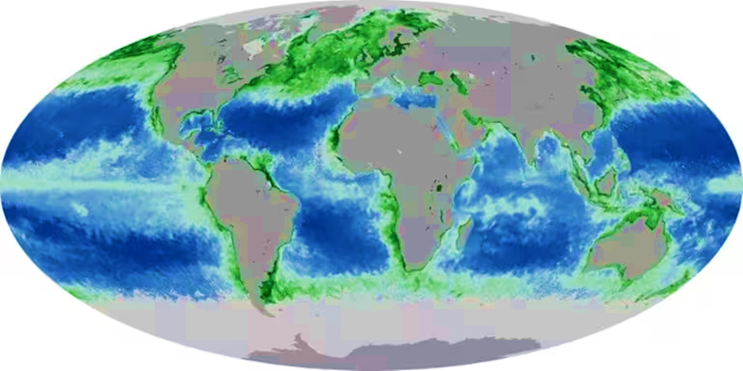
According to a new study, the colour of the Earth’s oceans has changed significantly over the last two decades, most likely as a result of human-caused climate change. The shift in colour has affected about 56% of the world’s oceans, which is more than the total land area.
Climate Change Is Altering The Colour Of The Oceans
Climate Change: Why In The News?
- The Colour Of The Earth’s Oceans Has Significantly Altered Over The Past Two Decades, Most Likely Due To Human-induced Climate Change, According To A New Study. Over 56 Per Cent Of The Oceans, More Than The Total Land Area On The Planet, Has Experienced The Shift In Colour, It Added.
- The Study, ‘Global Climate-change Trends Detected In Indicators Of Ocean Ecology’, Was Published Earlier In July In The Journal Nature.
- It Was Carried Out By BB Cael And Stephanie Henson Of The United Kingdom Based National Oceanography Centre, Kelsey Bisson Of The Oregon State University (USA), Emmanuel Boss Of The University Of Maine (USA), And Stephanie Dutkiewicz Of The Massachusetts Institute Of Technology (USA).
Climate Change: What Do We Know?
- Although The Change In the Colour Of The Oceans Doesn’t Impact Marine Life Directly, It Indicates That Marine Ecosystems Are In A State Of Flux And They Could Completely Go Out Of Balance In The Future, Severely Affecting Ocean Life And Humans Dependent On Them.
- Changes In These Ecosystems Could Impact How Productive They Are, Which Could, In Turn, Affect How Much Carbon The Ocean Stores And How Much Food Supply There Is For Fisheries.
Climate Change: What Makes The Oceans Colourful?
- In Most Regions Across The World, The Oceans Appear Blue Or Navy Blue For A Reason. This Happens Due To “The Absorption And Scattering Of Light,”.
- When The Sunlight Falls On Deep And Clear Water, Colours With Longer Wavelengths, Such As Red, Yellow And Green, Are Absorbed By The Water Molecules But Blue And Violet, Which Have A Much Shorter Wavelength, Are Reflected Back.
- But When The Water Isn’t Deep Or Clean, An Ocean Can Appear To Be Of A Different Colour. For Instance, Along Argentina’s Coastline, Where Major Rivers Merge Into The Atlantic Ocean, The Ocean Exudes A Brown Tint Because Of Dead Leaves And Sediments Spewing From The Rivers.
- In Other Parts Of The World, The Oceans Appear Green, Which Happens Due To The Existence Of Phytoplankton On The Upper Surface Of The Water.
- Phytoplankton Are Microscopic Marine Algae That Contain The Green-coloured Pigment Chlorophyll. The Pigment Helps Them Absorb Sunlight, Which They Use To Capture Carbon Dioxide From The Atmosphere And Convert It Into Sugars.
Climate Change: Why Is The Colour Of The Oceans Changing?
- The Study Says One Of The Most Affected Areas Is The Tropical Ocean Regions, Near The Equator, Where The Water Is Turning From Blue To Green. But This Doesn’t Mean That The Rest Of The Affected Areas Are Also Turning Greener.
