Dangrek mountain range. It’s an impressive piece of Khmer architecture, but also a source of national pride and dispute.
- The border clashes on Thursday led to at least nine civilian deaths and over a dozen injuries. Explosions hit a petrol station in Thailand’s Si Sa Ket province, killing several Thai civilians.
- In response, Thai jets launched airstrikes on Cambodian military positions near the disputed temple. Cambodia accused Thailand of bombing nearby roads. Skirmishes were reported in six different areas along the border.
- The violence follows weeks of growing tension. In May, a Cambodian soldier was killed, and in July, two Thai soldiers were badly injured in landmine blasts.
- Diplomatic relations quickly worsened, both countries expelled each other’s ambassadors and recalled their envoys, blaming one another for aggression and border violations.
- In 1962, the International Court of Justice (ICJ) ruled that the temple belonged to Cambodia, based on a 1907 French-drawn map. Thailand disagreed with the decision, arguing the map was not properly accepted.
- Still, the court decided Thailand had accepted the border and ordered it to withdraw troops and return any items taken from the temple.
DRDO Conducts Successful Trials of Drone Missile
- In a major boost to India’s defence capabilities, DRDO has successfully carried out flight-trials of UAV Launched Precision Guided Missile (ULPGM)-V3 at the National Open Area Range (NOAR) test range in Kurnool, Andhra Pradesh.
- The missile is an enhanced version of the ULPGM-V2 missile developed and delivered by DRDO earlier.
- The ULPGM-V3 is equipped with a high definition dual-channel seeker that can strike a wide variety of targets. It can be fired in plain and high-altitude areas.
- It has day-and-night capability and two-way data link to support post-launch target/aim-point update.
- The missile is equipped with three modular warhead options: Anti-armour to destroy modern age armoured vehicles equipped with Rolled Homogeneous Armour (RHA) with Explosive Reactive Armour (ERA);
- Penetration-cum-Blast warhead with Anti Bunker application and Pre-fragmentation warhead with a high lethality zone.
MoD inks Rs 2,000 Crore Contract with BEL
- MoD has signed a contract with Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL) for the procurement of Air Defence Fire Control Radars for the Indian Army, worth approx. Rs 2,000 crore, under the Buy (Indian-Indigenously Designed Developed and Manufactured) category.
- With minimum 70% indigenous content, these Fire Control Radars will be able to detect all forms of air-borne threats, including fighter aircraft, attack helicopters and enemy drones.
- This would mark a significant milestone in the modernisation of the Air Defence Regiments and enhance the Indian Army’s operational readiness, while contributing to the economic growth of the nation.
- The procurement marks a pivotal step towards empowering indigenous defence industries by encouraging Indian MSMEs through components’ manufacturing and raw material supply.
Exercise Bold Kurukshetra 2025
- The 14th edition of the India–Singapore Joint Military Exercise, Exercise Bold Kurukshetra 2025, is set to commence today at Jodhpur and will continue till 04 August 2025.
- The exercise will witness the participation of the 42 Singapore Armoured Regiment of the 4 Singapore Armoured Brigade and the Indian Army’s Mechanised Infantry Regiment.
- The exercise will be conducted as a Table Top Exercise and Computer-Based Wargame, aimed at validating operational procedures for mechanised warfare. It will culminate in an equipment display by the Indian Army.
- Exercise Bold Kurukshetra 2025 will further consolidate the strong defence ties between India and Singapore and foster greater mutual understanding and collaboration at both tactical and strategic levels.
Nibe Limited Signs Agreement with With Elbit Systems
- Private defence manufacturing company NIBE Limited signed a Technology Collaboration Agreement with Elbit Systems, a Israeli defence company for Advanced Universal Rocket Launcher manufacturing.
- The partnership is aimed at manufacturing and supply of Universal Rocket Launcher (SURYA), which is a highly advanced defence system capable of engaging targets with precision over a range of up to 300 km.
- This technology transfer will be the first time that such a sophisticated system will be produced in India, paving the way for both domestic and international markets.
Army Conducts ‘Drone Prahaar’ Drill
- The Indian Army recently conducted an advanced military exercise named ‘Exercise Drone Prahaar’ near the Myanmar border, specifically in the forward areas under the Dimapur-based Spear Corps (III Corps).
