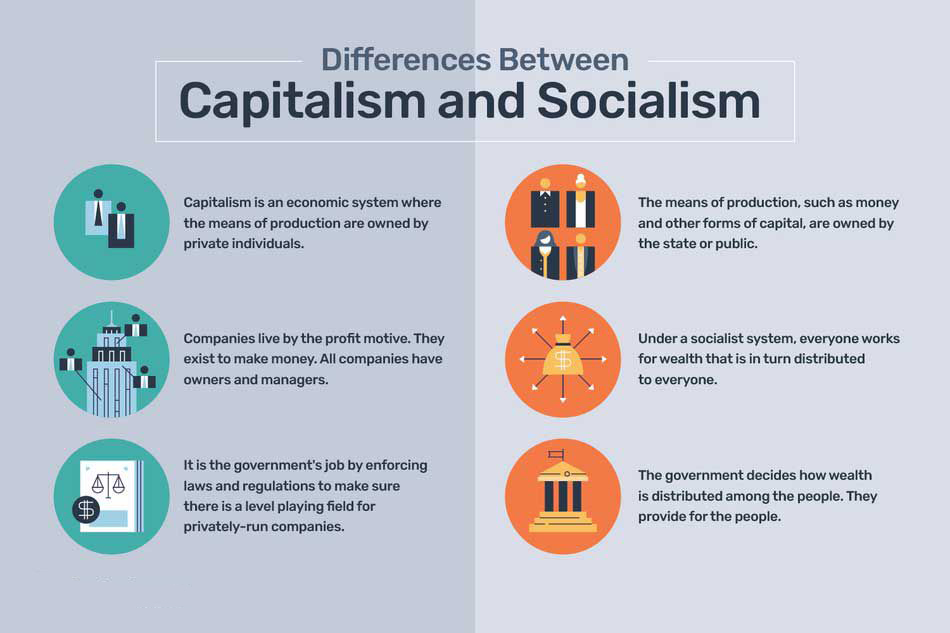
Capitalism and socialism are terms used to describe economic and political systems, respectively. Both of these terms also refer to specific schools of economic thought on a theoretical level. One of the most fundamental differences between capitalism and socialism is the extent of government intervention in the economy.
Market Economy with respect to Socialism and Capitalism
- For the creation of wealth, the capitalist economic model relies on free market conditions.
- The production of goods and services is determined by the general market’s supply and demand. A market economy is a name given to this economic structure.
- In a socialist economic model, the government either partially or completely regulates the production of goods and services. This is known as central planning, and the resulting economic structure is known as a planned economy or a command economy.
Capitalism
- Individuals own and control property and businesses in a capitalist economy. The supply of goods and services, as well as their prices, are determined by how much demand they generate and how difficult they are to produce.
- In theory, this dynamic drives companies to produce the best products possible for the lowest possible price; capitalism is intended to drive business owners to find more efficient ways of producing quality goods.
- This dynamic is intended to create a system in which consumers have the freedom to choose the best and cheapest products.
- This emphasis on efficiency comes before equality. Within a capitalist system, the equal distribution of goods and services among all members of a society is of little concern.
- Inequality, according to the economic theories that underpin capitalism, is a driving force that encourages innovation, which leads to economic development.
Socialism
- The state owns and controls the major means of production in a socialist economy. Worker cooperatives own and operate the primary means of production in some socialist economic models.
- A worker cooperative is a company that is owned and managed by its employees. Other socialist economic models permit individual ownership of business and property, albeit with higher taxes and more government control.
- The socialist economic model’s primary concern is the equitable distribution of wealth.
- Equitable wealth distribution is intended to ensure that all members of a society have an equal opportunity to achieve certain economic outcomes. To accomplish this, the government enters the labor market.
- The state is one of the primary employers in a socialist economy. During economic downturns, the socialist state can order hiring, resulting in near-full employment even if workers are not performing tasks that are in high demand in the market.
Special Considerations
- The majority of modern economies are mixed economies. This means they exist on a spectrum between pure capitalism and pure socialism, with the majority of countries employing a mixed system of capitalism in which the government regulates and owns some businesses and industries.
- Private individuals are unrestrained in the purest form of a capitalistic system (sometimes referred to as laissez-faire capitalism), and the economy operates without any government checks or controls. Individuals and businesses can decide where to invest, what to manufacture and sell, and how much to charge for goods and services.
- All means of production in a purely socialist system are collective or state-owned.
- To overcome the disadvantages of both systems, some countries combine the private sector system of capitalism and the public sector enterprise of socialism.
- In these economies, the government steps in to prevent any individual or company from taking a monopolistic position and concentrating economic power unduly. These systems’ resources may be owned by both the state and individuals.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
How does capitalism affect socialism?
Socialism is concerned with benefiting society, whereas capitalism is concerned with benefiting the individual. According to socialists, a capitalistic economy leads to inequality, with unequal wealth distribution and individuals who abuse their power at the expense of society.
Can socialism and capitalism coexist in the same country?
The majority of countries have a hybrid economic system that incorporates elements of both capitalism and socialism. There are still private businesses in many socialist countries, such as Sweden.
Is India a capitalist or socialist?
Socialism shaped the Indian government’s main economic and social policies, but it mostly followed Dirigisme after independence until the early 1990s, when India transitioned to a more market-based economy.
Is there ownership in socialism?
While socialism advocates collective or shared ownership of means of production, it does not preclude private ownership of personal property. Thus, corporations and factories would be shared among society’s members, but individuals and households would retain ownership of their personal effects.
Can a socialist country have a free market?
Socialist models entailed perfecting or improving the market mechanism and free-market system by eliminating distortions caused by exploitation, private property, and alienated labor. Because it does not involve planners, this type of market socialism is known as free-market socialism.
To crack the SSB Interview, You can join our SSB interview live classes batch and we recommend you to Enroll SSB INTERVIEW ONLINE COURSE. Trusted by thousands of defence aspirants.
Also Read:
- PM Narendra Modi Has Been Named The Most Popular Leader In The World
- India At WEF Davos Summit 2023: Here Are 10 Key Highlights
- Pakistan Economic Crisis 2023: SSB Interview Topic [Fully Explained]
- Joshimath Crisis: What Does “Land Subsidence” Mean, And Why Does It Happen?
- Top 10 Animal Conservation Projects In India [MUST WATCH]
- What Is Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) Summit 2022? [Fully Explained]
- 20 SSB Interview Questions On Russia Ukraine Crisis
- What Is The (India-Israel-UAE-USA) I2U2 Summit? [Fully Explained]
- What Is International North South Transport Corridor (INSTC)?
- What Is Sri Lankan Crisis? [Fully Explained]
- What Is The BIMSTEC Grouping And How Is It Significant? [EXPLAINED]
- What Is The Places Of Worship (Special Provisions) Act, 1991? [Explained]
- What Is Bodo Accord | SSB Interview Notes [Fully Explained]
- What Is AFSPA: Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act?
- What Is G20 Or Group Of Twenty Countries?
- What Is AFSPA: Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act?
- What Is The Financial Action Task Force (FATF)? [Fully Explained]
- What Is Quadrilateral Security Dialogue (QUAD)?
- Difference Between NATO Vs Russia [Expained]
- What Is United Nations Security Council (UNSC) [Explained]
- Everything You Need To Know About SAARC: South Asian Association For Regional Cooperation
- All About Russia Ukraine War: SSB Interview Topic [Fully Explained]