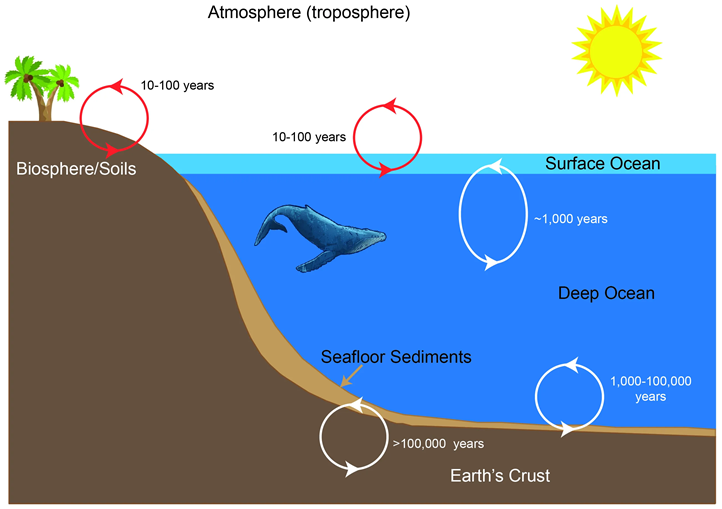
- The Findings Suggest That A Shift In Colour Is Happening In Those Regions Where The Oceans Are Getting More Stratified.
- Ocean Stratification Is The Natural Separation Of An Ocean’s Water Into Horizontal Layers By Density, With Warmer, Lighter, Less Salty, And Nutrient-poor Water Layering On Top Of Heavier, Colder, Saltier, Nutrient-rich Water.
- Usually, Ocean Ecosystems, Currents, Wind, And Tides Mix These Layers, Creating Smoothed Temperature And Salinity Transitions Between Them.
- But Because Of Climate Change, Stratification Has Increased, Making It Harder For Water Layers To Mix With Each Other, Which Has Severe Consequences – Oceans Are Able To Absorb Less Carbon Dioxide From The Atmosphere And The Oxygen Absorbed Isn’t Able To Mix Properly With Cooler Ocean Waters Below, Threatening The Survival Of Marine Life.
- Moreover, Nutrients Aren’t Able To Travel Up To The Surface Of The Oceans From Below. This Directly Impacts Phytoplankton, Which Thrives, As Mentioned Before, On The Upper Surface Of The Oceans.
- Changes In The Composition Of The Plankton Population Have Larger Effects On The Marine Ecosystem. Plankton Has Two Major Types: Phytoplankton, Which Are Plants, And Zooplankton, Which Are Animals.
- Phytoplankton Are Eaten By Zooplankton, Which Are Then Eaten By Other Marine Animals Such As Crabs, Fish And Sea Stars, And Therefore, Plankton Are Critical In Supporting Marine And Freshwater Food Webs. Any Alteration In Their Population Could Throw Off The Whole Marine Ecosystem.
To crack the SSB Interview, You can join our SSB interview live classes batch and we recommend you to Enroll SSB INTERVIEW ONLINE COURSE. Trusted by thousands of defence aspirants.
Also read:
- 20th ASEAN-India Summit & 18th East Asia Summit Highlights
- Manipur Police Register Criminal Case Against Assam Rifles
- Pakistan’s Ex-PM Imran Khan Jailed For 3 Years In ‘Toshakhana Case’
- Four Years After Removal Of Art 370: How Is The Actual Situation In Kashmir?
- Putin’s Critic Alexei Navalny Sentenced To 19 More Years In Prison
- Delhi Services Bill Tabled In Lok Sabha: Govt Of NCT Of Delhi (Amendment) Act, 2023
- Gurugram Nuh Violence: How A Religious Procession Turned Into A Communal Clash
- Govt Imposes Import Restrictions On Laptops, Tablets, Computers
- How Climate Change Is Altering The Colour Of The Oceans?
- New IPCC Assessment Cycle Begins: Why Is It So Significant?
- Difference Between NATO Vs Russia? [Explained]
- Italy Regrets Joining China Belt & Road Initiative (BRI)
- What Is Doping: Why Is It Banned In Sports?