- This drill took place just days after multiple drone strikes destroyed bases of the outlawed United Liberation Front of Asom-Independent (ULFA-I) in Myanmar, although the Indian Army officially denied any involvement in those strikes.
- The primary objective of Exercise Drone Prahaar was to validate and showcase the integration of drone technology into tactical operations involving infantry and supporting arms.
- The exercise was executed under realistic operational environments, emphasising the deployment of drones for Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance (ISR), real-time sensor-to-shooter communication links, and precision targeting across tactical and operational battlefield layers.
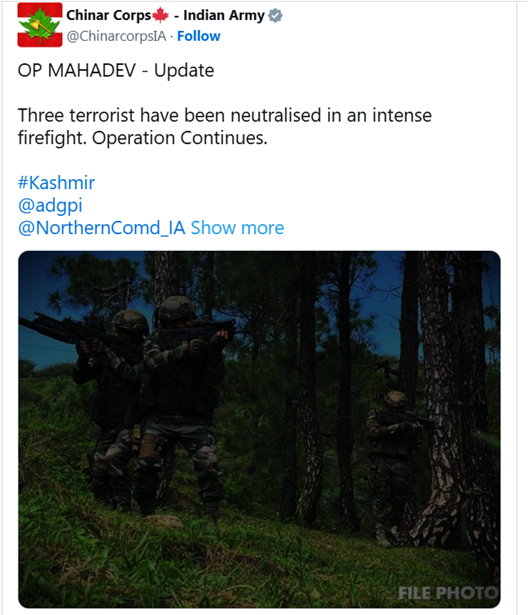
Operation Mahadev
- In a joint counter-terror operation on Monday, Indian Army para commandos shot dead three terrorists in the Harwan area near Dachigam Forest on the outskirts of Srinagar. Among those killed was Hashim Musa, also known as Suleman or Sulieman, who officials say was behind the deadly Pahalgam attack in April that left 26 people dead, including 25 tourists and a local resident.
- The Indian Army confirmed the operation, codenamed Mahadev, was launched after security forces picked up a satellite phone signal. The same device, according to officials, had been used by those involved in the Pahalgam massacre.
- At 12:37 PM, the Chinar Corps said that a contact was established with the terrorists in General Area Lidwas and in less than an hour drone footage showed three bodies, confirming that three terrorists were neutralised.
- The anti-terror operation had been in progress for two days, following the interception of suspicious communication from deep inside the Dachigam forests. Local nomads also provided crucial inputs, helping the forces narrow down the location of the suspects, sources said.
- Intelligence indicated that the terrorists were affiliated with Lashkar-e-Taiba (LeT), the group that had claimed responsibility for the Pahalgam attack.
- The operation was launched after a lone Chinese satellite phone was detected as active in the Baisaran area on July 11. This triggered a coordinated search involving the Army, J&K Police, and CRPF. Subsequent intelligence inputs, including information from local nomads, further confirmed terrorist movement in the region.
Drones At Home In Rare Tech Transfer Deal
- India is on the verge of finalising a landmark defence deal with US-based Shield AI that will enable the IAF to acquire the advanced V-BAT combat drones while also establishing local manufacturing under a rare full technology transfer agreement.
- As part of a $4.5 billion emergency procurement program initiated after Operation Sindoor, the Indian Ministry of Defence is in advanced talks to purchase enhanced V-BAT drones from Shield AI for $35 million—the ceiling for emergency contracts.
- Parallel to this, Shield AI and JSW Defence (a division of the JSW Group) have inked a $90 million joint venture agreement to transfer full drone technology to India.
- The V-BAT is a Group 3 unmanned aerial system (UAS) featuring fixed wings and vertical take-off and landing (VTOL) capability, providing long endurance for intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) missions.