- India Tiger Census 2023: India Is Now Home To 75% Of Tigers In The World
- Military Coup In Niger – President Detained, All Institutions Suspended
- No-Confidence Motion Against PM Modi’s Government
- Elon Musk’s SpaceX Rocket Punches Hole In Ionosphere
- Israeli Parliament Passes Controversial Law Stripping Supreme Court Of Power
- Significance Of 1999 Kargil War: How It Became A Major Game Changer For Indian Military?
- Controversy Over Movie Oppenheimer Gita Scene: How Are Films Certified In India?
- The Curious Case Of Qin Gang: China’s Foreign Minister Who Went Missing
- Twitter’s Iconic Blue Bird Logo Set To Be Replaced By An X Logo
- India Pulls Out Of Games In China Over Stapled Visas For Arunachal Athletes
- PM Modi Urges Sri Lanka President To Implement 13th Amendment
- India Pulls Out Of Games In China Over Stapled Visas For Arunachal Athletes
- Rajasthan CM Sacks Minister After Remarks Over Crimes Against Rajasthan Women
- Manipur Sexual Assault: Video Sparks Outrage Across The Country
- BRICS Summit 2023 In August: Why Putin Won’t Go To South Africa For The Summit?
- Robert Oppenheimer: The Father Of Atomic Bomb, Impact Of Bhagavad Gita On Him
- Russia-Ukraine Black Sea Grain Deal, Why Russia Has Halted It?
- Henley Passport Index 2023, India Passport Ranked 80th
- Indian Opposition Parties Form ‘INDIA’ Alliance, 26 Parties Unite For 2024
- Britain Joins Asia-Pacific Trade Group ‘CPTPP’ – Biggest Trade Deal Since UK Left EU
- NITI Aayog Report On National Multidimensional Poverty Index
- PM Modi UAE Visit: Highlights & Key Takeaways
- PM Modi’s Visit To France: Highlights & Key Takeaways
- NATO Summit Vilnius 2023: Highlights & Key Takeaways
- Turkey Supports Sweden’s Bid For NATO Membership At Vilnius Summit 2023
- Why ISRO Wants To Explore The Moon’s South Pole: Chandrayaan-3 Mission
- Bengal’s Panchayat Polls Turned Violent: SSB Interview Topic 2023
- First Ever IIT Campus Outside India In Tanzania
- RBI’s Report On “Internationalisation Of Rupee” Why And What Are The Benefits?
- Japan To Release Nuclear Wastewater Into Ocean – Gets Approval From IAEA
- PM Modi Chairs 23rd SCO Summit: Highlights & Key Takeaways
- Israel Raids Jenin Camp: Massive Military Operation In West Bank
- Dutch King Apologizes For Netherlands’ Role In Slavery: A Look At The Dutch Role In History
- Constitutional Crisis In Tamil Nadu: The Tussle Between Governor & DMK Government
- Why Has France Been Engulfed By Protests Again?
- Paris Summit – World Leaders Unite For A New Global Financing Pact
- India Ranked 67th On Energy Transition Index – Sweden On Top Of List By World Economic Forum
- Four Minor Planets Named After Indian Scientists
- NASA Recovers 98% Water From Urine & Sweat On ISS: Breakthrough In Long Space Missions
- ESA Space Telescope Euclid Is All Set For Launch To Observe Dark Side Of Universe
- PM Modi’s Trip To USA: Key Takeaways & Highlights
- PM Modi-Led Yoga Session Creates A New Guinness World Record
- Sajid Mir, The Mastermind Behind 26/11 – His Designation As Global Terrorist Blocked By China
- UN Adopts First Historic ‘High Seas Treaty’ To Protect Marine Life
- International Yoga Day 2023 – How It Was Celebrated Across The World?
- Gender Apartheid – Why Is Afghanistan At Stand Off With UN?
- Gandhi Peace Prize 2021 For Gita Press Why It Triggered A Congress-BJP Brawl?
- The New Pride Flag – Why The Change & What The Colours Signify?
- 48 Years Of Emergency – PM Modi Refers It As India’s Darkest Period In Mann Ki Baat
- Groundwater Extraction Has Tilted Earth’s Spin – How Will It Impact The Climate Change?
- Europe’s Worst Migrant Boat Disaster – 78 Dead, Hundreds Missing Off Greek Coast
- MOVEit Global Hacking Attack – Government Agencies In The USA Targeted
- Karnataka Govt Decides To Repeal Anti-Conversion Law: Why Was The Law Controversial?
- IIT Bombay Among Top 150 Varsities In QS Rankings 2024
- China’s Xi Jinping Backs ‘Just Cause’ Of Palestinian Statehood – Chinese Middle Eastern Diplomacy
- Turkey Won’t Back Sweden’s Bid To Join NATO – Why Is Erdogan Against Sweden’s Application
- UN Report Reveals Chronic Bias Against Women – 25% Of Population Thinks Beating Wife Justifiable
- Zinnai – Space Flower Grown On International Space Station By NASA – Why Is It Significant?
- Who Are Meira Paibis: Manipur’s ‘Torch-Bearing’ Women Activists?
- USA Set To Re-Join UN Cultural Agency UNESCO
- CoWIN Data Leak – Aadhaar, PAN Card Info, On Covid Portal, Made Public By Telegram
- $10bn Investment Deals Signed At Arab-China Summit – Is Arab World Moving Towards China?
- Cyclone Biparjoy Turns Into Extremely Severe Cyclonic Storm – 10 Points To Know
- PM Modi’s Trip To Egypt: Highlights & Key Takeaways
- El Nino Returns After 7 Years: Will Impact Second Half Of Monsoon
- Europe’s Copernicus Programme Completes 25 Years: SSB Interview Topic
- Trump Charged Over Secret Documents In A First For An Ex-US President
- 39 Years Since Operation Bluestar: What Actually Happened?
- Wagner Chief Vows To Topple Russian Military Leaders
- Arctic Could Be Ice-Free In The Summer By 2030: SSB Interview Topic
- PM Modi’s School In Gujarat Will Host Students From Across India
- Major Dam Collapse In Ukraine – Accuses Russia Of Blowing Up Kakhovka Dam
- Microsoft To Pay $20 Million For Illegally Collecting Children’s Info
- NIRF Ranking 2023: IIT Madras Tops The List For 5th Consecutive Year
- TRAI’s ‘Digital Consent Acquisition’ (DCA) Facility’- Unified Platform For Customers’ Consent
- 34th Anniversary Of Tiananmen Square Protest – Hong Kong Police Detains Activists
- Asia Security Summit 2023 Shangri-La Dialogue Begins Amid China-US Tensions
- Coromandel Express Accident – How 3 Trains Derailed, Crashed At Same Place In Odisha
- Law Commission Against Scrapping Of Sedition Law, Says It Will Protect India’s Unity
- Radical Changes In NCERT Textbooks – Poverty, Inequality, Democracy Among Topics Removed
- India GDP Data Beats Expectations – Stays Fastest Growing Economy
- Maharashtra’s Ahmednagar To Be Renamed Ahilyanagar
- Scientists Discover 2nd Moon Near Earth Orbiting Since 100 BC
- Erdogan’s Victory In Turkish Election – What Can Be The Impact On India?
- NASA Alert! GIANT Asteroid Racing Towards Earth
- Uganda Signs Anti-Gay Law With Death Penalty – Sparks Global Outrage
- RBI’s ‘Lightweight’ Payments System For Emergencies – An Alternative To UPI, NEFT, RTGS
- Significance Of ISRO’s Newly Launched NavIC Satellite In Regional Navigation
- What Is The Model Prisons Act – Reforms In The Indian Prisons System?
- Global Plastic Treaty – Negotiations Underway For A Plastic-Free Planet: SSB Interview Topic
- China Sends First Civilian Astronaut To Space As Shenzhou-16 Blasts Off
- US Congressional Panel Suggests Making India Part Of NATO Plus: SSB Interview Topic
- India Conducts National Cyber Defence Exercise
- What Is XPoSat, India’s First Polarimetry Mission?
- Germany Falls Into Recession As Inflation Hits Economy
- Bangladesh Faces Fuel Crisis – Dollar Shortage Issue
- Australian Universities Ban Student Applications From Certain Indian States
- What Is Volt Typhoon: China-Backed Hackers Targeting USA?
- Death Of Six Cheetahs At Kuno National Park: SSB Interview Topic 2023
- India-Australia Relations Get Stronger – What Is Migration Deal?