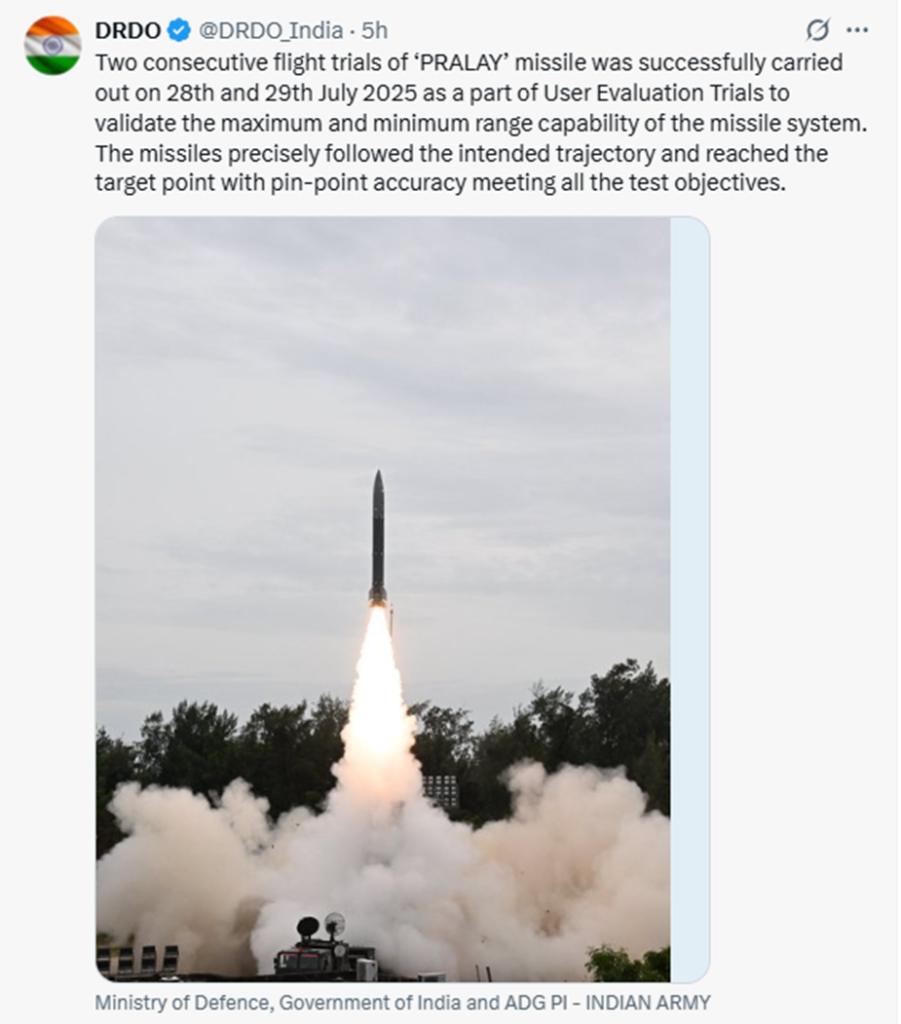
DRDO Successfully Conducts Two Consecutive Flight-tests of Pralay Missile
- DRDO conducted two consecutive successful flight-tests of Pralay missile from Dr APJ Abdul Kalam island off the coast of Odisha on July 28 & 29, 2025.
- The flight tests were carried out as a part of User Evaluation Trials to validate the maximum and minimum range capability of the missile system.
- Pralay is an indigenously-developed solid propellant quasi-ballistic missile employing state-of-the-art guidance and navigation to ensure high precision. The missile is capable of carrying multiple types of warheads against various targets.
- What Pralay is
- Role: Canister‑launched, road‑mobile, solid‑fuel quasi‑ballistic missile for precision, conventional strikes against high‑value targets (radars, air bases, logistics nodes) without crossing the nuclear threshold.
- Developer: DRDO’s Research Centre Imarat with multiple DRDO labs; production partners include BDL and BEL.
- Key technical features
| Parameter | Current figures* | Notes |
| Range | 150 – 500 km (upgrade path to ~700 km reported) | Terminal maneuvers help evade BMD. |
| Warhead | 350–700 kg HE fragmentation, PCB, RDPS | Conventional only. |
| Accuracy | < 10 m CEP | INS + GPS / MMW seeker. |
| Mobility | Twin‑cell launcher on 12×12 Ashok Leyland HMV TEL | 10 min from move‑stop to launch. |
| Speed | Supersonic; terminal > Mach 5 | Quasi‑ballistic trajectory. |
Indian Army to raise all-arms brigade ‘Rudra’, light commando battalions ‘Bhairav’
- The Indian Army is in process of raising a new fighting formation with all arms configuration while the army is continuously evolving into a modern and future-oriented power, said Army Chief.