- What Is Sengol: To Be Placed In The New Parliament Building?
- Annual Misery Index – India Ranks 103 Out Of 157 Nations: SSB Interview Topic
- Russia Pressures India For Help To Avoid Getting Blacklisted By FATF
- What Is Mission LiFE – How It Will Fight Against Climate Change?
- What Is The ‘Pandemic Treaty’: How WHO Could Fight Future Pandemics?
- Assam CM Himanta Biswa Sarma Announces Withdrawal Of AFSPA
- El Nino Could Hit World Economy By $3 Trillion? SSB Interview Topic 2023
- Tussle Between Delhi Govt And Centre – Delhi Ordinance Issue: SSB Interview Topic
- China Braces For New Covid Wave With Up To 65 Million Weekly Cases
- Colour-Coded Warnings By The IMD: SSB Interview Topic 2023
- Saudi Scripts History As First Arab Woman Astronaut Lifts Off Into Space
- Controversy Behind Inauguration Of Parliament Building: SSB Interview GD Topic
- Uniform Civil Code: Is Time Ripe For the Indian Government To Act On It?
- Indian-Origin Ajay Banga To Be The Next World Bank President
- AI ‘Godfather’ Geoffrey Hinton Quits Google Warns Of Danger Ahead
- India Ranks 161 Out Of 180 Countries – World Press Freedom Index
- Supreme Court Rules It Can Directly Grant Divorce To Couples: SSB Interview GD Topic
- Kashmir All Set To Hold G20 Summit In India
- Go First Airlines Files For Insolvency: SSB GD Topic
- India Becomes Europe’s Largest Supplier Of Refined Fuels
- What Is The Met Gala – Fashion’s Biggest Night?
- Clashes In France Against Pension Reforms By Macron Govt
- Why Are Indian Wrestlers Protesting Against WFI Chief?
- China Offers Ukraine To Mediate To End War With Russia
- 50 Years Of Kesavananda Bharati Case: SSB Interview Lecturette Topic
- Assam-Arunachal Pradesh Border Dispute: SSB Interview Lecturette Topic 2023
- Same-Sex Marriages In India: Key Supreme Court Verdicts On LGBTQ Rights
- What Is China Plus One? SSB Interview Lecturette Topic 2023
- India-Maldives Relations: SSB Interview Lecturette Topic 2023
- India-Bangladesh Relations: SSB Interview Lecturette Topic 2023
- India-Japan Relation: SSB Interview Lecturette Topic 2023
- Geopolitical Importance Of The Indian Ocean: SSB Interview Lecturette Topic 2023
- All About Paris Club: SSB Interview Lecturette Topic
- PM Narendra Modi Has Been Named The Most Popular Leader In The World
- Hindenburg Report On Adani – Here’s What You Need To Know
- India At WEF Davos Summit 2023: Here Are 10 Key Highlights
- Pakistan Economic Crisis 2023: SSB Interview Topic [Fully Explained]
- Joshimath Crisis: What Does “Land Subsidence” Mean, And Why Does It Happen?
- Top 10 Animal Conservation Projects In India [MUST WATCH]
- What Is Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) Summit 2022? [Fully Explained]
- 20 SSB Interview Questions On Russia Ukraine Crisis
- What Is The (India-Israel-UAE-USA) I2U2 Summit? [Fully Explained]
- What Is International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC)?
- What Is Sri Lankan Crisis? [Fully Explained]
- What Is The BIMSTEC Grouping And How Is It Significant? [EXPLAINED]
- What Is The Places Of Worship (Special Provisions) Act, 1991? [Explained]
- What Is Bodo Accord | SSB Interview Notes [Fully Explained]
- What Is AFSPA: Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act?
- What Is G20 Or Group Of Twenty Countries?
- What Is AFSPA: Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act?
- What Is The Financial Action Task Force (FATF)? [Fully Explained]
- What Is Quadrilateral Security Dialogue (QUAD)?
- Difference Between NATO Vs Russia [Expained]
- What Is United Nations Security Council (UNSC) [Explained]
- Everything You Need To Know About SAARC: South Asian Association For Regional Cooperation
- All About Russia Ukraine War: SSB Interview Topic [Fully Explained]