- General Upendra Dwivedi said, “The Indian Army is in the process of raising an all-arms brigade named ‘Rudra’, wherein the fighting components of infantry, mechanised infantry, armoured units, artillery, special forces and Unmanned Aerial Systems will be integrated, backed by specially designed logistics and combat support.
- The initial proposals pertaining to the Integrated Battle Groups were that the IBGs are expected to be led by a Major-General rank officer. Each IBG will have a troop strength of around 5,000 personnel, larger than a brigade (3,000-3,500 troops) but smaller than a division (10,000-12,000 troops).
- General Dwivedi announced the establishment of ‘Rudra’ all arms brigades, ‘Bhairav’ light commando battalions, ‘Shaktibaan’ artillery regiments and ‘Divyastra’ batteries, drone-equipped infantry battalions, and indigenous air defence systems.
Multiple Choice Questions of DCA
- How many dedicated satellites does India plan to launch for its armed forces?
A. 25
B. 40
C. 52
D. 60
ANSWER: C - What is the main goal of the ‘QUAD at Sea Ship Observer Mission’ launched
under the Wilmington Declaration?
A. Conduct trade negotiations among QUAD countries
B. Promote tourism in the Indo-Pacific region
C. Enhance maritime security and interoperability among QUAD Coast Guards
D. Train navy personnel in joint warfare
ANSWER: C - Which of the following is the Indo-French defence exercise between the Indian
and French Air Forces?
A. VARUNA
B. SHAKTI
C. GARUDA
D. SURYA KIRAN
ANSWER: C - Brazil is particularly interested in collaborating with India in the acquisition
and possible co-production of which Indian military platform?
A. Akash Surface-to-Air Missile
B. Arjun Main Battle Tank
C. Garuda 105_v2 artillery gun
D. Pinaka Multi-Barrel Rocket Launcher
ANSWER: C - What significant achievement was announced by IG Drones?
A. Launch of a new satellite
B. Development of anti-drone guns
C. Patent for India’s first defence drone simulator
D. Merger with Garuda Aerospace
ANSWER: C - Who has become the first woman to be inducted into the fighter stream of
naval aviation?
A. Lt Commander Shubhangi Swaroop
B. Sub Lt Aastha Poonia
C. Lt Shivangi
D. Sub Lt Riti Singh
ANSWER: B - What is the range of the K-4 submarine-launched ballistic missile?
A. 500 km
B. 750 km
C. 1,500 km
D. 3,500 km
ANSWER: D - Where was the 17th BRICS Summit held in July 2025?
A. New Delhi, India
B. Beijing, China
C. Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
D. Moscow, Russia
ANSWER: C - What was the theme of PM Modi’s address at the inaugural session of the
BRICS Summit 2025?
A. Energy Cooperation and Trade
B. Reform of Global Governance and Peace and Security
C. Climate Change and Global Warming
D. Technological Innovation and Development
ANSWER: B - Which country is the world’s second-largest holder of lithium reserves after
Bolivia?
A. Brazil
B. Argentina
C. Chile
D. Australia
ANSWER: B - What is the name of the long-range precision strike weapon system developed
by TASL?
A. ALS-250
B. Trishul-X
C. Pralay-II
D. TASL-R1
ANSWER: A - Which of the following is the first Project 17A stealth frigate inducted by the
Indian Navy?
A. INS Udaygiri
B. INS Taragiri
C. INS Nilgiri
D. INS Himgiri
ANSWER: C - Which two Project 17A warships are being built by Mazagon Dock
Shipbuilders Limited (MDL)?
A. Taragiri and Mahendragiri
B. Dunagiri and Vindhyagiri
C. Udaygiri and Himgiri
D. Nilgiri and Dunagiri
ANSWER: A - What is ‘Nistar’, recently delivered to the Indian Navy by Hindustan Shipyard
Limited?
A. Amphibious assault ship
B. Drone carrier vessel
C. Diving Support Vessel
D. Fleet Oil Tanker
ANSWER: C - What type of missile is Air LORA classified as?
A. Subsonic cruise missile
B. Quasi-ballistic, supersonic missile
C. Hypersonic glide vehicle
D. Short-range surface-to-air missile
ANSWER: B - What is the purpose of the X Guard fibre optic towed decoy system ordered by
the Indian Air Force?
A. To enhance radar capabilities of Rafale
B. To increase the speed of fighter jets
C. To provide protection against enemy missiles
D. To improve aerial refueling systems
ANSWER: C - From which aircraft platform was the indigenous BVRAAM ‘Astra’ tested by
DRDO and IAF?
A. Mirage-2000
B. Rafale
C. Tejas Mk1A
D. Su-30 Mk-I
ANSWER: D - Which cultural sites from India were recently added to the UNESCO World
Heritage List?
A. Ajanta Caves
B. Hampi Temples
C. 12 Maratha forts
D. Sun Temple, Konark
ANSWER: C - Romania is the first European country to acquire which Israeli defence
system?
A. Arrow-3
B. David’s Sling
C. Iron Dome
D. Barak-8
ANSWER: C - Which ship’s induction marks the final step in Project 17A?
A. INS Himgiri
B. INS Udaygiri
C. INS Mahendragiri
D. INS Vindhyagiri
ANSWER: C - Where was the first Make-in-India advanced Carbon Fibre Foot Prosthesis
unveiled?
A. AIIMS Delhi
B. AIIMS Bibinagar
C. DRDO Headquarters, New Delhi
D. AFMC Pune
ANSWER: B - What is the strategic importance of India’s proposed ULRA (Ultra Long-Range
Strike Aircraft)?
A. It will replace all existing fighter jets
B. It will enable global strike capability without refueling
C. It will be used for surveillance missions only
D. It is meant to support maritime operations exclusively
ANSWER: B - What is the name of the maritime exercise between India and Singapore?
A. MILAN
B. SLINEX
C. VARUNA
D. SIMBEX
ANSWER: D - Which two short-range ballistic missiles were successfully test-fired by India
from Chandipur?
A. Agni-III and BrahMos
B. Nirbhay and K-15
C. Prithvi-II and Agni-1
D. Akash and Trishul
ANSWER: C - What is the main radar technology to be featured on India’s NETRA MK-II
AWACS system?
A. Pulse-Doppler Radar
B. Phased Array Radar
C. Passive Electronically Scanned Array
D. Active Electronically Scanned Array (AESA)
ANSWER: D - What is the name of the high-intensity annual security exercise launched by
the Indian Army to protect the Shri Amarnath Yatra in 2025?
A. Operation Shiva
B. Operation Trident
C. Operation Rakshak
D. Operation Vajra
ANSWER: A - Which country hosted the multinational military exercise Talisman Sabre
2025, marking India’s first participation?
A. Japan
B. United States
C. Germany
D. Australia
ANSWER: D - In which city did the Indian Army conduct the ‘Prachand Shakti’ military drill?
A. Meerut
B. Lucknow
C. Jodhpur
D. Pune
ANSWER: A - Which country does the Preah Vihear temple officially belong to, as per the
1962 ruling by the International Court of Justice?
A. Thailand
B. Vietnam
C. Cambodia
D. Laos
ANSWER: C - What is the name of the missile recently flight-tested by DRDO at the NOAR
test range in Andhra Pradesh?
A. BrahMos
B. Agni-P
C. ULPGM-V3
D. NAG
ANSWER: C
ALSO READ:
- Latest Daily Current Affairs and Defence Updates
- Monthly Defence Current Affairs June 2025 [DOWNLOAD PDF]
- Monthly Defence Current Affairs May 2025 [DOWNLOAD PDF]
- Monthly Defence Current Affairs April 2025 [DOWNLOAD PDF]
- Monthly Defence Current Affairs March 2025 [DOWNLOAD PDF]
- Monthly Defence Current Affairs February 2025 [DOWNLOAD PDF]
- Monthly Defence Current Affairs January 2025 [DOWNLOAD PDF]
- Defence Current Affairs Year End Review 2024
- Monthly Defence Current Affairs November 2024 [DOWNLOAD PDF]
- Monthly Defence Current Affairs October 2024 [DOWNLOAD PDF]
- Monthly Defence Current Affairs September 2024 [DOWNLOAD PDF]
- Monthly Defence Current Affairs August 2024 [DOWNLOAD PDF]
- Monthly Defence Current Affairs July 2024 [DOWNLOAD PDF]
- Monthly Defence Current Affairs June 2024 [DOWNLOAD PDF]
- Monthly Defence Current Affairs May 2024 [DOWNLOAD PDF]